How does breast cancer stroma contribute to tumor growth?
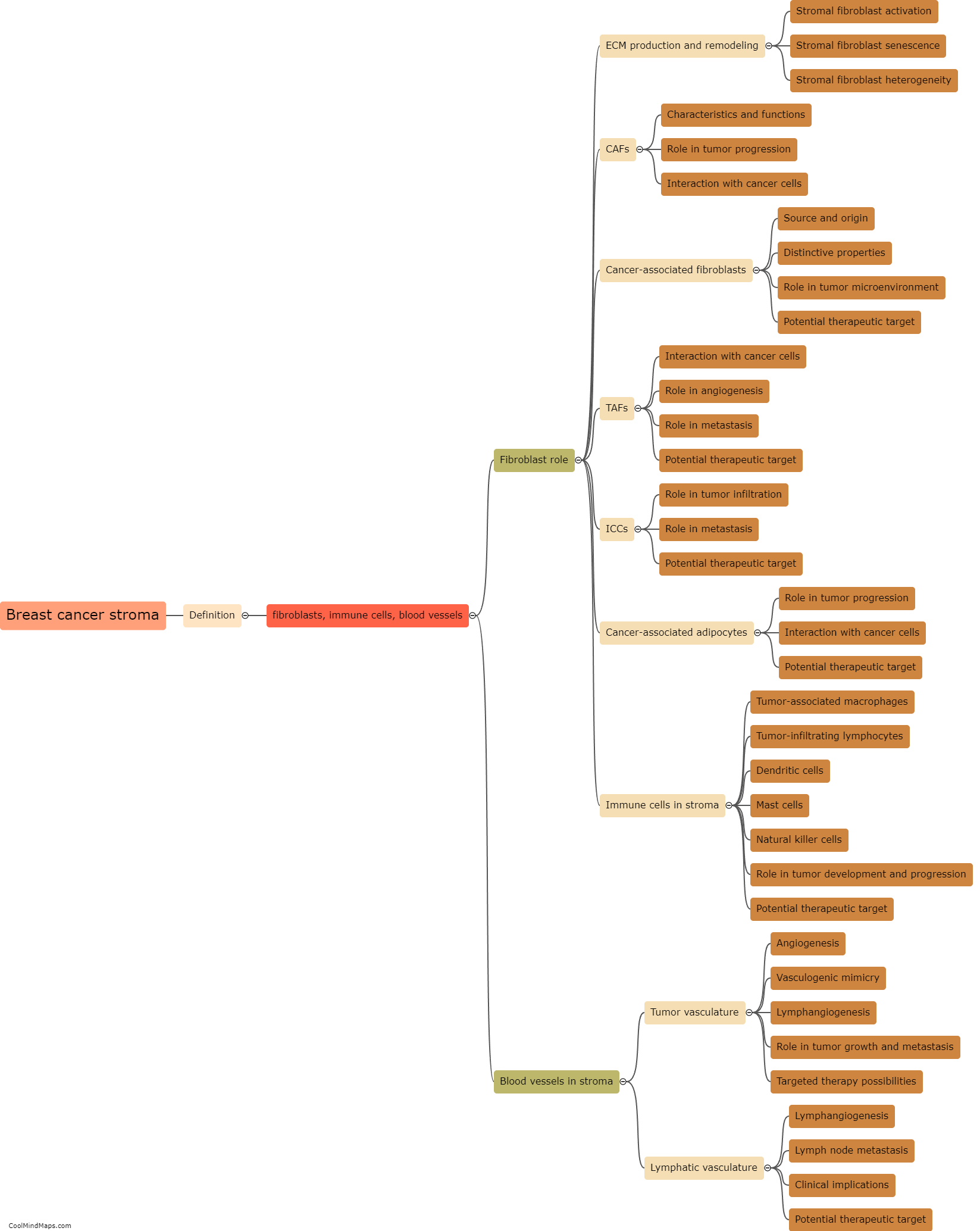
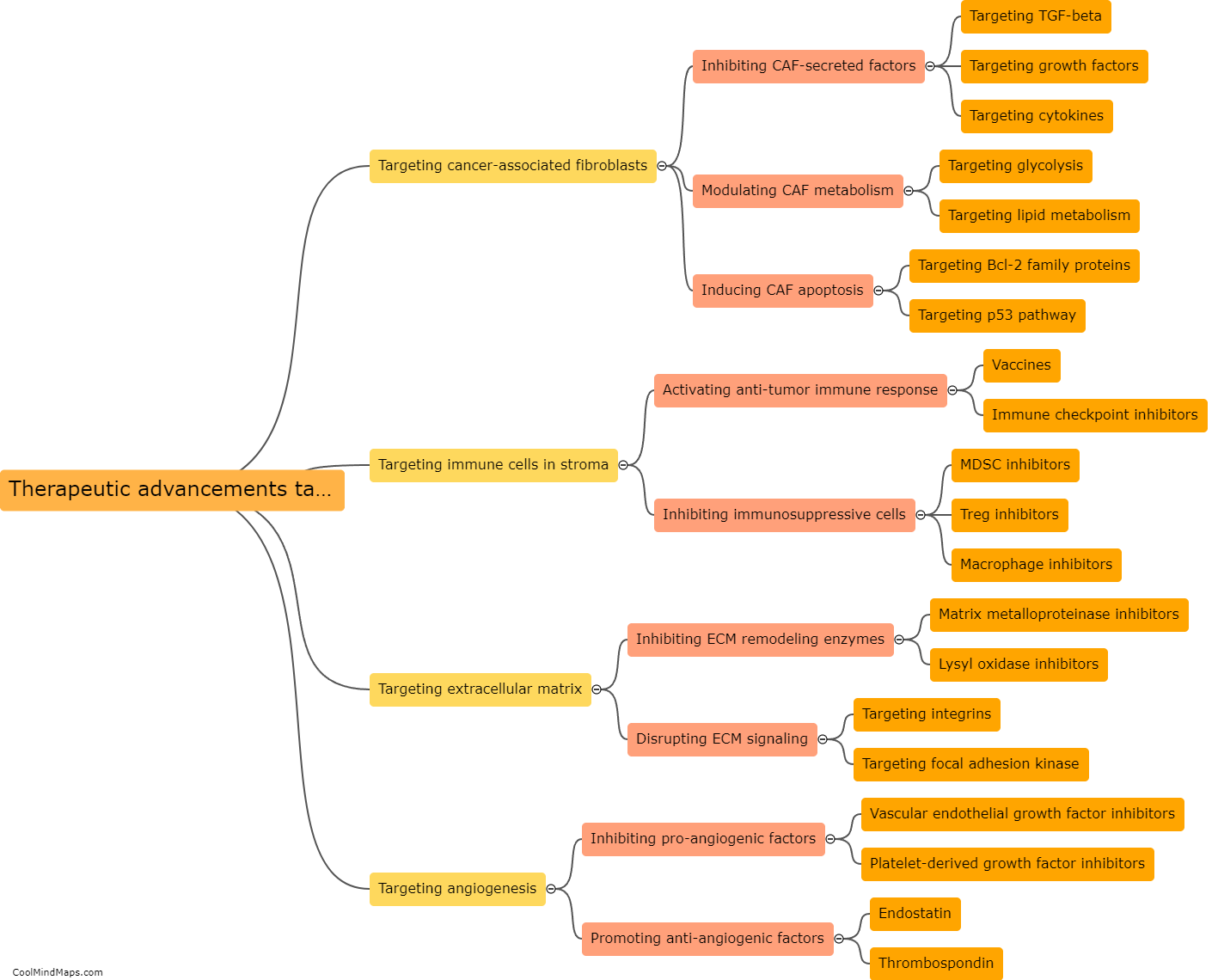
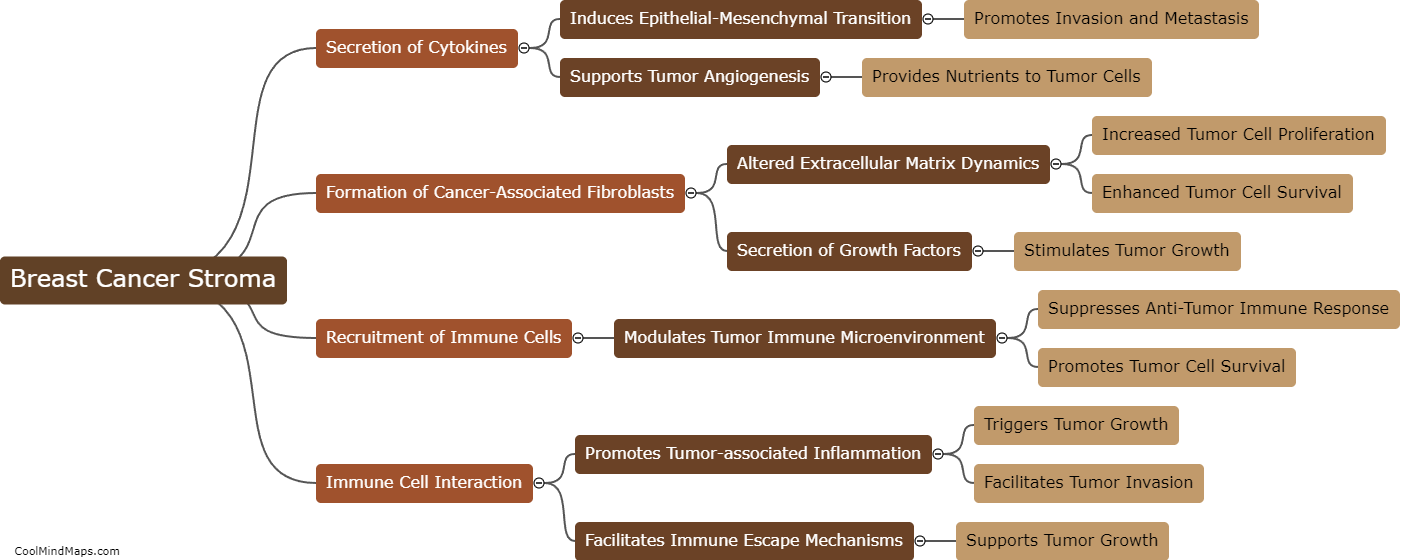
The breast cancer stroma, which is the supportive connective tissue surrounding the tumor, plays a crucial role in tumor growth. It provides a microenvironment that promotes the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of cancer cells. The stroma is composed of various components, including fibroblasts, immune cells, blood vessels, and extracellular matrix. Cancer-associated fibroblasts within the stroma produce growth factors, cytokines, and other signaling molecules that stimulate tumor cell growth and survival. Moreover, the stroma facilitates angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, which is essential for supplying the growing tumor with nutrients and oxygen. Additionally, immune cells in the stroma can exhibit immunosuppressive properties, enabling the tumor to evade the immune system's recognition and destruction. Understanding the complex interactions between the breast cancer stroma and tumor cells is thus crucial for developing new strategies to target and inhibit tumor growth.
This mind map was published on 5 December 2023 and has been viewed 93 times.