What is the main purpose of the Krebs cycle?
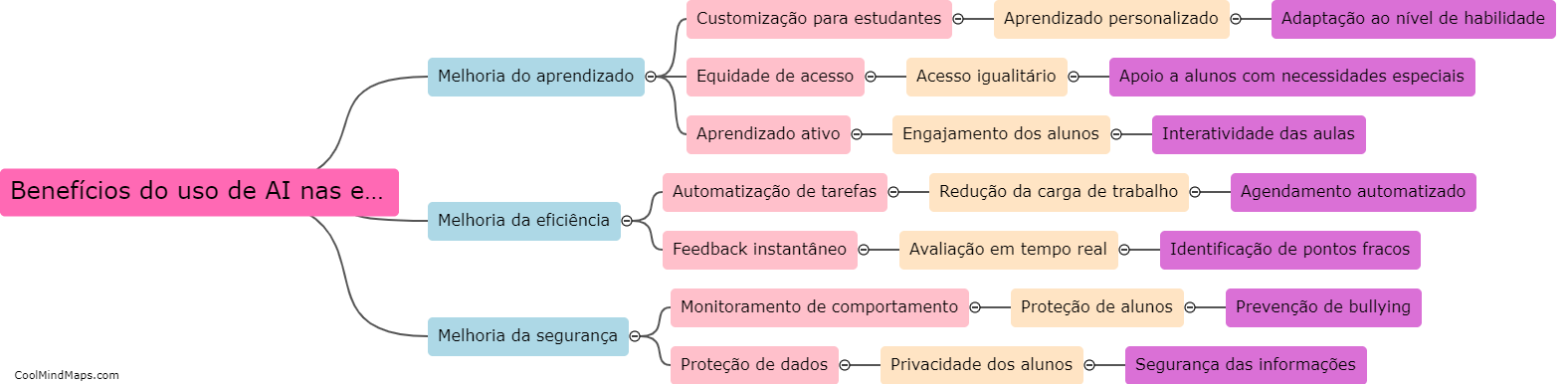
The main purpose of the Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is to facilitate the production of energy in the form of ATP. It is a vital component of cellular respiration, the process by which cells convert nutrients into usable energy. The cycle takes place in the mitochondria and involves a series of chemical reactions that break down acetyl-CoA, a molecule derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the Krebs cycle generates high-energy molecules such as NADH and FADH2. These molecules then proceed to the electron transport chain, where they donate electrons to produce ATP, the primary energy currency of cells. Overall, the Krebs cycle acts as a key intermediary step in the efficient conversion of nutrient molecules into energy for cellular processes.

This mind map was published on 11 July 2023 and has been viewed 105 times.