How did the Opium War impact China's economy?
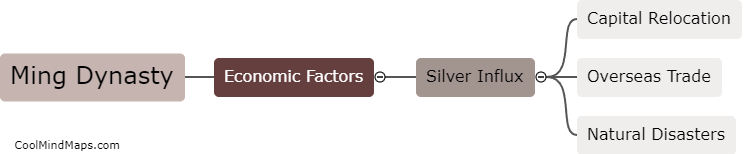
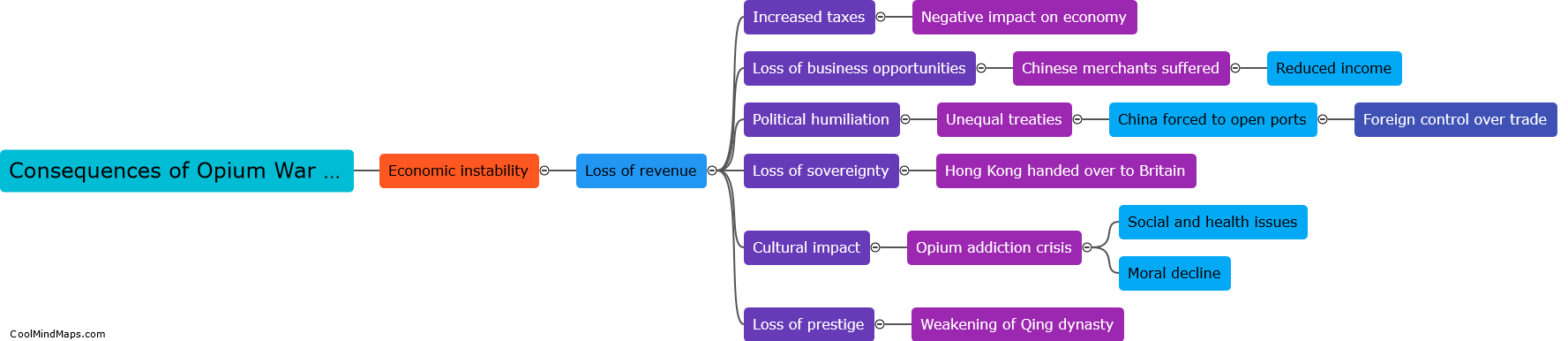
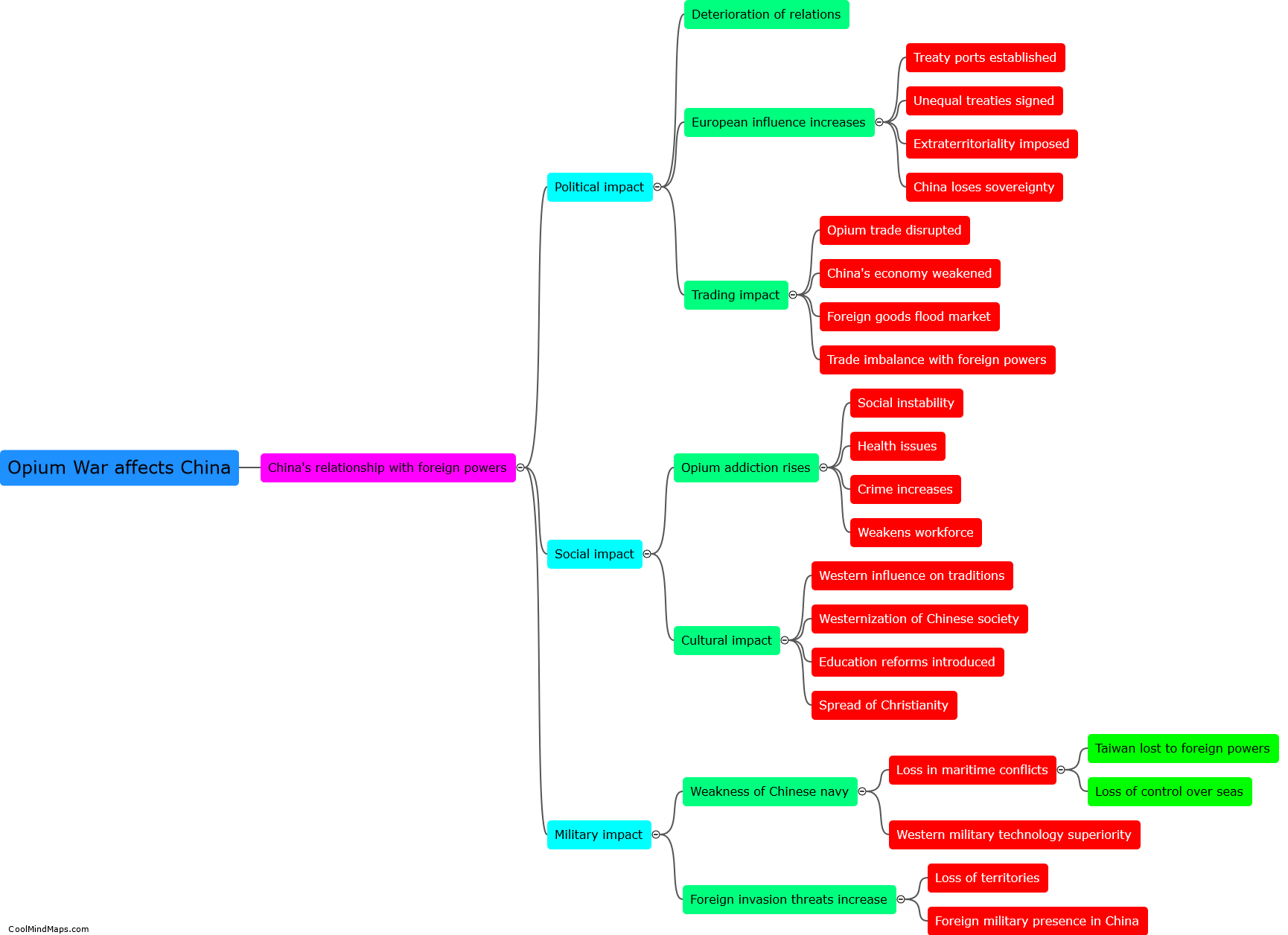
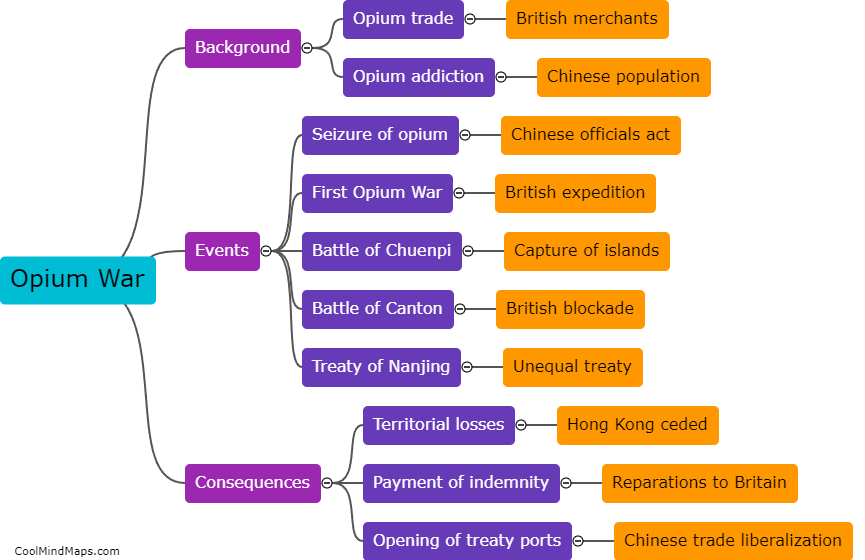
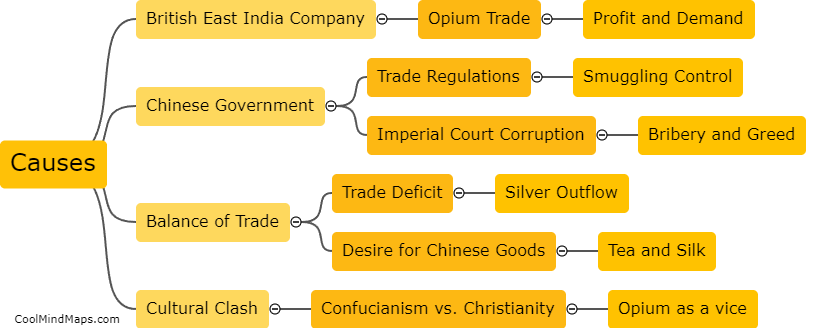
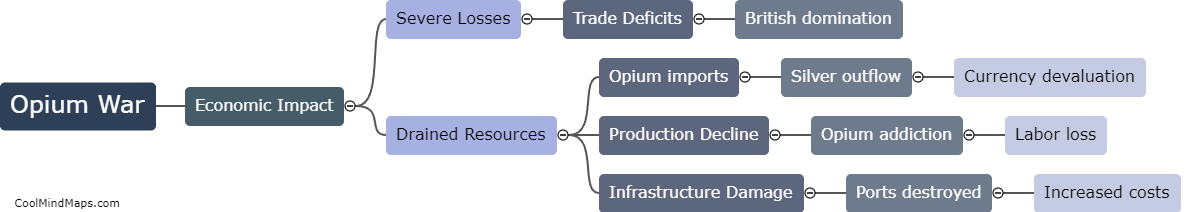
The Opium War, which took place between 1839 and 1842, had a significant impact on China's economy. Prior to the war, China had a trade balance heavily in favor of exports, with a strong agricultural base and self-sufficiency in many areas. However, as a result of the war, China was forced to sign the Treaty of Nanking, which opened several ports to foreign trade and imposed heavy financial reparations. This led to an influx of foreign goods and a shift towards importing rather than producing goods domestically. Additionally, China lost control of its trade tariffs, leading to a decline in revenue for the government. Moreover, the war created a lasting impression of Chinese weakness and humiliation, which had a detrimental effect on both domestic and foreign investments. Overall, the Opium War severely disrupted China's economy, contributing to its decline as a global economic power.
This mind map was published on 18 September 2023 and has been viewed 96 times.