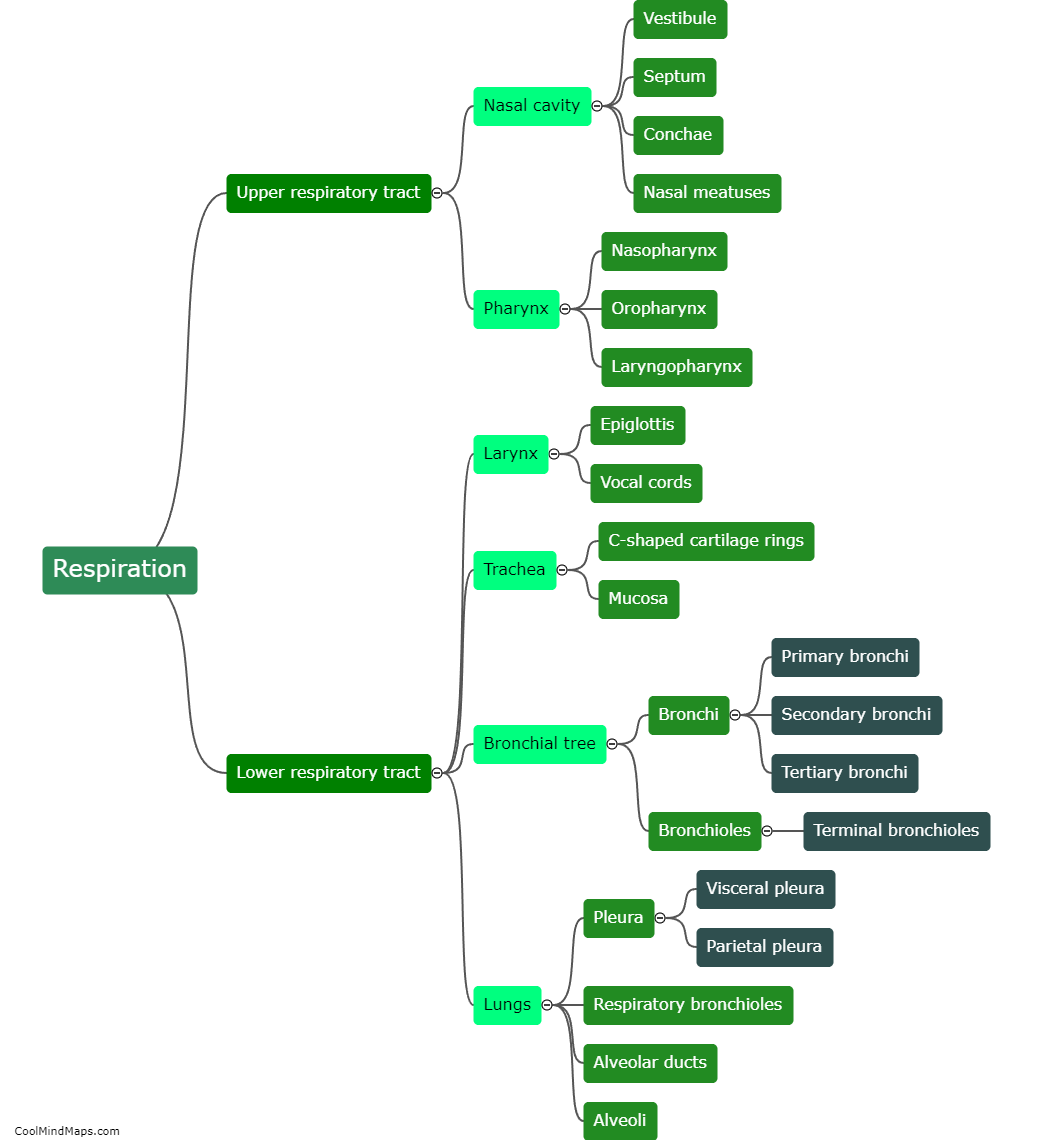
How does gas exchange occur in the lungs?
Gas exchange in the lungs occurs through a process called respiration. When we inhale, air enters the lungs and travels through various airways until it reaches the alveoli, which are small, clustered air sacs. The alveoli have thin walls that are surrounded by a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses across the walls of the alveoli and into the surrounding capillaries, binding with red blood cells. At the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration, diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli and is exhaled during the process of exhaling. This exchanging of gases allows for oxygen to enter the bloodstream and be transported to the body's cells, while carbon dioxide is eliminated from the body. This gas exchange process is facilitated by the large surface area of the alveoli and the close proximity of the alveolar walls to the capillaries, ensuring efficient and rapid exchange of gases.

This mind map was published on 8 August 2023 and has been viewed 87 times.