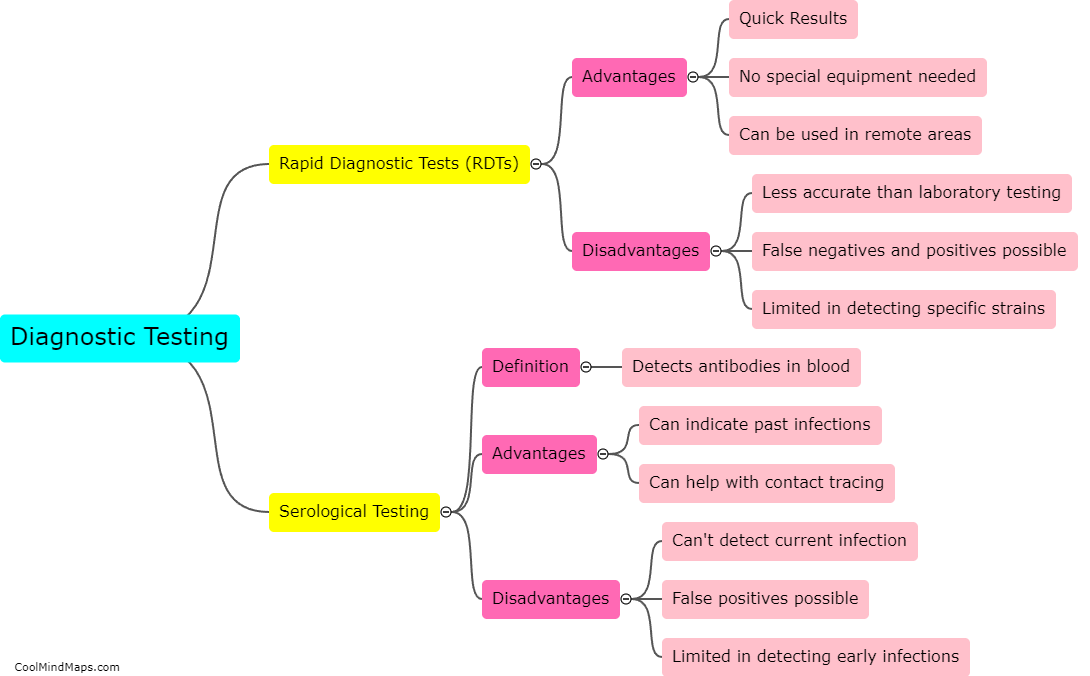
What are Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs) and serological testing, and their limitations?
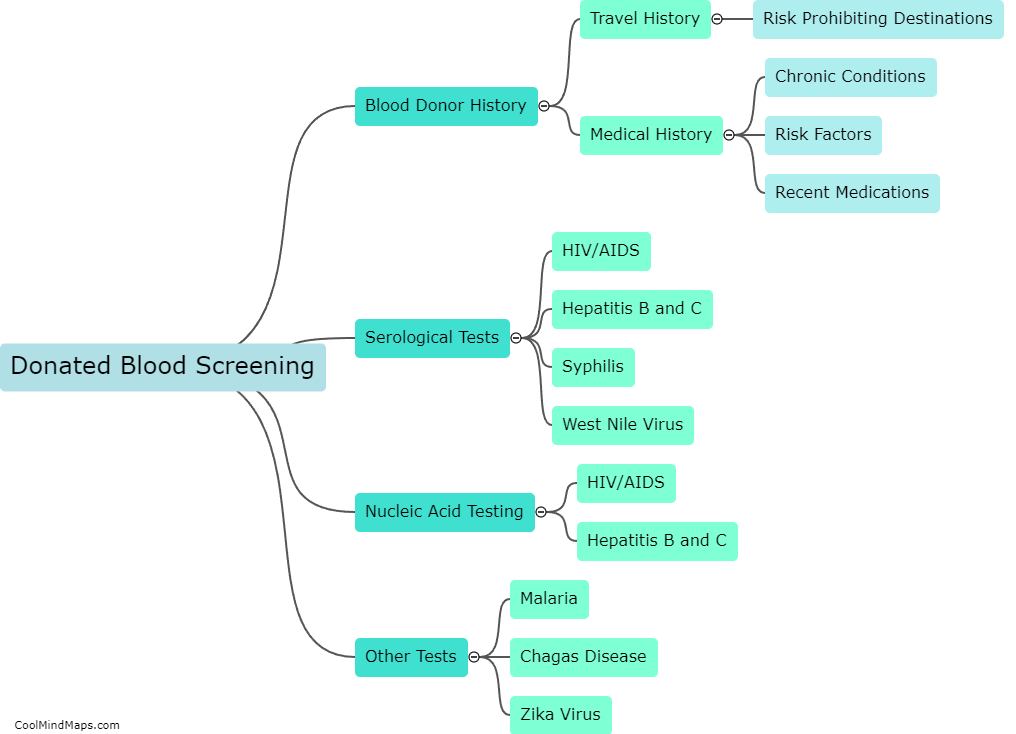
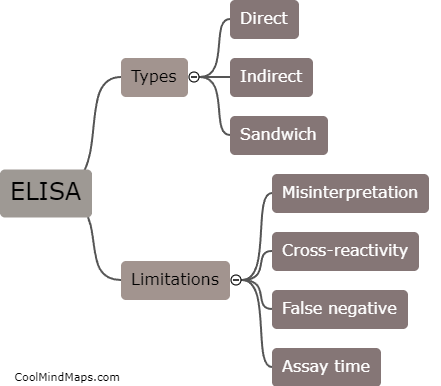
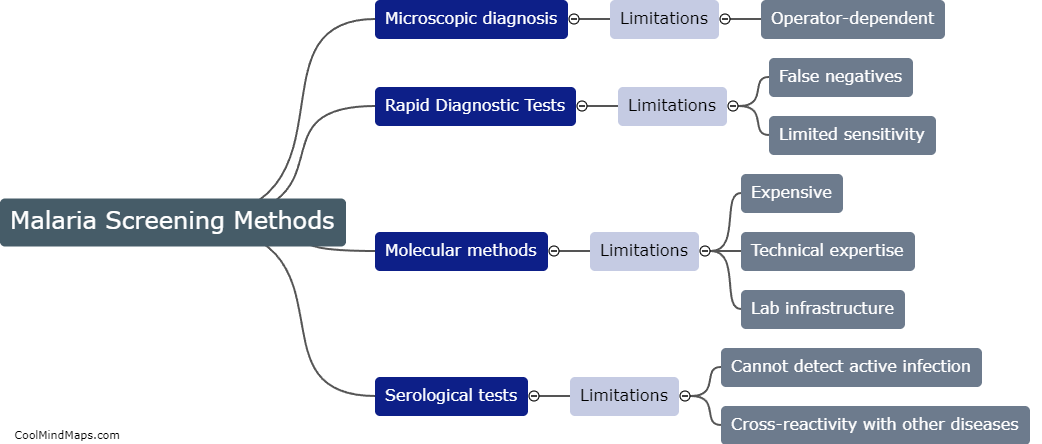
Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs) and serological testing are diagnostic tools used to detect the presence of antibodies or antigens in individuals. RDTs are designed for rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases such as malaria, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS in resource-limited settings. Serological testing detects the presence of antibodies in a person's blood to determine if they have been exposed to an infectious agent. Both RDTs and serological testing have limitations, including potential false positives or negatives, as well as the inability to distinguish between active and past infections. Additionally, these tests may not be sensitive enough to detect low levels of antibodies, and results may vary depending on the quality and timing of the sample collected. Therefore, it is important to interpret test results in the context of the patient's medical history and clinical presentation.
This mind map was published on 25 June 2023 and has been viewed 110 times.