What are the characteristics of typical antipsychotics?
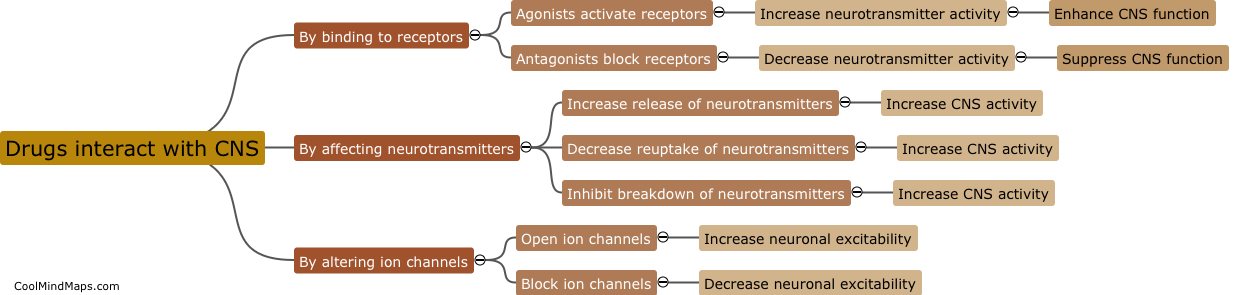
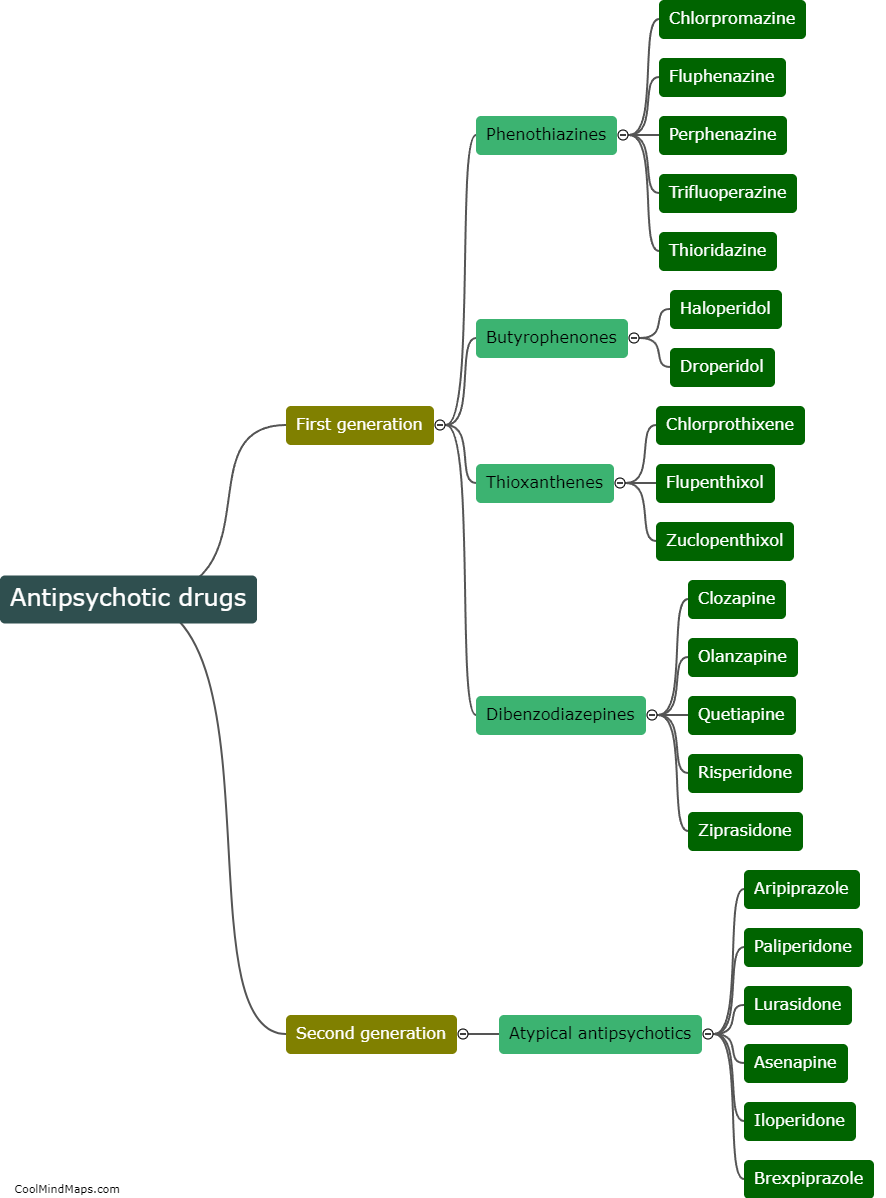
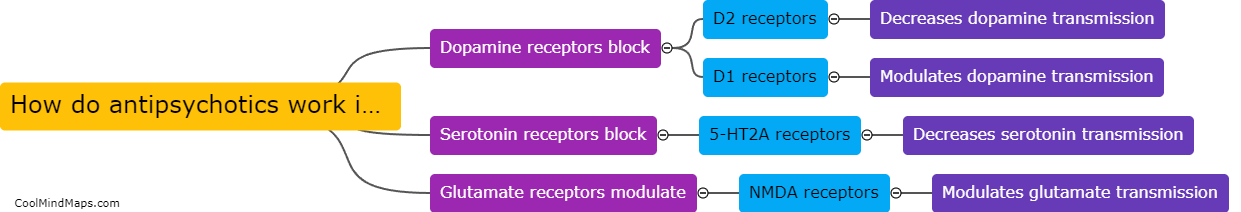
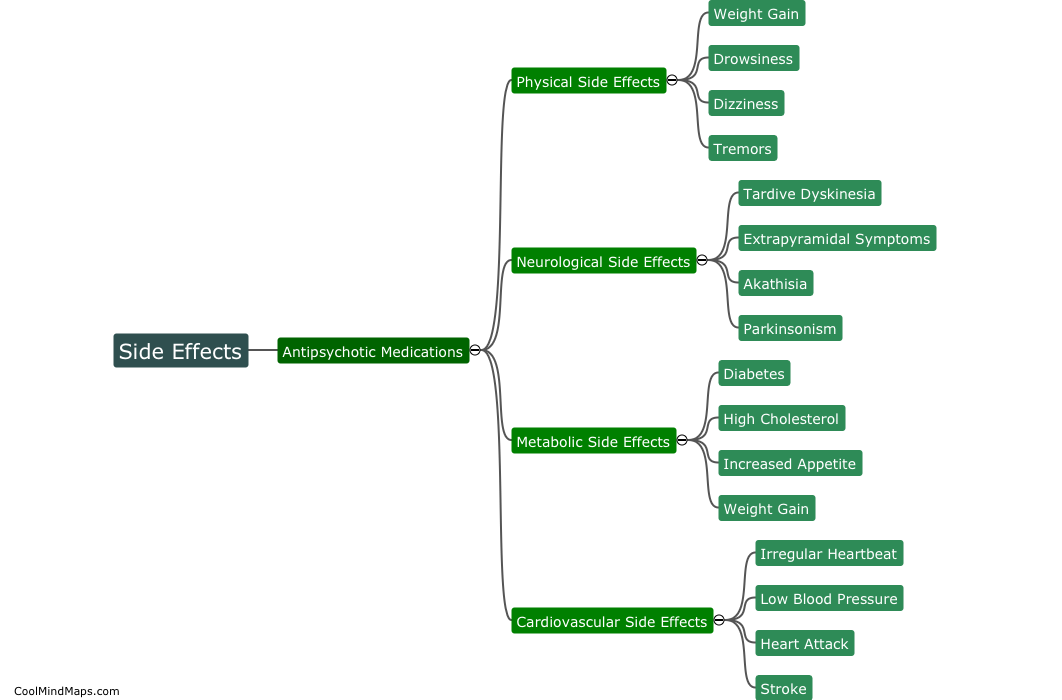
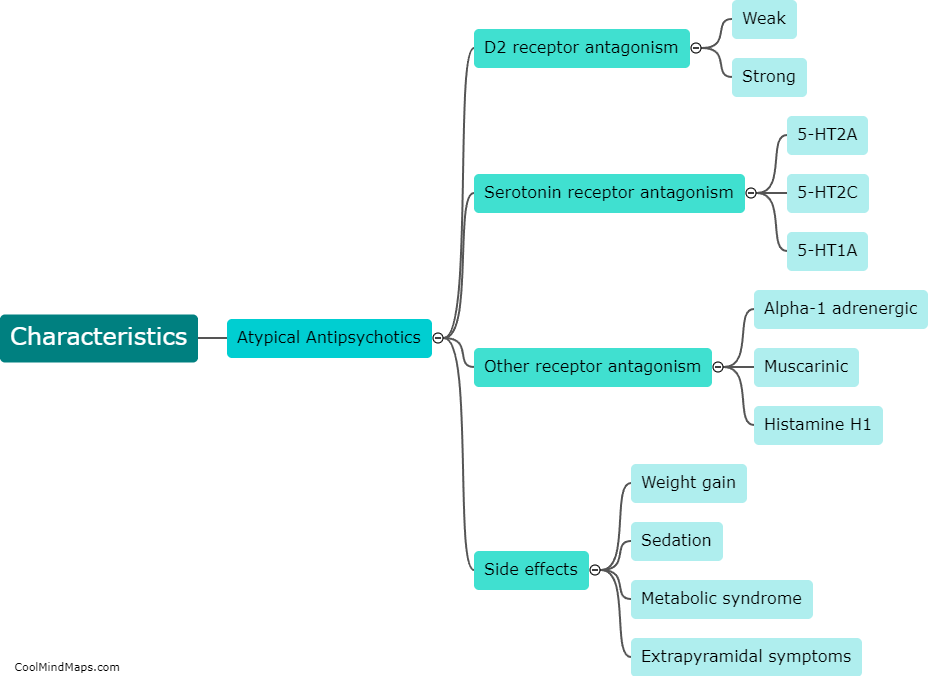
Typical antipsychotics, also known as first-generation antipsychotics, are a class of medications primarily used to treat psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. These medications work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain, reducing the activity of dopamine, which is thought to be involved in the development of psychosis. Typical antipsychotics are characterized by their ability to effectively alleviate positive symptoms of psychosis, such as hallucinations and delusions. However, they are generally less effective in managing negative symptoms, cognitive impairments, and mood symptoms associated with psychotic disorders. Additionally, typical antipsychotics are known to have a range of potential side effects, such as motor disturbances, sedation, weight gain, and an increased risk of developing movement disorders, including tardive dyskinesia. Due to these drawbacks, newer atypical antipsychotics have become more commonly prescribed in recent years as they tend to have a more favorable side effect profile.

This mind map was published on 4 July 2023 and has been viewed 111 times.