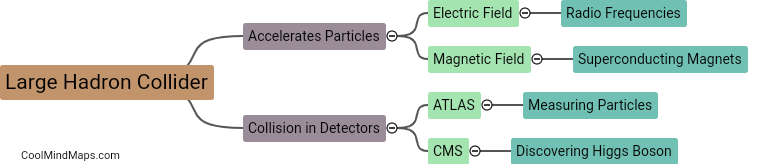
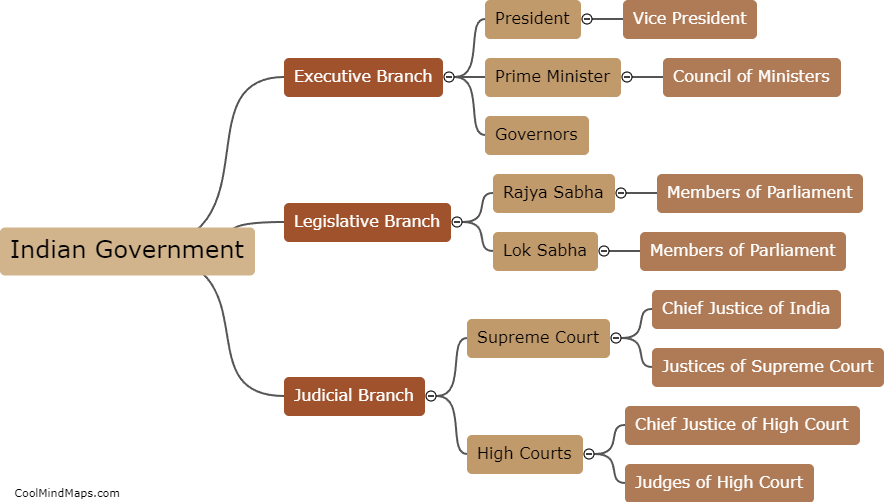
What is the structure of Indian government?
The Indian government is democratic in nature and follows a federal system, which means it consists of both national and state governments. The national government is headed by the President and has three branches of power: the legislative, the executive, and the judiciary. The legislative branch is composed of the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the People). The executive branch is led by the Prime Minister, who heads the Council of Ministers. The judiciary is independent of the other two branches and is represented by the Supreme Court of India. The state governments also have a similar structure with a Governor as the head of the state and a Chief Minister as the head of the executive branch. The Indian Constitution lays out the powers and jurisdictions of each level of government, and both national and state governments have their own roles and responsibilities.
This mind map was published on 20 June 2023 and has been viewed 153 times.