What are the fundamental rights in the Indian constitution?
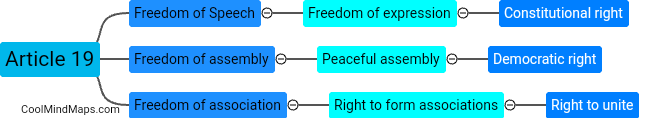
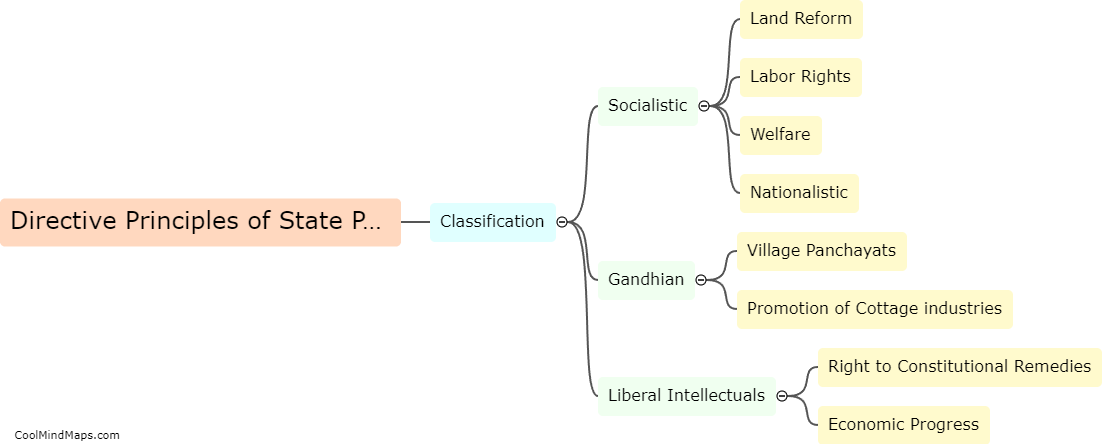
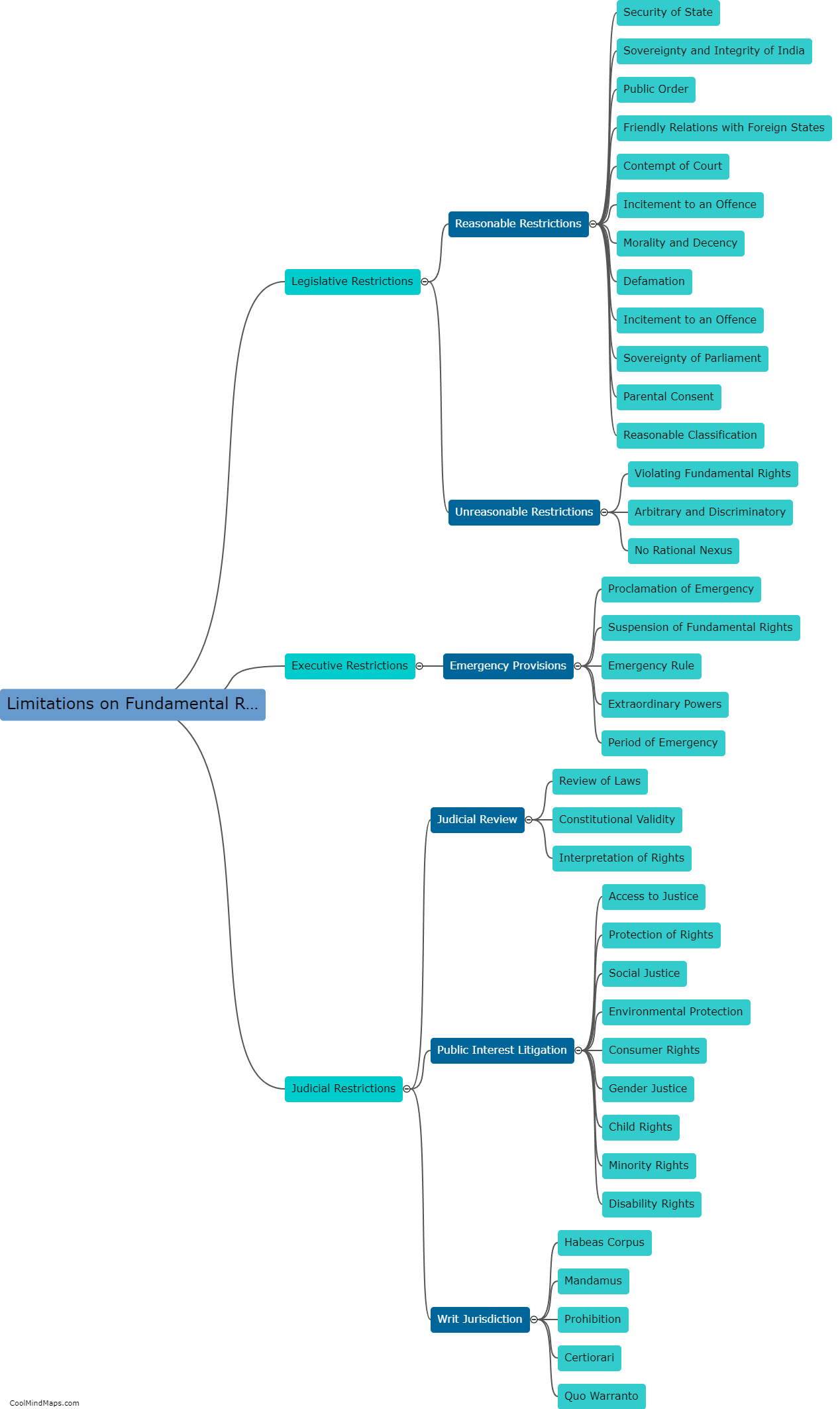
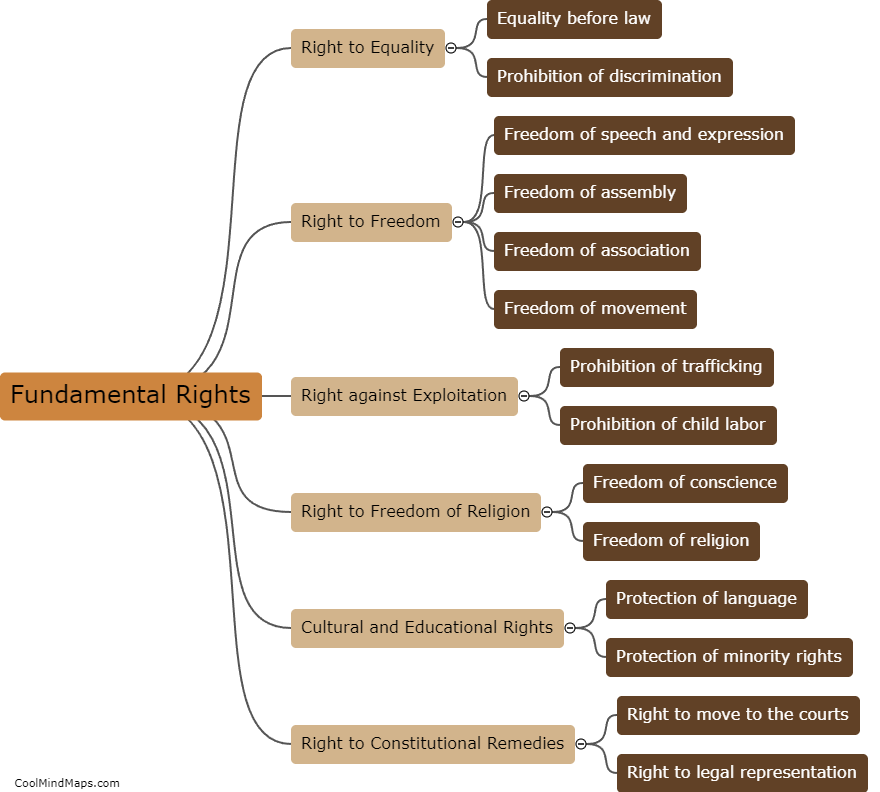
The Indian constitution guarantees fundamental rights to the citizens of India. These rights are enshrined in Part III of the constitution and are considered essential for the growth and development of individuals. Some of the fundamental rights include the right to equality, which ensures equal treatment and prohibits discrimination based on religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. The right to freedom grants citizens the freedom of speech and expression, assembly, association, and movement. The constitution also guarantees the right to life and personal liberty, the right to protection from arbitrary arrest and detention, and the right to education. Additionally, fundamental rights protect cultural and educational rights of minorities and the right to constitutional remedies, ensuring the right to seek legal recourse in case of violation of these rights. Overall, these fundamental rights play a crucial role in upholding the democratic and inclusive values of the Indian constitution.
This mind map was published on 5 September 2023 and has been viewed 94 times.