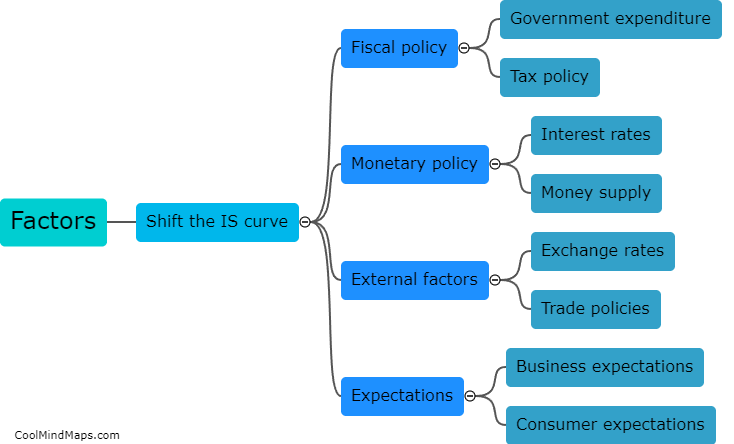
What are the factors that shift the IS curve?
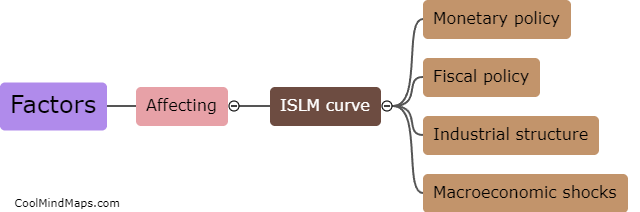
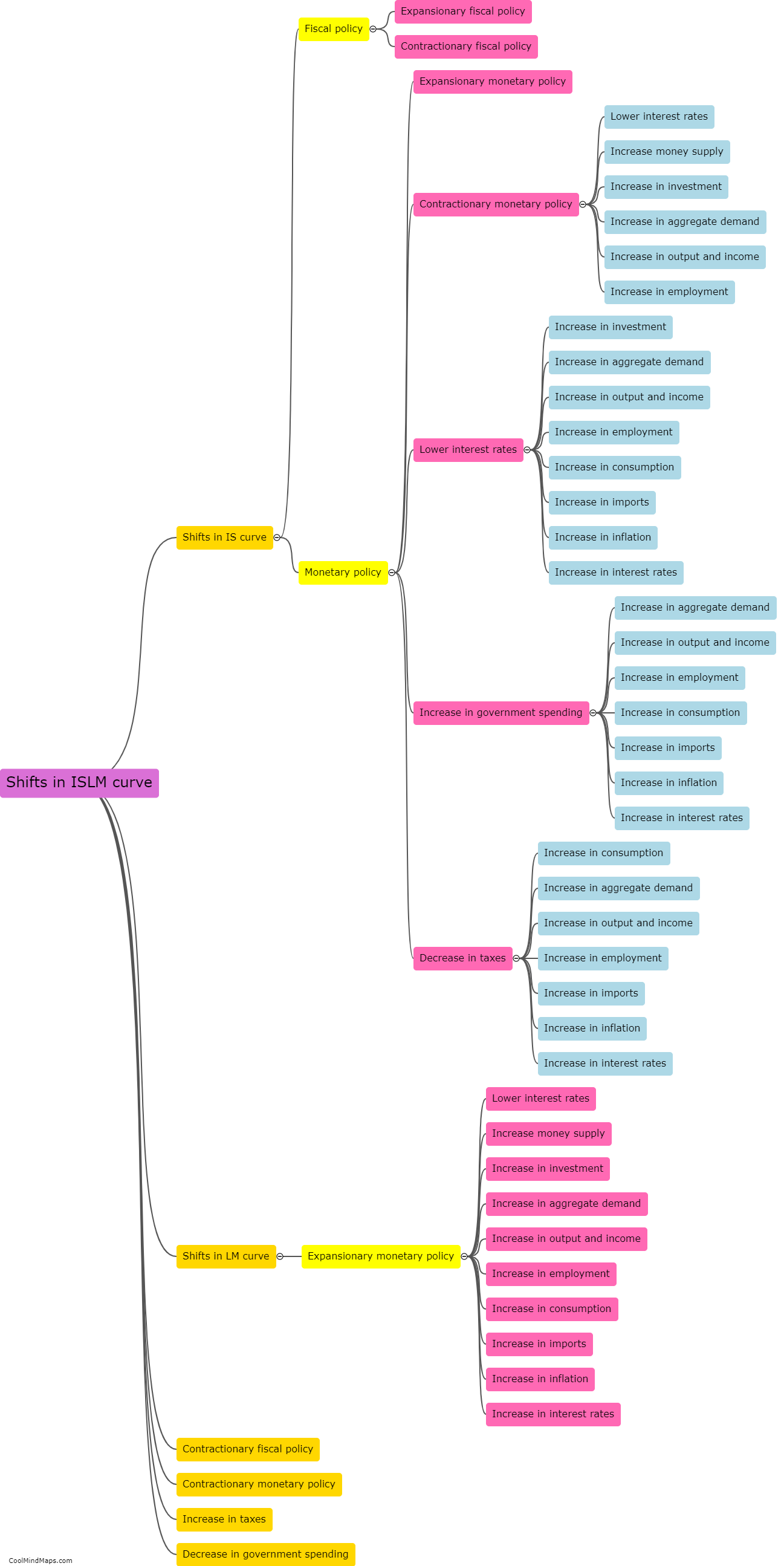
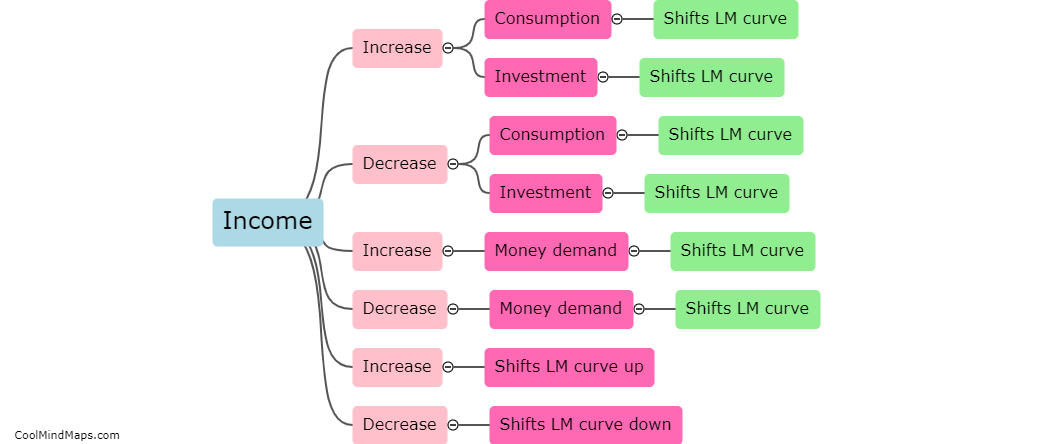
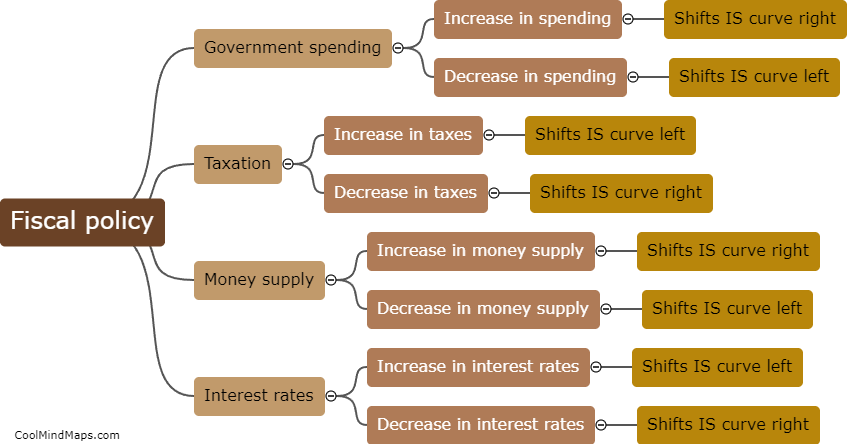
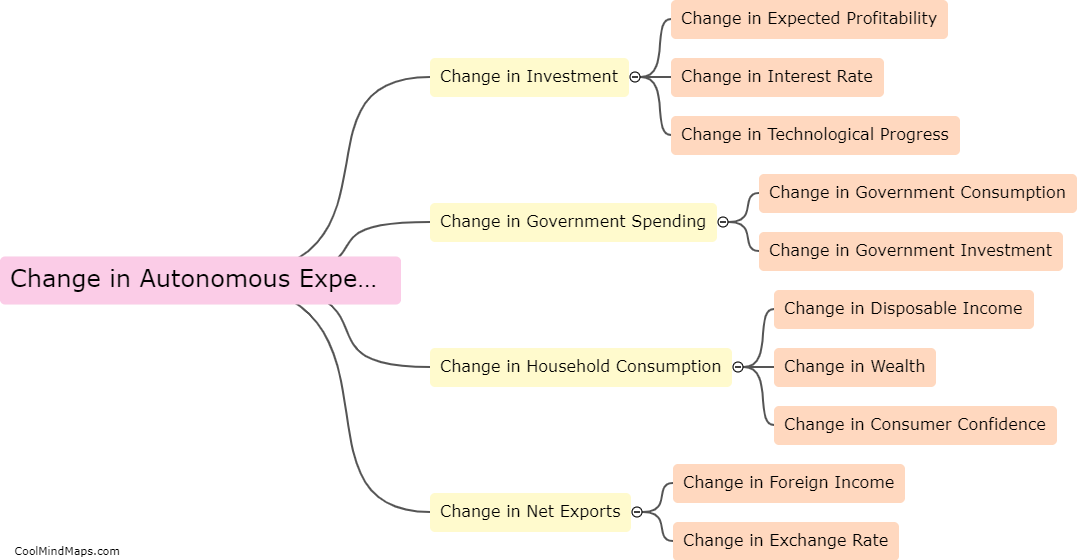
The IS (investment-saving) curve represents the relationship between a country's output and the interest rate in the short run. Several factors can shift the IS curve, impacting the equilibrium level of output. Changes in fiscal policy, such as variations in government spending or taxation, can shift the IS curve. Increased government spending or reduced taxes lead to higher output and shift the IS curve to the right, while decreased spending or increased taxes have the opposite effect. Additionally, changes in investment spending by firms or changes in consumer spending can also shift the IS curve. Increases in investment or consumer spending raise output and shift the curve to the right, while decreases in these components have the opposite effect. Finally, changes in expectations about future income or economic conditions can shift the IS curve. If individuals or firms become more optimistic about the future, they are likely to increase spending, shifting the IS curve to the right. Conversely, if expectations turn negative, spending will decline, shifting the curve to the left.
This mind map was published on 26 September 2023 and has been viewed 145 times.