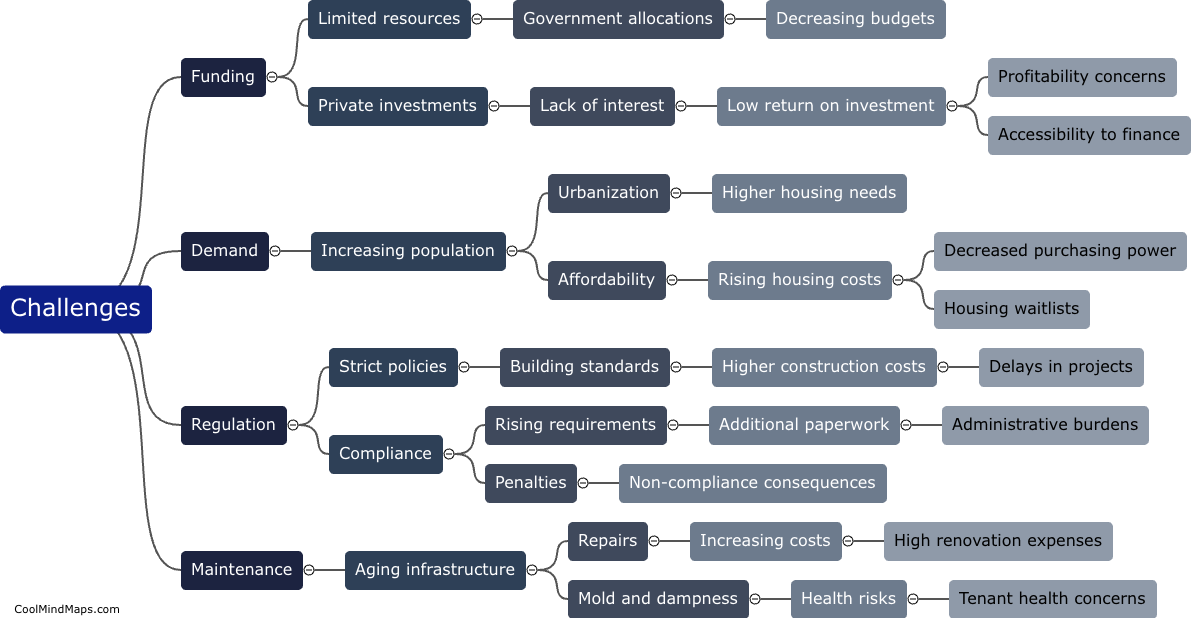
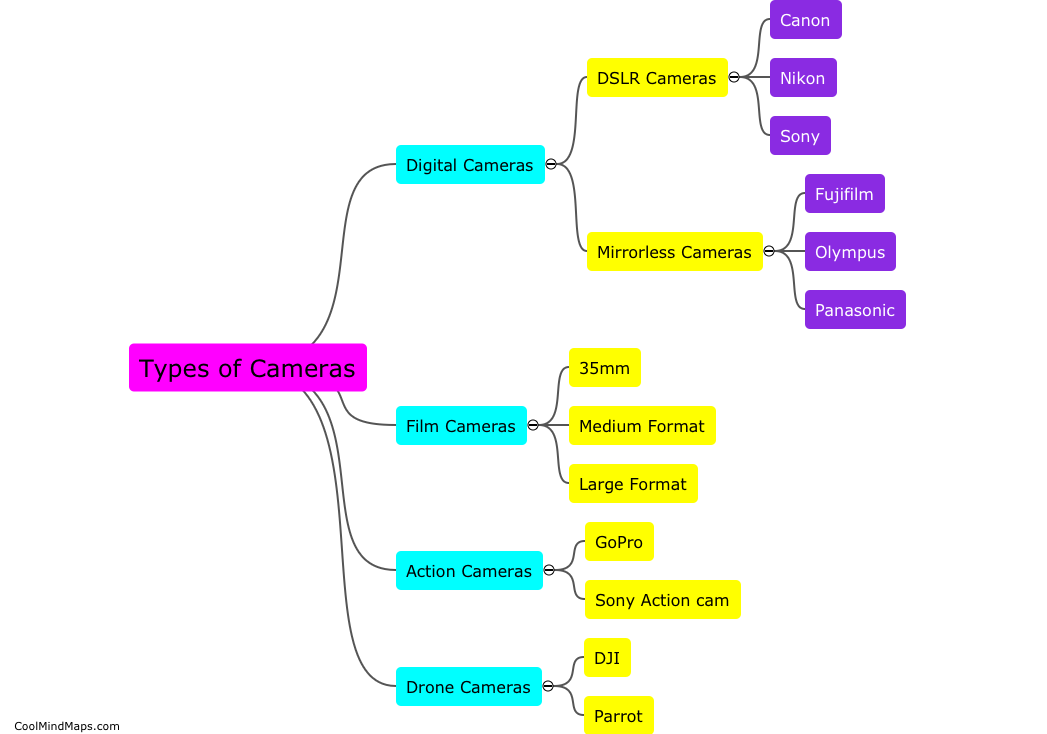
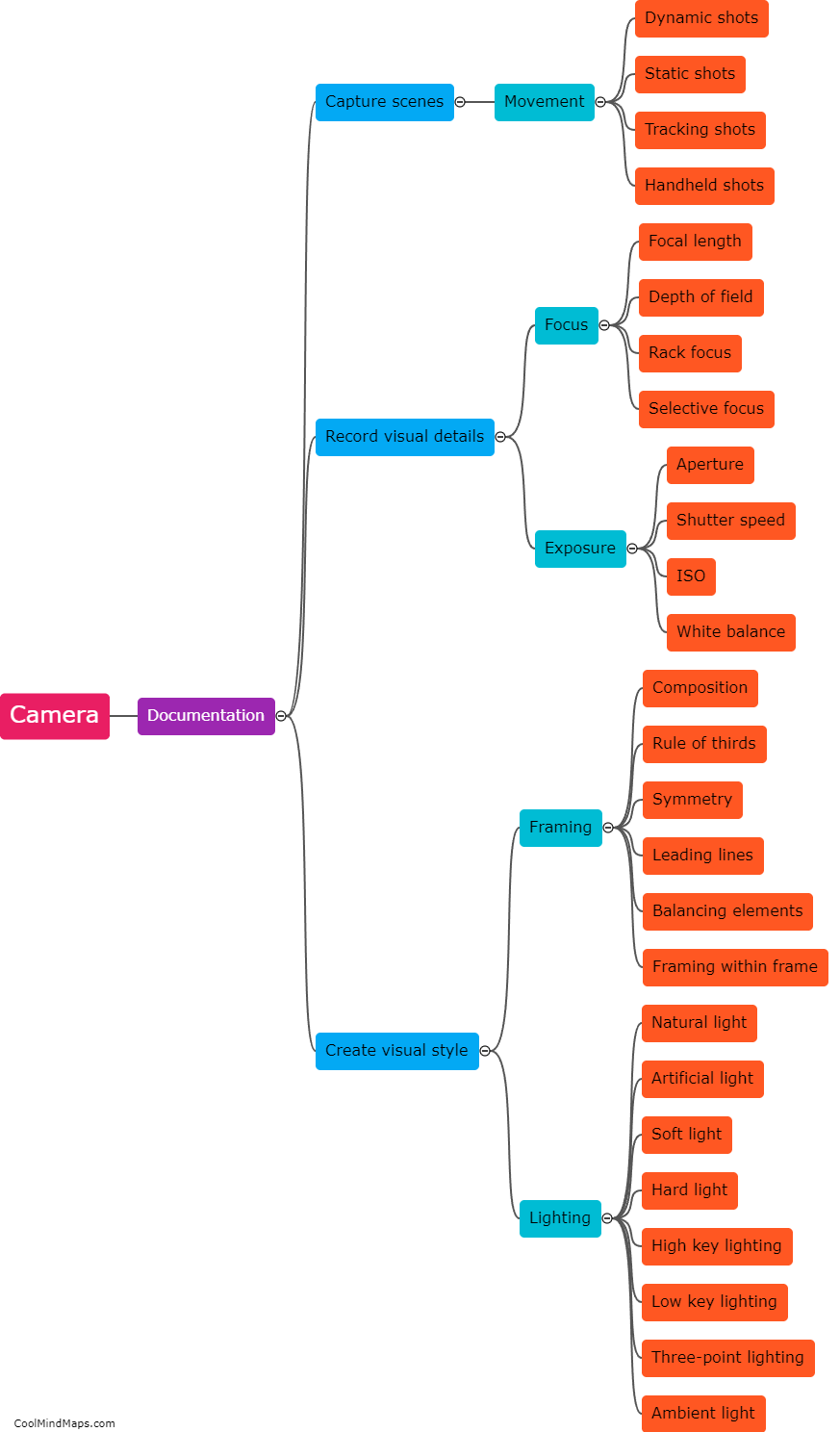
