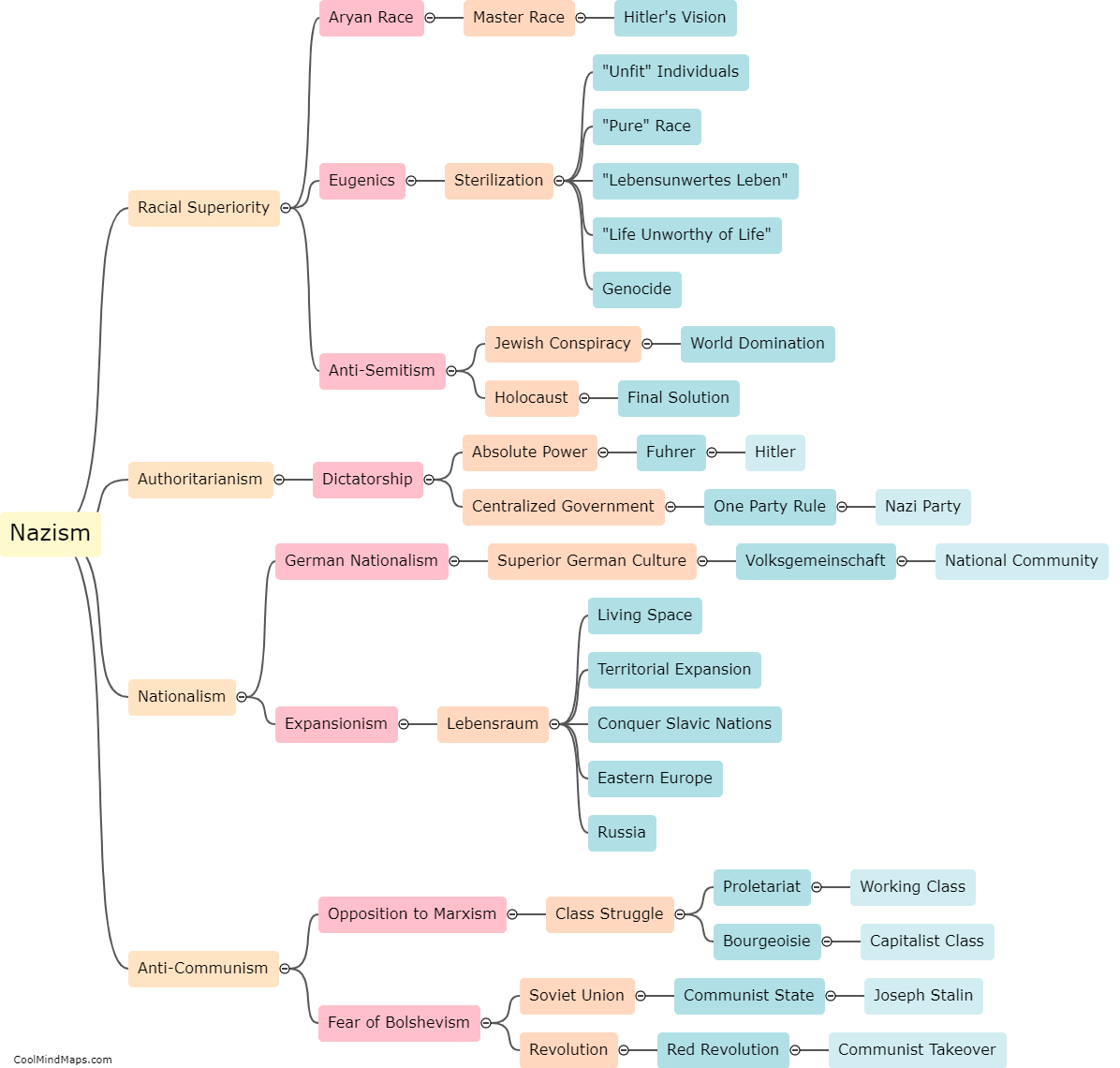
How does a chiller system work?
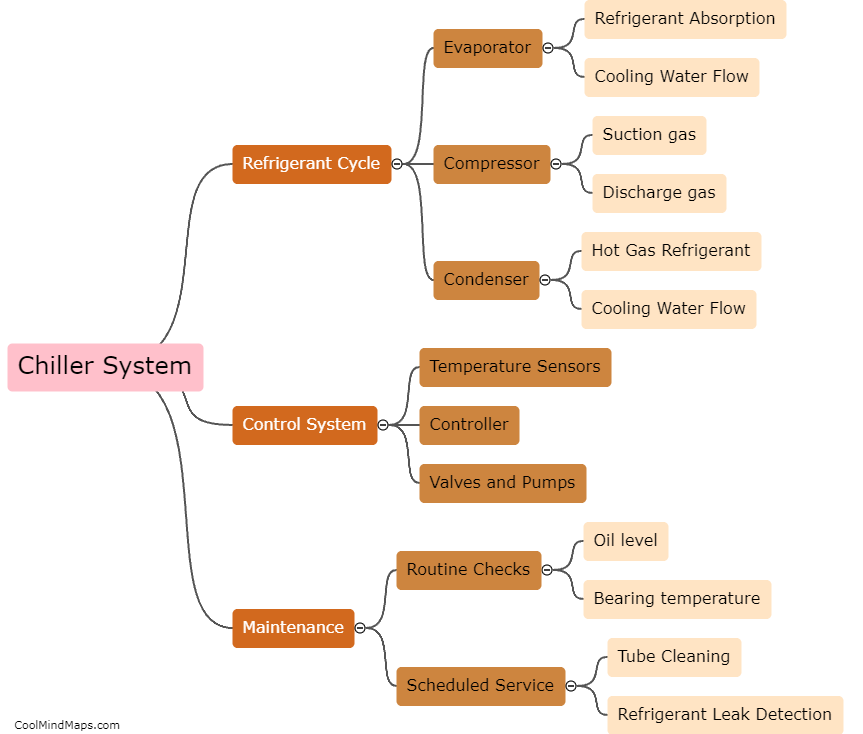
A chiller system works by removing heat from a liquid through the process of refrigeration. The liquid, typically water or a mixture of water and glycol, is circulated through a closed loop system where it absorbs heat from the surrounding environment. The liquid is then pumped through the chiller unit where it passes over a heat exchanger and is cooled by a refrigerant, such as R-134a or R-410a. The cooled liquid is then circulated back through the system and used to cool the surrounding area or equipment. Chiller systems are commonly used in large commercial buildings, hospitals, and industrial applications where large amounts of cooling are required.
This mind map was published on 12 June 2023 and has been viewed 207 times.