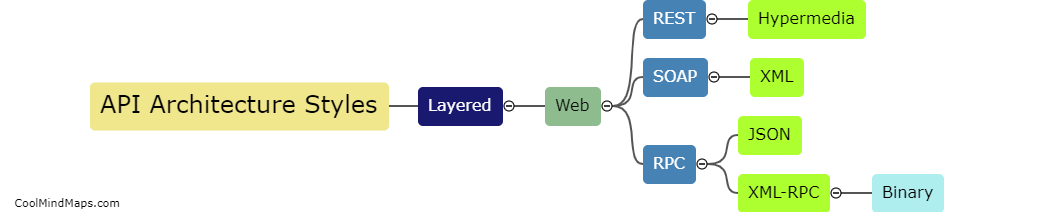
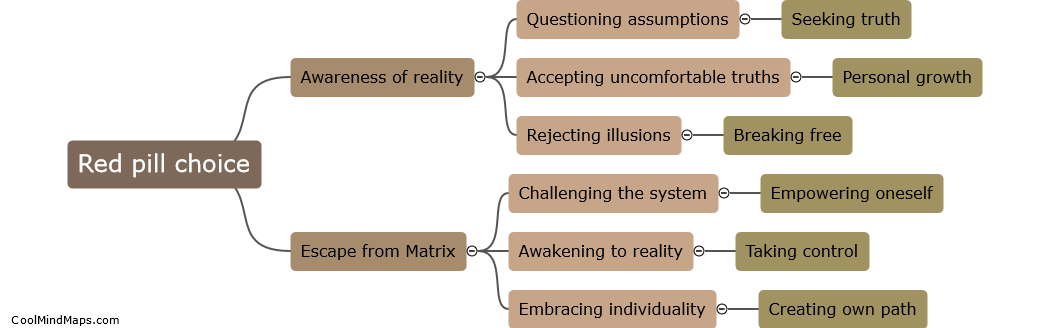
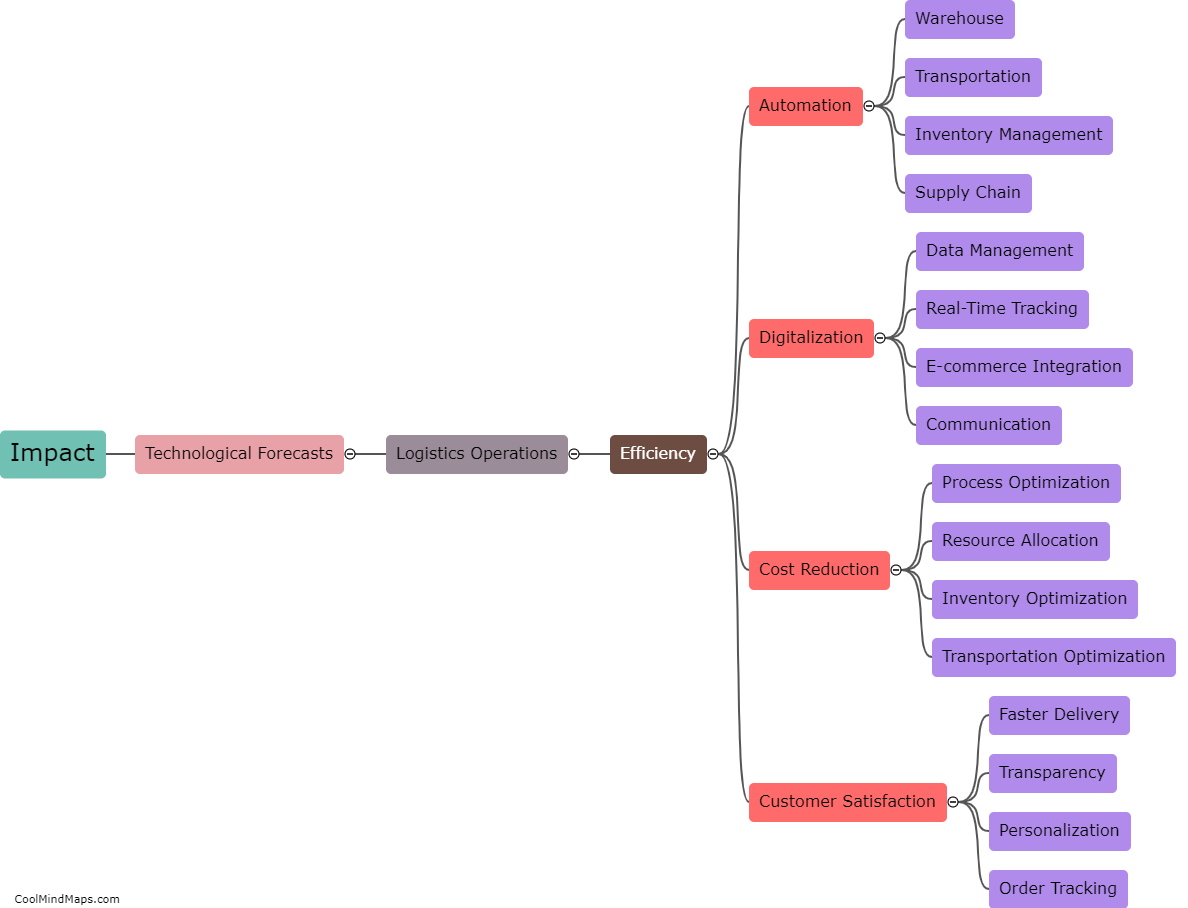
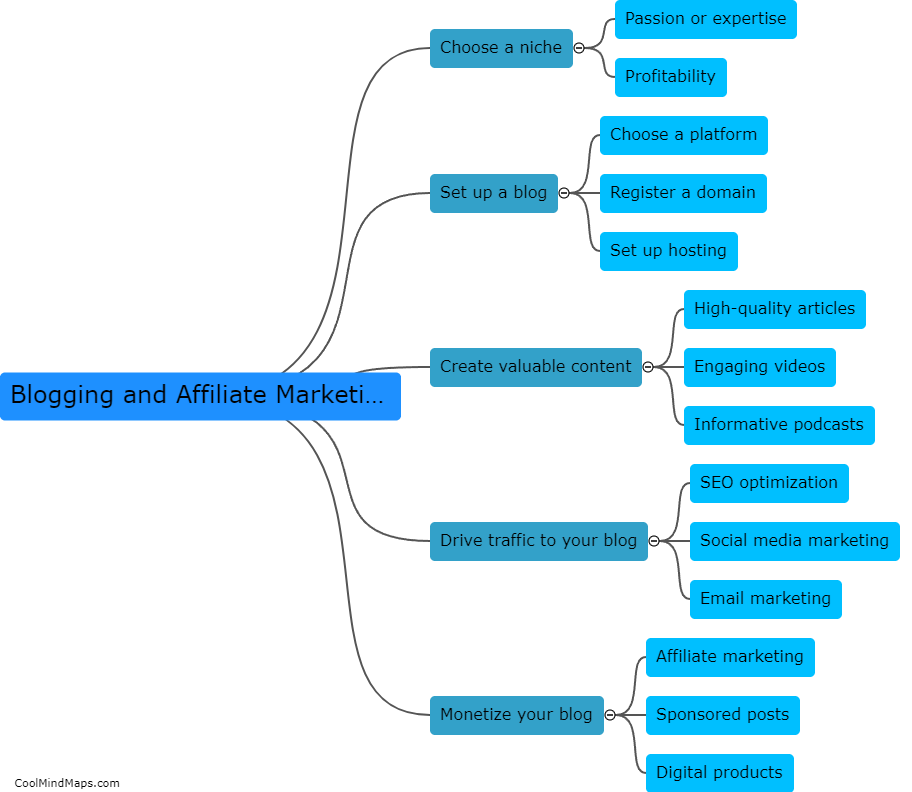
What are Kepler's three laws?
Kepler's three laws are a set of principles that describe the motion of planets and other objects in orbit around the Sun. These laws were formulated by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler in the early 17th century, building upon the observational data of his predecessor Tycho Brahe. The first law, often referred to as the law of orbits, states that the planets move in elliptical paths around the Sun, with the Sun located at one of the foci of the ellipse. The second law, known as the law of areas, states that an imaginary line connecting a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times, meaning that a planet moves faster when it is closer to the Sun and slower when it is farther away. Lastly, Kepler's third law, or the law of periods, establishes a mathematical relationship between the average distance of a planet from the Sun and the time it takes to complete one orbit. This law states that the square of the period of revolution of a planet is proportional to the cube of its average distance from the Sun. These laws revolutionized our understanding of celestial mechanics and played a crucial role in the development of Isaac Newton's theory of gravity.
This mind map was published on 30 October 2023 and has been viewed 107 times.