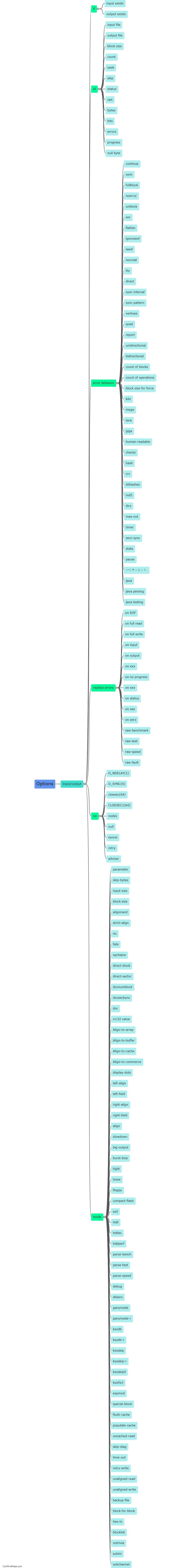
What is the purpose of the Linux command dd?
The purpose of the Linux command dd is to create a bit-by-bit copy of data, known as disk duplication or disk imaging. It allows users to copy data between disks or create backups. dd is a highly versatile and powerful tool with various use cases, such as creating bootable USB drives, cloning entire hard drives, or securely wiping data from disks. It operates at a low-level, directly manipulating the data, and offers extensive options and flexibility to control the copying process. Overall, dd is a critical tool in the Linux system administrator's toolbox for handling disk-related tasks efficiently and effectively.

This mind map was published on 4 February 2024 and has been viewed 92 times.