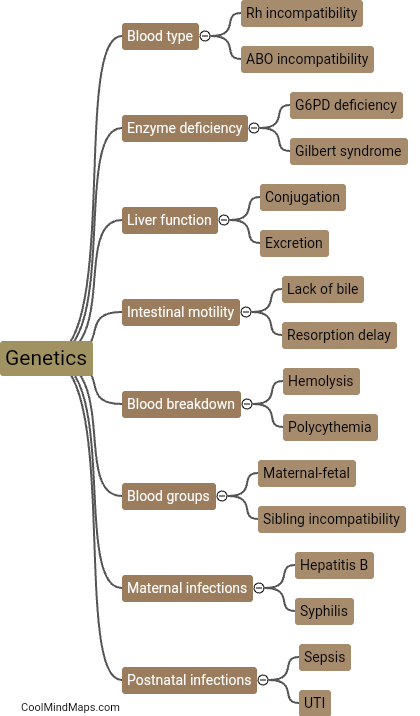
What causes neonatal jaundice?
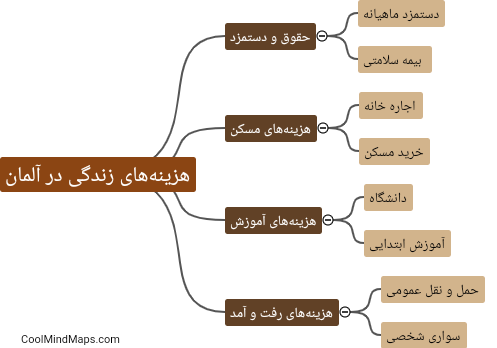
Neonatal jaundice, also known as hyperbilirubinemia, occurs in newborn babies when there is a build-up of bilirubin in their blood. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment that is released when red blood cells break down. In newborns, their liver is not fully developed yet, which can lead to difficulty in processing and excreting bilirubin. This can result in the characteristic yellowing of the skin and eyes seen in jaundice. Other factors that can contribute to neonatal jaundice include premature birth, blood type incompatibility between the mother and baby, and certain medical conditions affecting the liver or bile ducts.
This mind map was published on 20 September 2024 and has been viewed 43 times.