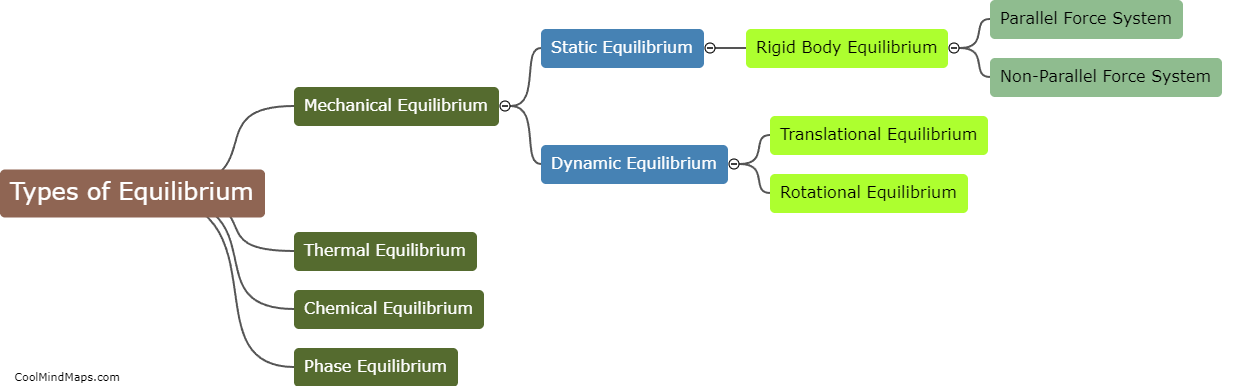
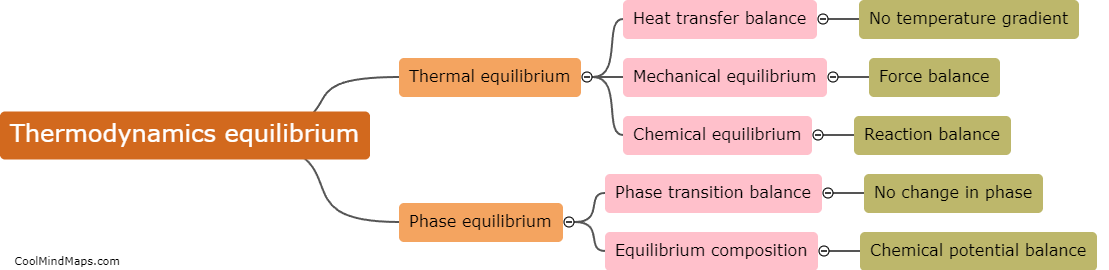
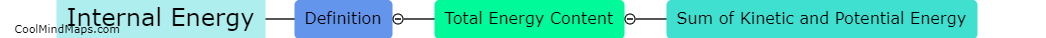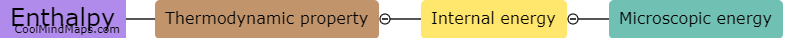What is equilibrium in thermodynamics?
In thermodynamics, equilibrium refers to a state in which all macroscopic properties of a system remain constant over time. It is characterized by a balance between opposing factors that result in a stable and unchanging condition. In equilibrium, there is no net flow of matter or energy within the system or between the system and its surroundings. At this state, the system's temperature, pressure, and other thermodynamic properties reach a state of uniformity, allowing for accurate predictions and analysis. Equilibrium in thermodynamics plays a crucial role in understanding and studying various aspects of physical and chemical processes.
This mind map was published on 18 September 2023 and has been viewed 105 times.