How do real gases differ from ideal gases?
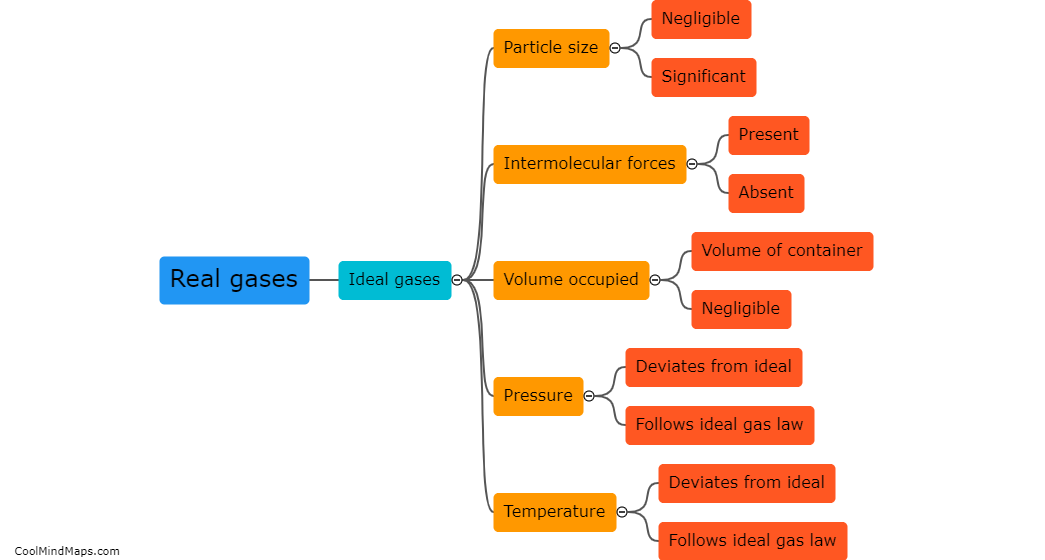
Real gases differ from ideal gases in several ways. While ideal gases are assumed to occupy no volume and exert no intermolecular forces, real gases have finite volumes and experience intermolecular forces. Real gases also deviate from ideal behavior at high pressures and low temperatures, where the particles are closer together and the attractive forces become more significant. Additionally, ideal gases follow the ideal gas law exactly, while real gases may deviate from it due to their non-ideal behavior. Real gases also exhibit changes in their properties when subjected to extreme conditions, such as exhibiting liquefaction at low temperatures or undergoing phase transitions. Thus, real gases are more accurately described by considering their actual behavior and characteristics, rather than assuming the simplified ideal gas model.
This mind map was published on 11 September 2023 and has been viewed 116 times.