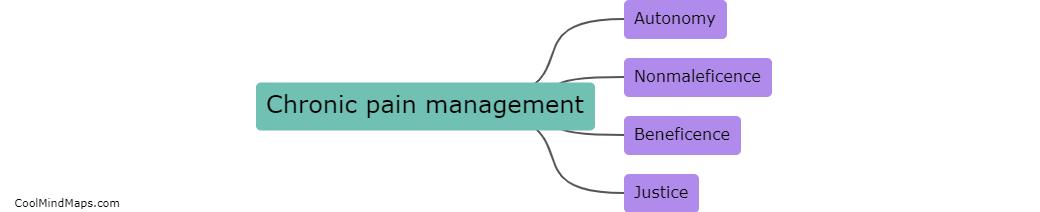
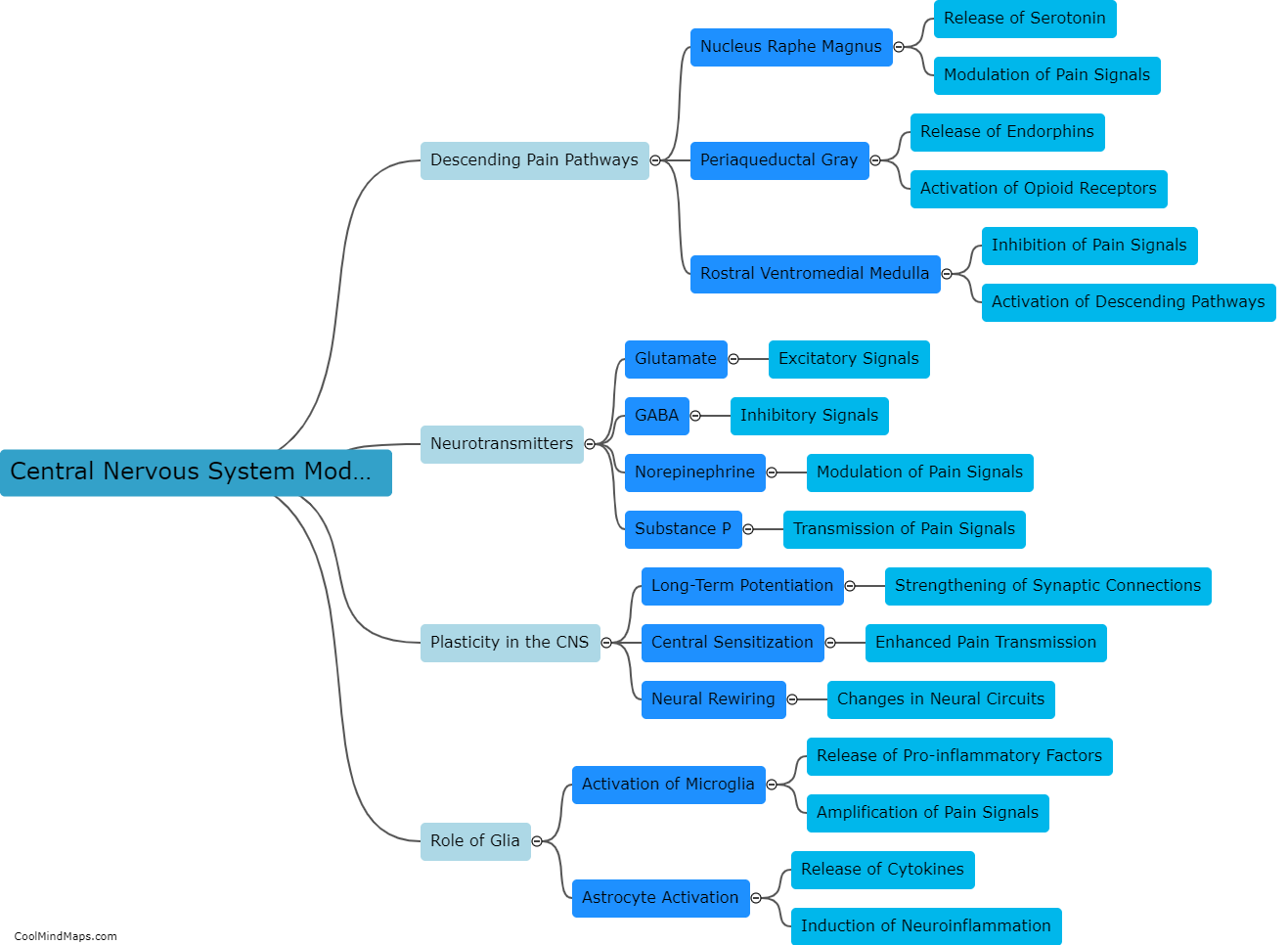
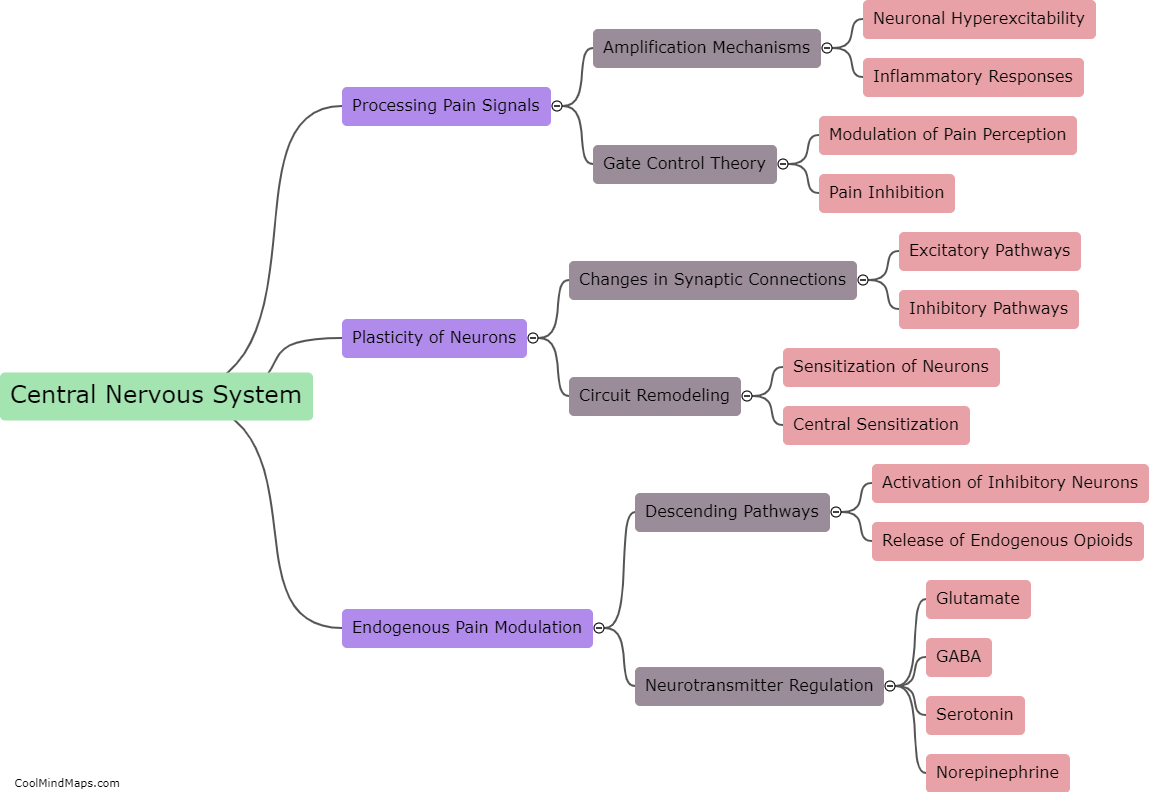
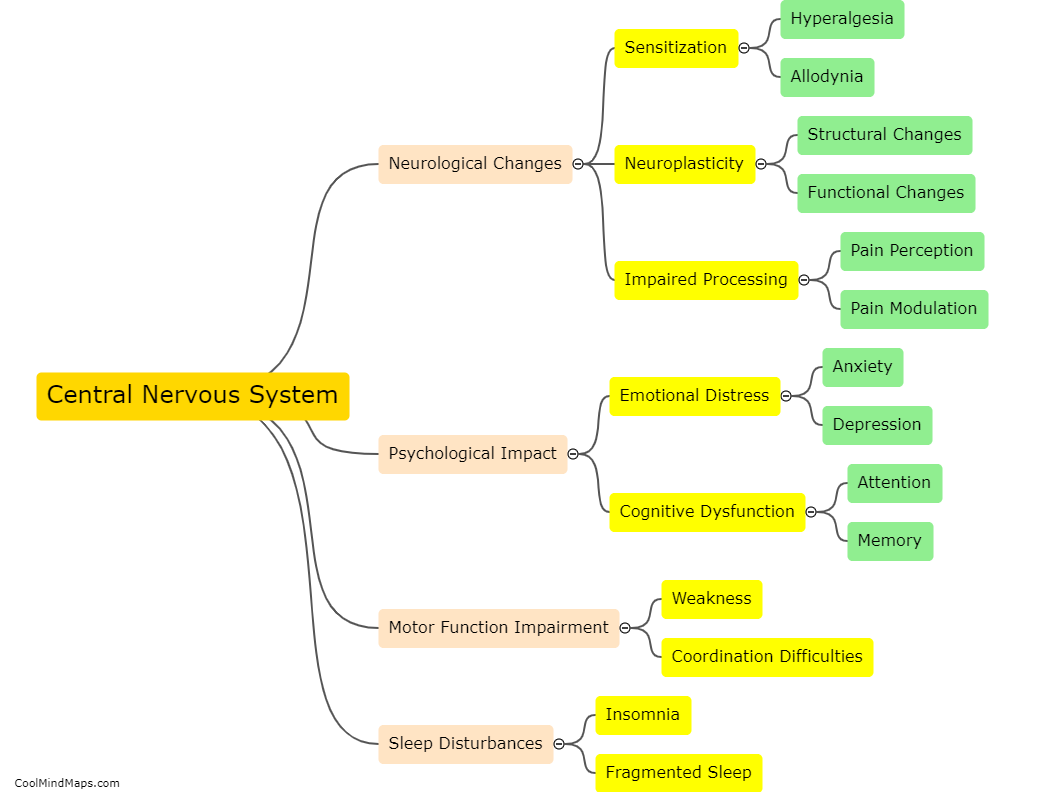
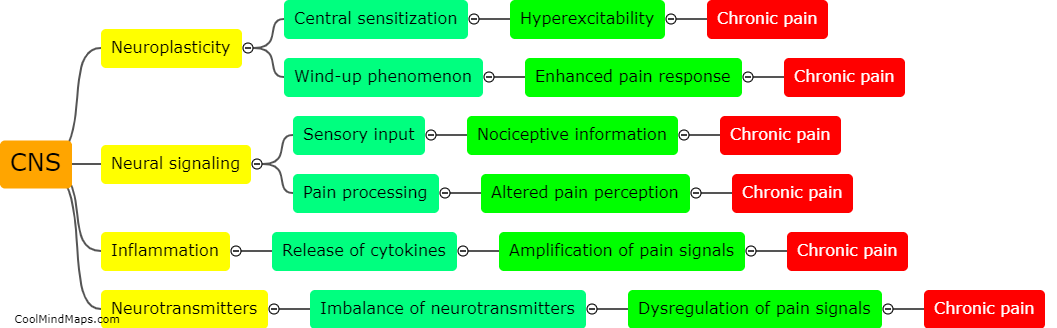
How does the central nervous system contribute to chronic pain development?
The central nervous system (CNS) plays a crucial role in the development of chronic pain. When an injury or damage occurs, sensory signals are transmitted to the CNS, where they are processed and translated into pain sensations. In cases of acute pain, the CNS responds appropriately by initiating protective mechanisms and promoting healing. However, in chronic pain, the CNS maladaptively amplifies pain signals, leading to a persistent and often debilitating condition. This can occur due to a variety of factors, including changes in the structure and function of the neurons involved in pain processing, alterations in neurotransmitter levels and pathways, and abnormal activation of glial cells. Additionally, long-term exposure to pain can induce a phenomenon known as central sensitization, in which the CNS becomes hypersensitive to pain signals, amplifying their perceived intensity and duration. Ultimately, an understanding of the CNS's contribution to chronic pain is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies to manage and alleviate this complex condition.
This mind map was published on 2 December 2023 and has been viewed 89 times.