What is transfection?
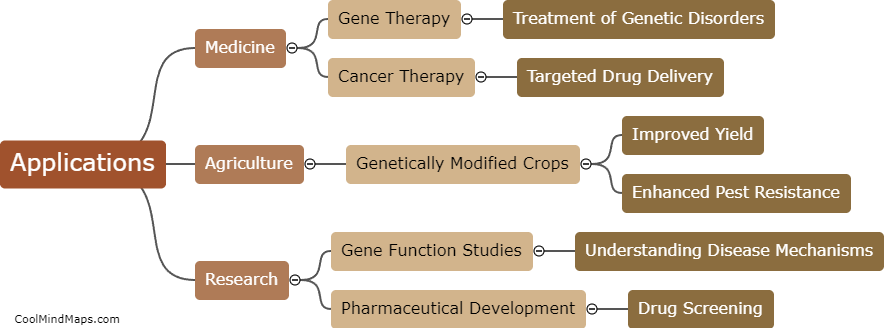
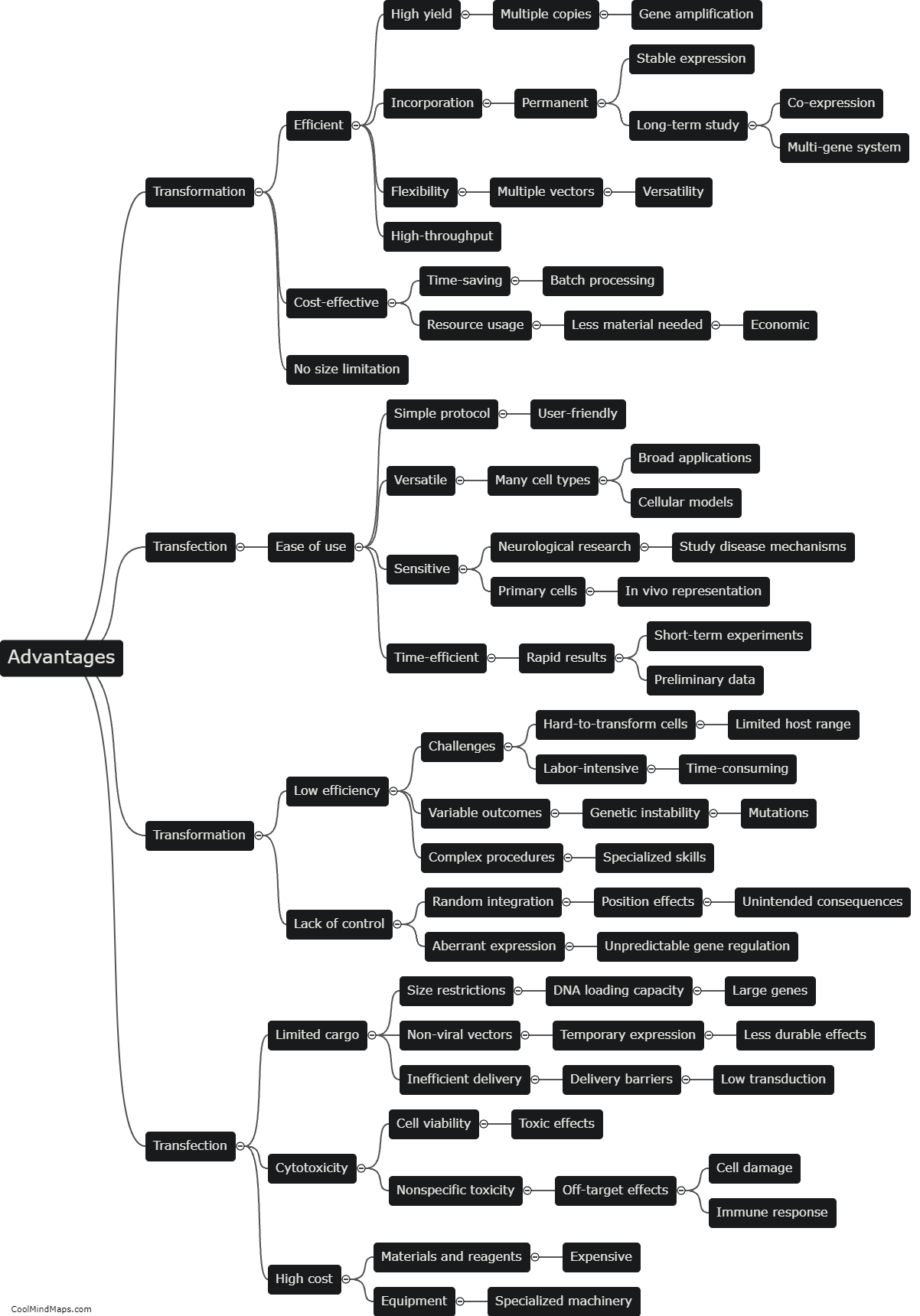
Transfection is a laboratory technique used to introduce foreign genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, into cells. It allows researchers to manipulate gene expression and study how specific genes or molecules affect cell function. Transfection can be achieved using different methods, including chemical, physical, or viral-based approaches. Chemical transfection involves using lipid or polymer-based reagents to form complexes with the genetic material, which can then be efficiently taken up by the cells. Physical methods, such as electroporation or gene gun, utilize electric pulses or high-pressure shockwaves to increase cell membrane permeability, enabling the uptake of foreign DNA. Viral-mediated transfection exploits the natural ability of viruses to infect cells, genetically modifying them in the process. Transfection has revolutionized various areas of research, including molecular biology, genetics, and biotechnology, by enabling the study of gene function, gene therapy, and the production of recombinant proteins.

This mind map was published on 16 October 2023 and has been viewed 102 times.