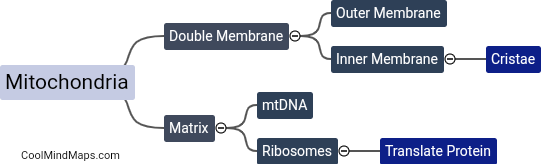
What is the structure of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are organelles that are responsible for generating most of the energy required by the cell to carry out various functions. The structure of mitochondria is characterized by two distinct membranes: the outer mitochondrial membrane and the inner mitochondrial membrane. The outer membrane is porous and allows various substances to pass through, while the inner membrane is folded into numerous cristae, which increase the surface area and provide space for several enzymes involved in cellular respiration. The space between the outer and inner membranes is called the intermembrane space, which contains several metabolic enzymes that facilitate the breakdown of macromolecules. Overall, the structure of mitochondria is highly specialized and essential for maintaining cellular energy balance.
This mind map was published on 29 April 2023 and has been viewed 90 times.