What is the Law of Coulomb?
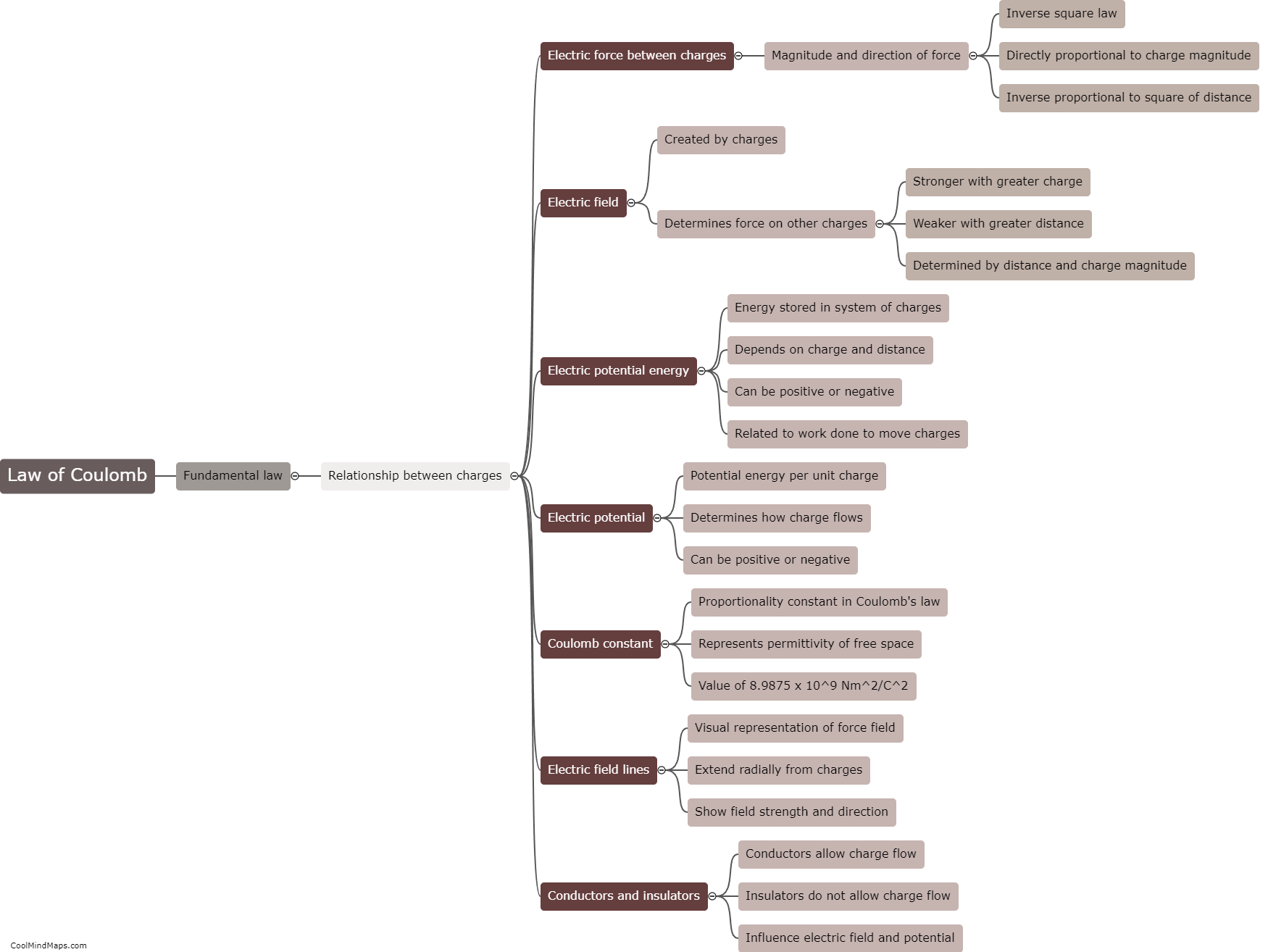
The Law of Coulomb, named after French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, is a fundamental principle in electromagnetism that describes the force between two charged objects. According to this law, the force between two charged particles is directly proportional to the product of their charges, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Simply put, if the charges are of the same sign, they repel each other, whereas oppositely charged objects attract each other. The magnitude of this force can be calculated using the equation F = k(q1*q2)/r^2, where F represents the force, q1 and q2 denote the charges, r is the distance between them, and k is the proportionality constant. The Law of Coulomb plays a crucial role in understanding and predicting the behavior of charged particles within electrical and electrostatic systems.
This mind map was published on 16 November 2023 and has been viewed 80 times.