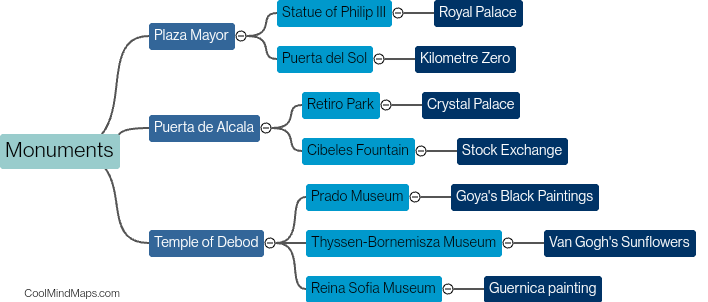
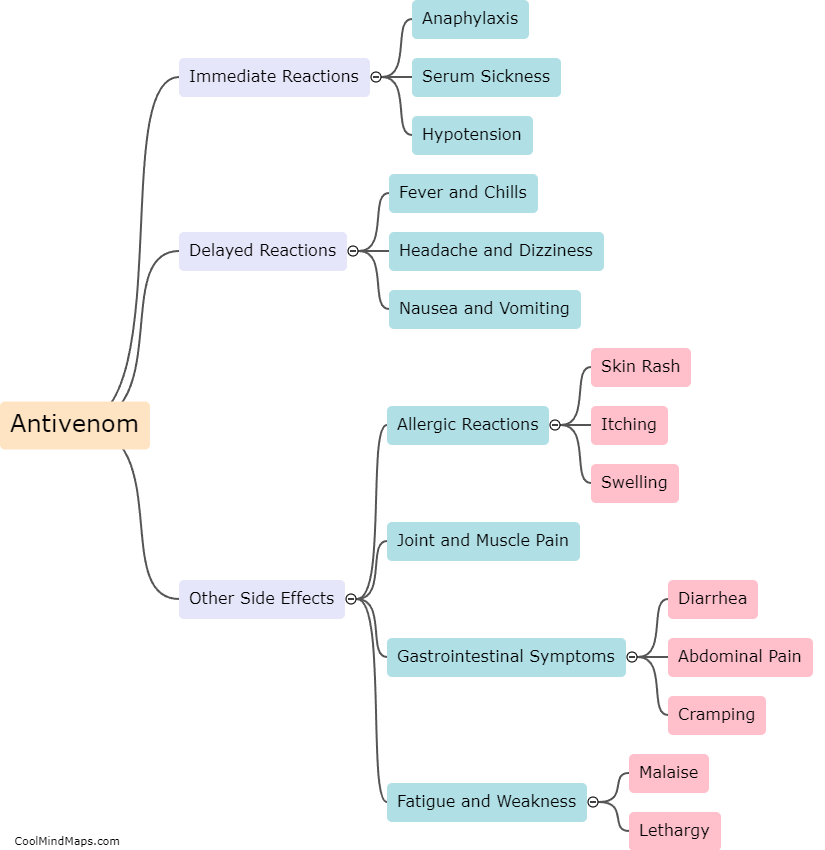
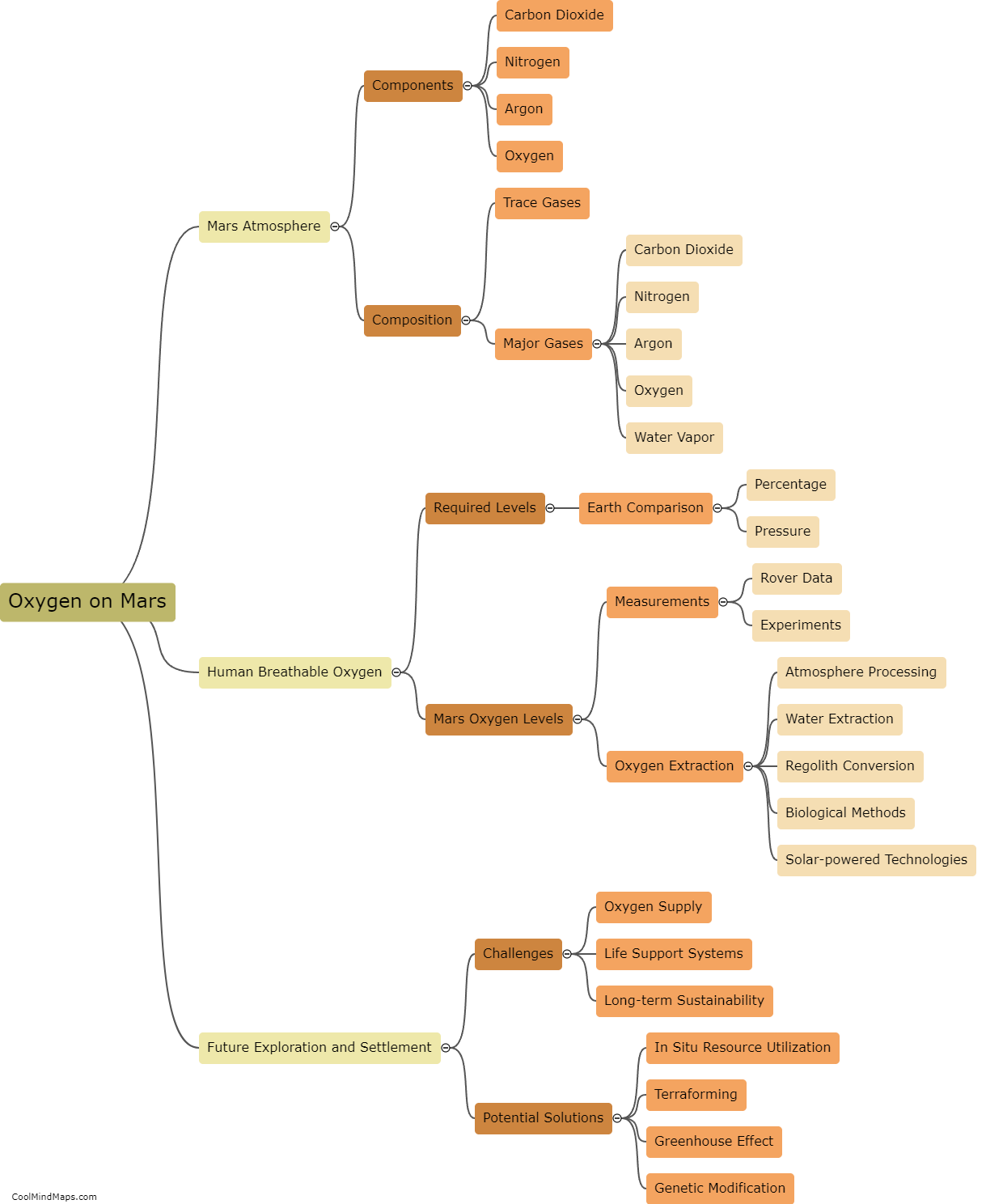
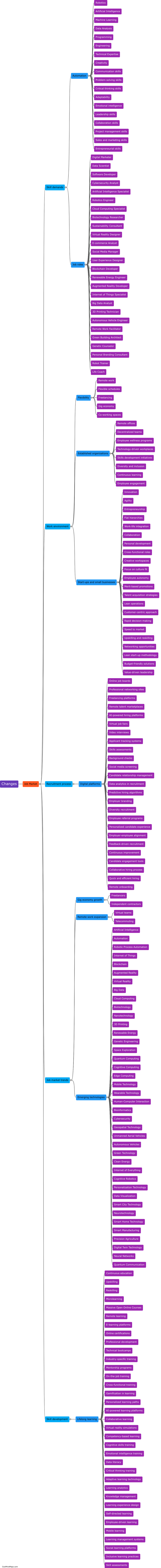
What factors determine the duration of day and night on each planet?
