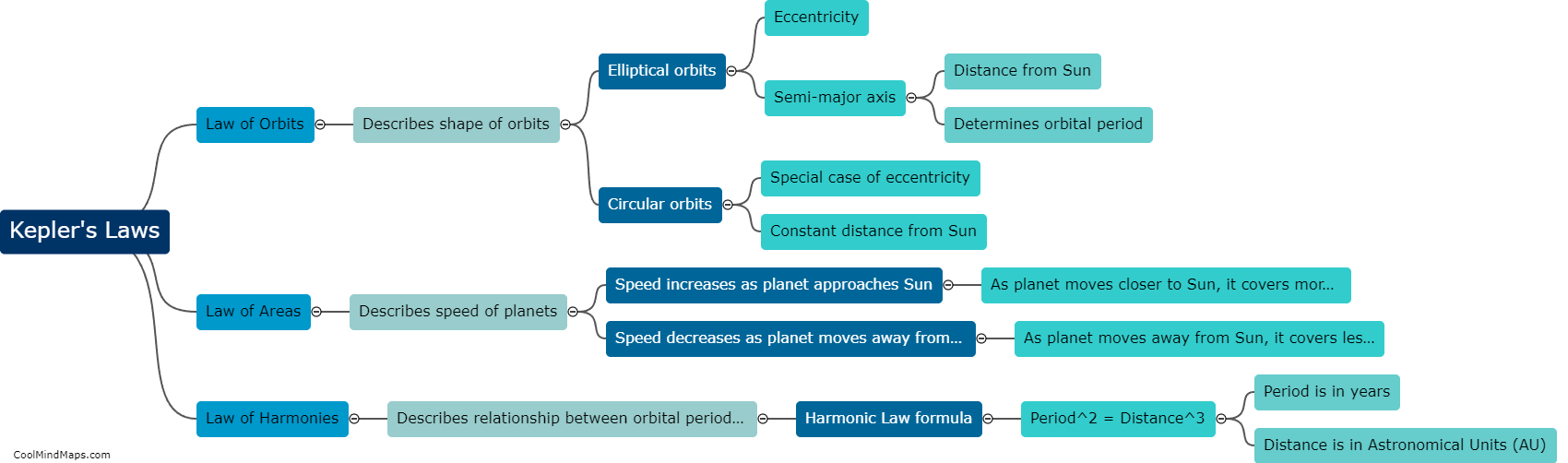
How do Kepler's laws explain the movement of planets?
Kepler's laws, formulated by the German astronomer Johannes Kepler in the early seventeenth century, provide a comprehensive explanation of how planets move in their orbits around the Sun. The first law, also known as the law of elliptical orbits, states that planets move in elliptical paths with the Sun at one of the two foci. This means that planets do not orbit in perfect circles, but rather in slightly elongated oval-shaped paths. The second law, known as the law of equal areas, states that a planet will sweep out equal areas in equal time intervals as it moves around its orbit. This implies that a planet moves faster when it is closer to the Sun and slower when it is farther away, thereby maintaining conservation of angular momentum. Finally, Kepler's third law, also referred to as the law of harmonies, establishes a relationship between a planet's period (the time it takes to complete one orbit) and its average distance from the Sun. The square of a planet's period is proportional to the cube of its average distance from the Sun. In summary, Kepler's laws explain how planets move in non-circular orbits at varying speeds depending on their distance from the Sun, and how these factors are mathematically related.
This mind map was published on 29 November 2023 and has been viewed 107 times.