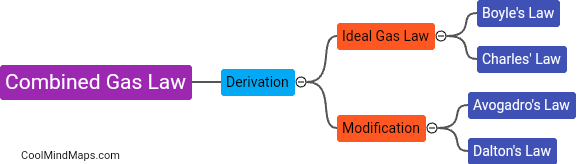
What is the combined gas law and how is it derived?
The combined gas law is a mathematical equation that describes the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas sample. It is derived from the individual gas laws - Boyle's law, Charles's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. Boyle's law states that at a constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume. Charles's law states that at a constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature. Gay-Lussac's law states that at a constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature. By combining these three laws and manipulating the equations, the combined gas law equation is derived as P₁V₁/T₁ = P₂V₂/T₂, where P represents pressure, V represents volume, and T represents temperature. This equation allows us to calculate changes in any of the variables when others are known in a gas sample, assuming constant amount of gas.
This mind map was published on 30 October 2023 and has been viewed 208 times.