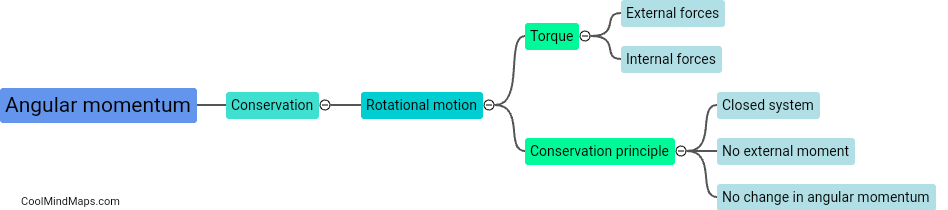
What is conservation of angular momentum?
Conservation of angular momentum is a fundamental principle in physics that states that the total angular momentum of a system remains constant unless acted upon by an external torque. Angular momentum is a vector quantity that measures the rotational motion of an object or a system. It depends on two factors: the moment of inertia, which is a measure of an object's resistance to changes in its angular motion, and the angular velocity, which represents the rate of change of the object's angular position. When no external torque is applied, the total angular momentum of a system is conserved, meaning it remains constant over time. This principle is significant in various fields such as astronomy, mechanics, and quantum physics.
This mind map was published on 24 September 2023 and has been viewed 115 times.