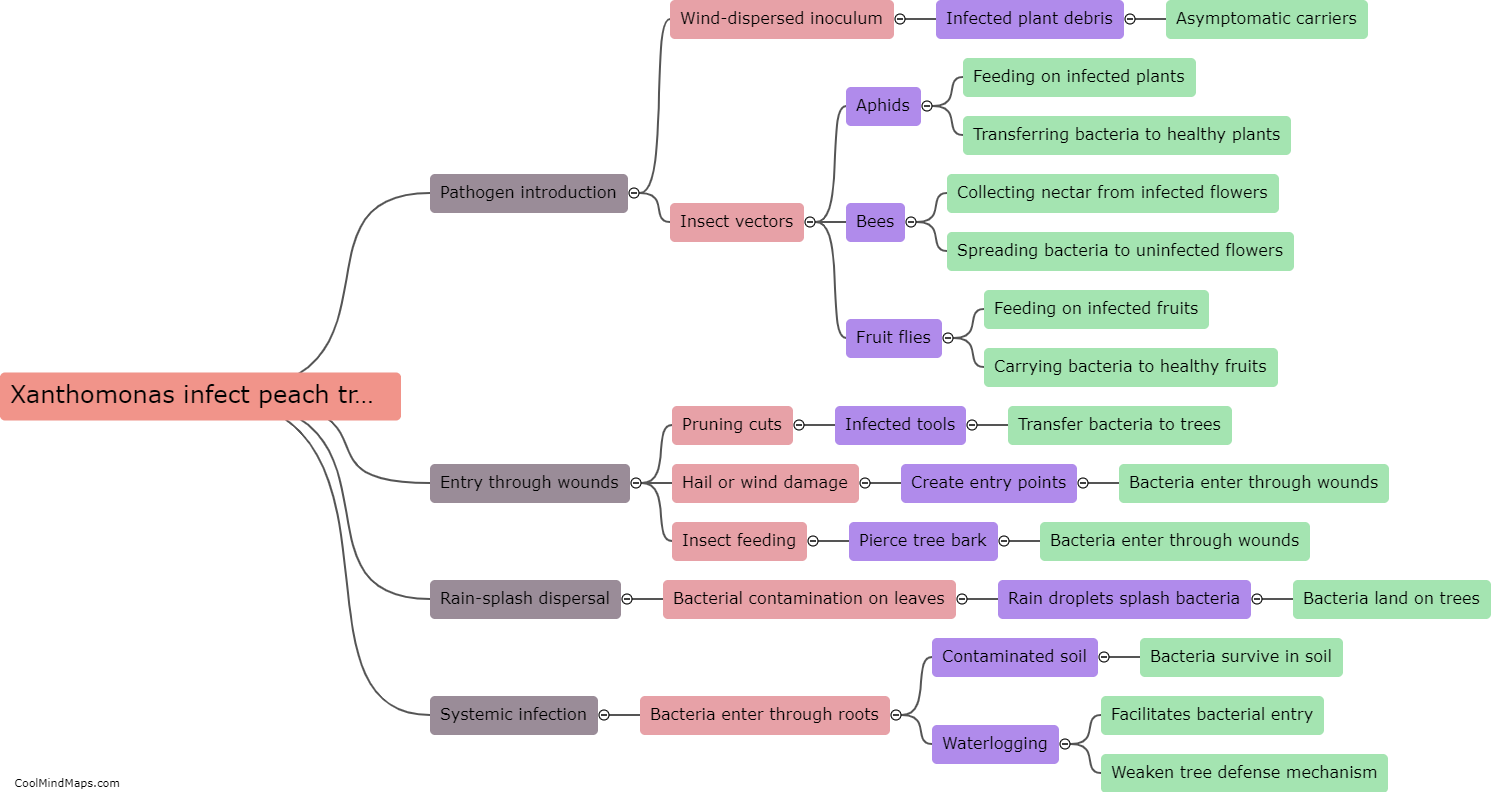
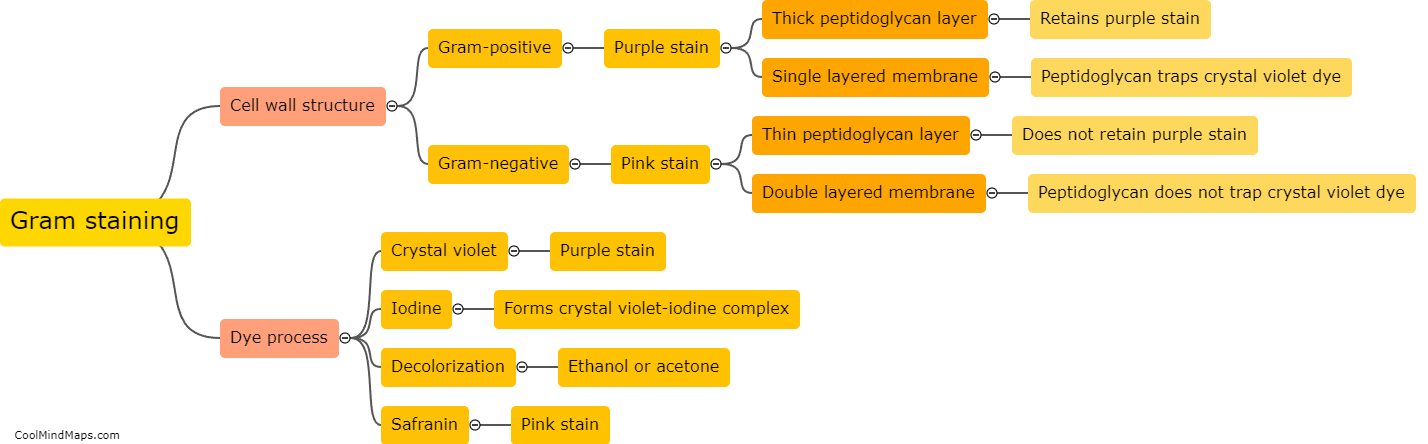
How does Gram staining differentiate between bacteria?
Gram staining is a common technique used in microbiology to differentiate between different types of bacteria based on the composition of their cell walls. The staining process involves several steps, starting with the application of crystal violet dye, followed by iodine to form a complex with the dye, and then decolorization using alcohol or acetone. The final step involves counter-staining with safranin. The key difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria lies in the structure of their cell walls. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet-iodine complex and appear purple under the microscope, whereas Gram-negative bacteria lose this complex and take up the safranin counterstain, appearing pink or red. This differential staining pattern helps microbiologists identify and classify bacteria into these two major groups.
This mind map was published on 15 August 2023 and has been viewed 97 times.