How does the central bank influence interest rates?
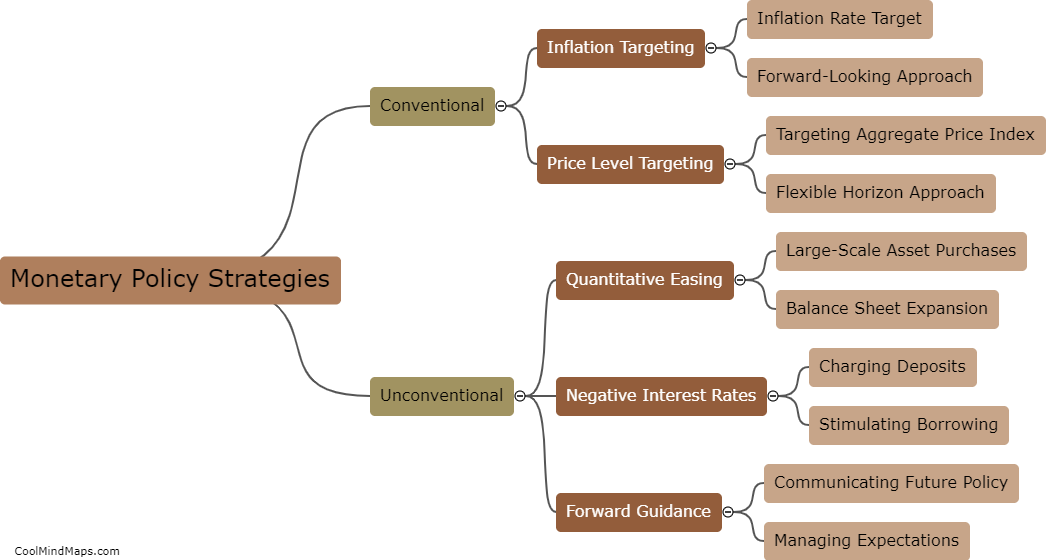
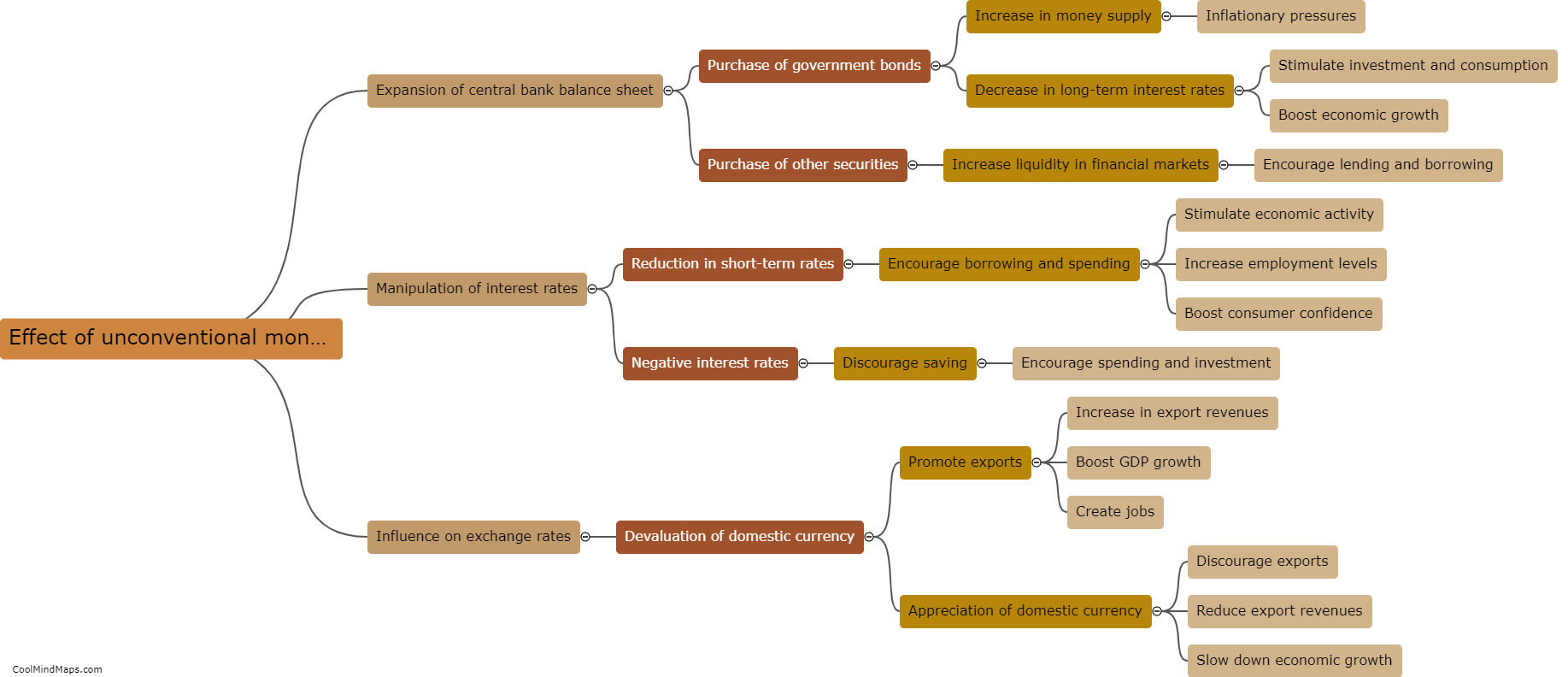
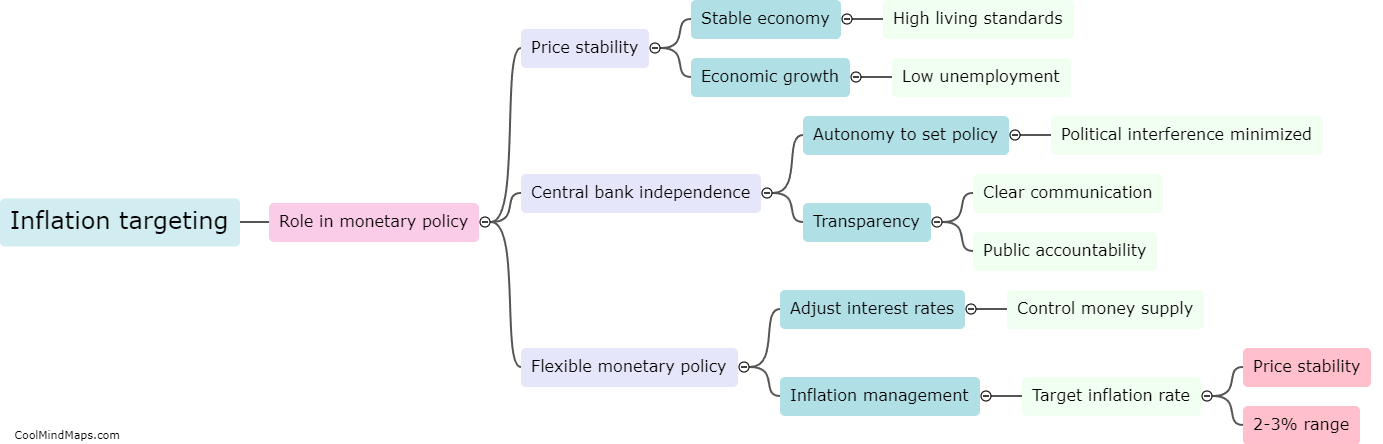
The central bank has a significant influence on interest rates by using various monetary policy instruments. One way the central bank influences interest rates is through open market operations, where it buys or sells government securities to adjust the money supply in the economy. By buying securities, the central bank increases the money supply, leading to lower interest rates as more funds are available for lending. Conversely, selling securities reduces the money supply, increasing interest rates due to limited funds. Additionally, the central bank can change the reserve requirement, which imposes a certain percentage of deposits that banks must hold in reserves. Lowering the reserve requirement allows banks to lend more, leading to lower interest rates. Lastly, the central bank sets a benchmark interest rate known as the policy rate or discount rate, which affects other interest rates in the economy. By adjusting this rate, the central bank can directly influence borrowing costs and overall interest rates.

This mind map was published on 18 September 2023 and has been viewed 88 times.