What were the consequences of the Opium War for China?
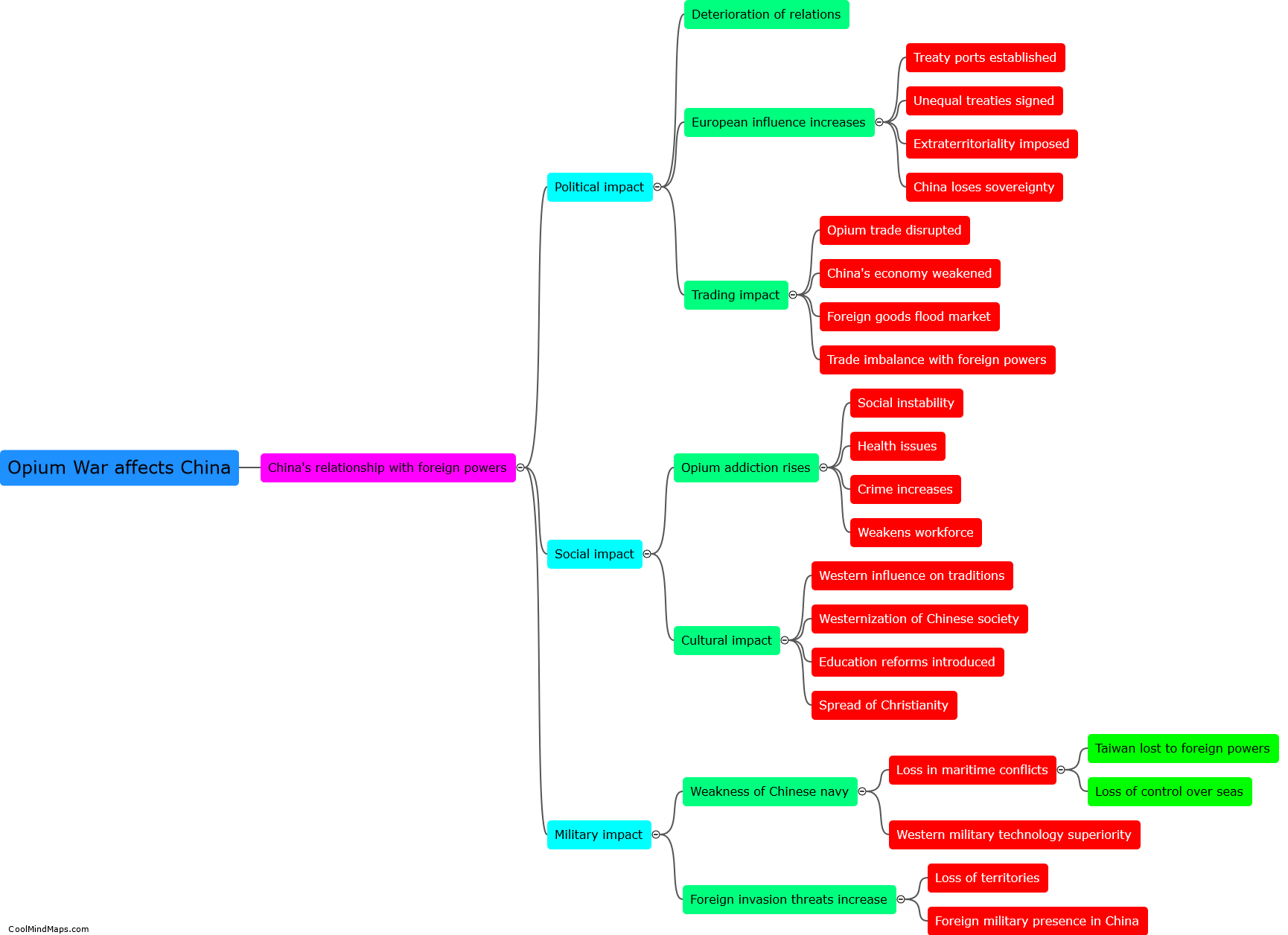
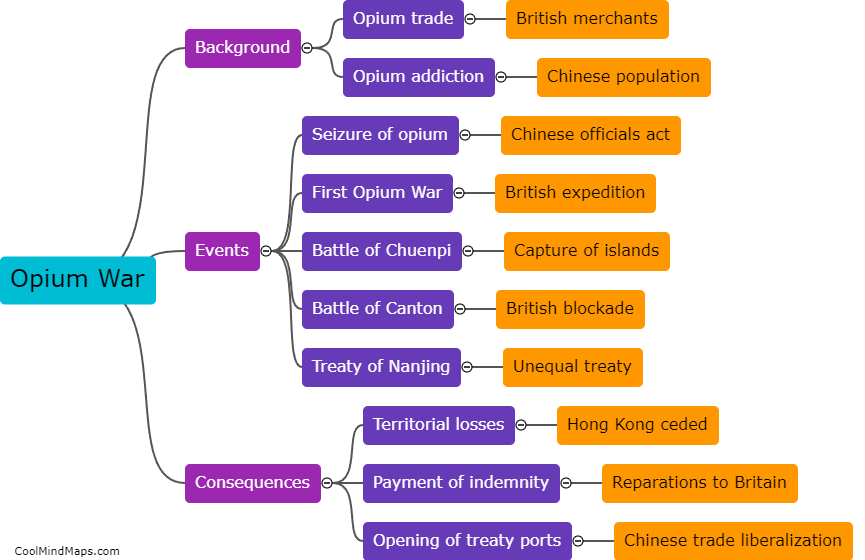
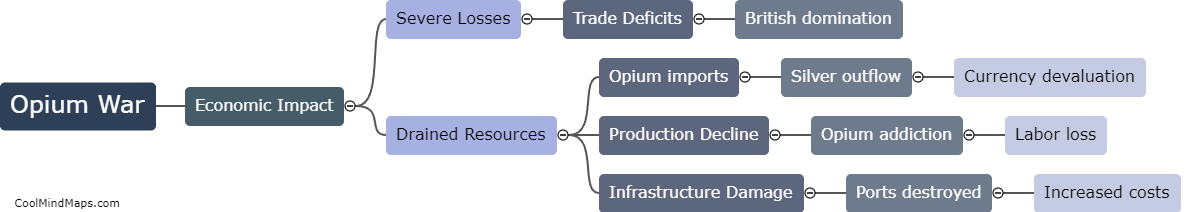
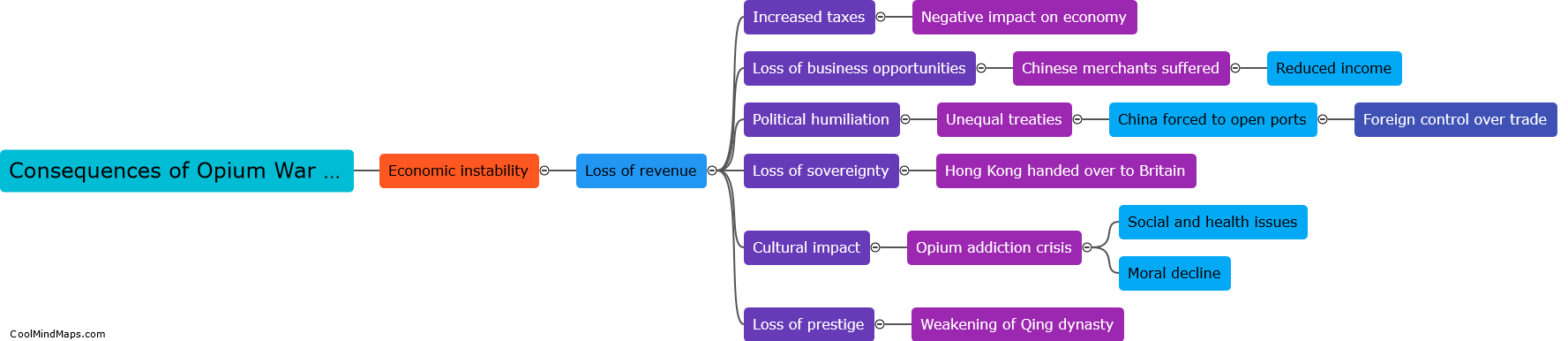
The Opium War, which took place from 1839 to 1842, had profound consequences for China. The defeat resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Nanjing, which forced China to pay a large indemnity and cede Hong Kong to the British. Furthermore, the treaty opened up additional treaty ports, leading to increased foreign influence and control over China's economy and trade. This resulted in unequal treaties with other foreign powers, such as the United States and France, which further weakened China's sovereignty. The Opium War also highlighted the weaknesses of the Qing dynasty and sparked widespread resentment among the Chinese population, eventually leading to the Taiping Rebellion and other anti-Qing movements. Overall, the Opium War marked the beginning of a long period of foreign dominance and internal turmoil for China.
This mind map was published on 6 September 2023 and has been viewed 89 times.