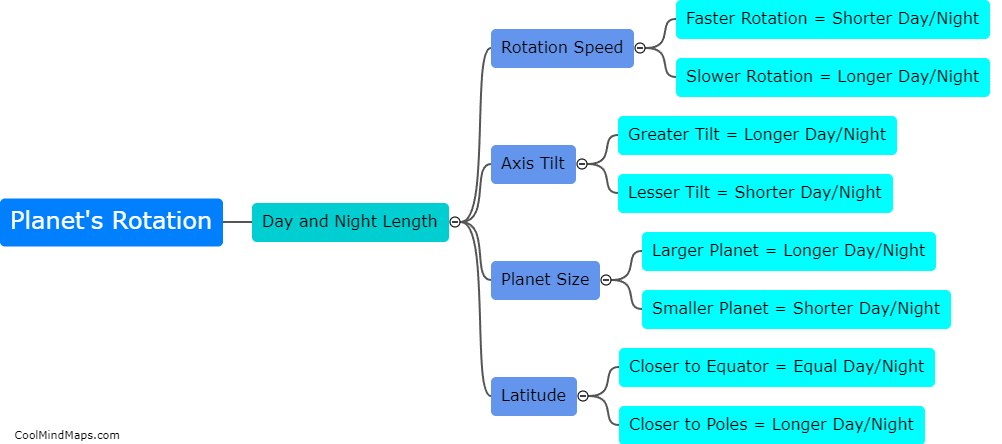
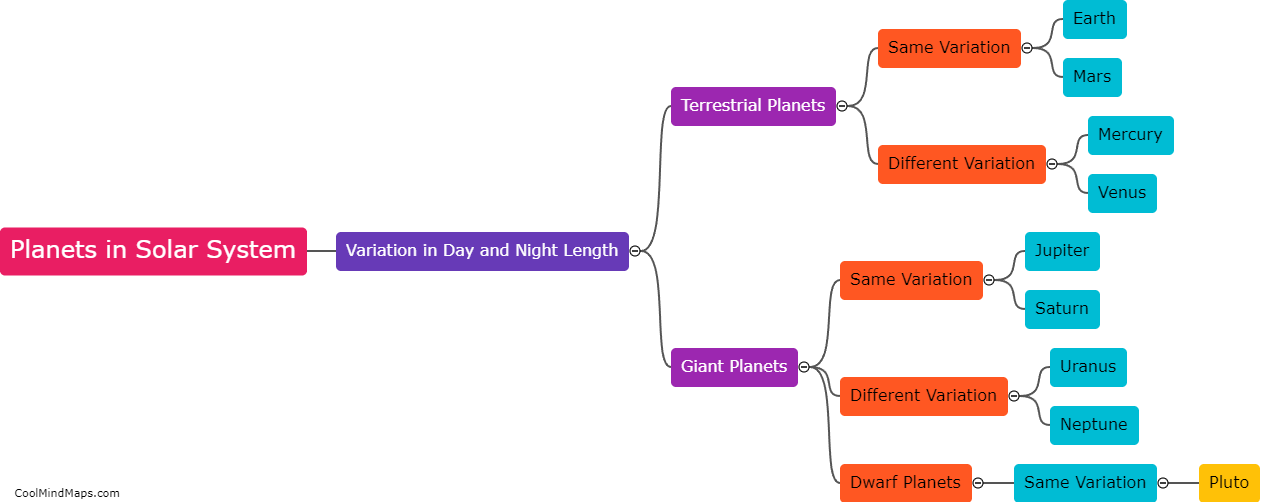
The duration of day and night on each planet is primarily determined by two key factors: the planet's rotation period and its axial tilt. The rotation period refers to the time it takes for a planet to complete one full rotation on its axis. This rotation determines the length of a day and night on the planet. For instance, Earth takes approximately 24 hours to complete one rotation, resulting in 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness. However, the axial tilt of a planet can significantly affect the duration of day and night. A planet's axial tilt determines the angle at which its axis is tilted relative to its orbit around the Sun. This tilt causes variations in the intensity and duration of sunlight received by different regions of the planet throughout its year, resulting in longer or shorter days and nights. For example, Earth has an axial tilt of about 23.5 degrees, which leads to the changing lengths of day and night as we experience throughout the year. In contrast, planets with more extreme axial tilts like Uranus (98 degrees) or with no axial tilt like Mercury (0 degrees) experience different day-night patterns. Hence, the interaction between a planet's rotation period and its axial tilt are the primary factors that determine the duration of day and night on each planet.
This mind map was published on 13 October 2023 and has been viewed 97 times.