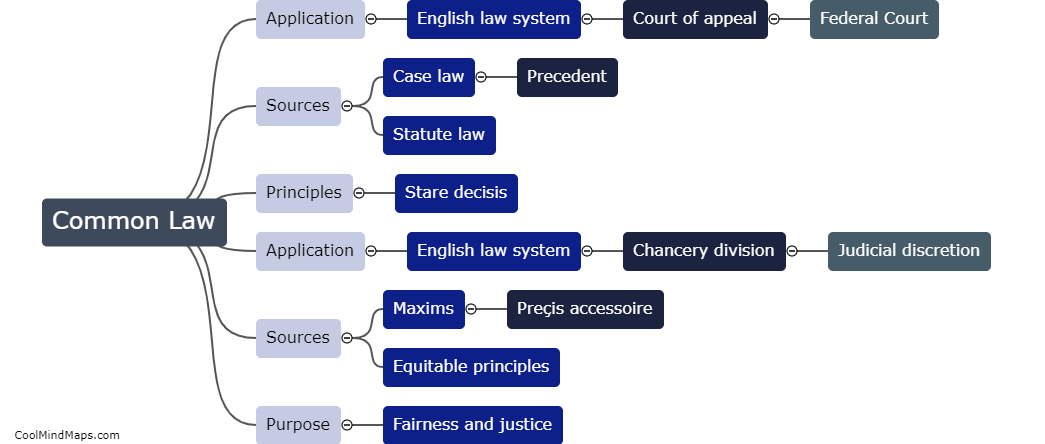
How do common law and equity differ in Malaysia?
In Malaysia, common law and equity are two distinct legal systems that coexist and complement each other. Common law refers to the body of law derived from historical judicial decisions and statutes, whereas equity refers to a set of principles developed by courts to provide fairness and justice when the strict application of common law would lead to unjust outcomes. One fundamental difference between the two is their sources of law. Common law primarily relies on precedents and statutory laws, while equity draws on moral principles and equitable maxims. Furthermore, common law is generally inflexible and follows the doctrine of stare decisis, ensuring consistency and predictability, whereas equity allows for more flexibility and discretion in decision-making, focusing on individual circumstances and providing remedies where strict legal rules fall short. Despite their differences, common law and equity are harmoniously applied in Malaysia, as courts have the inherent power to apply principles of equity when necessary to do justice in individual cases.
This mind map was published on 8 November 2023 and has been viewed 83 times.