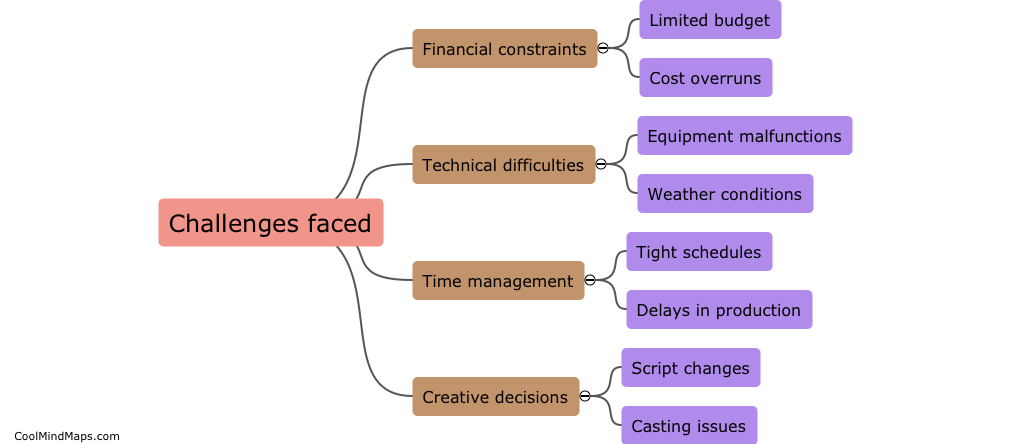
How does DNA contribute to molecular biology?
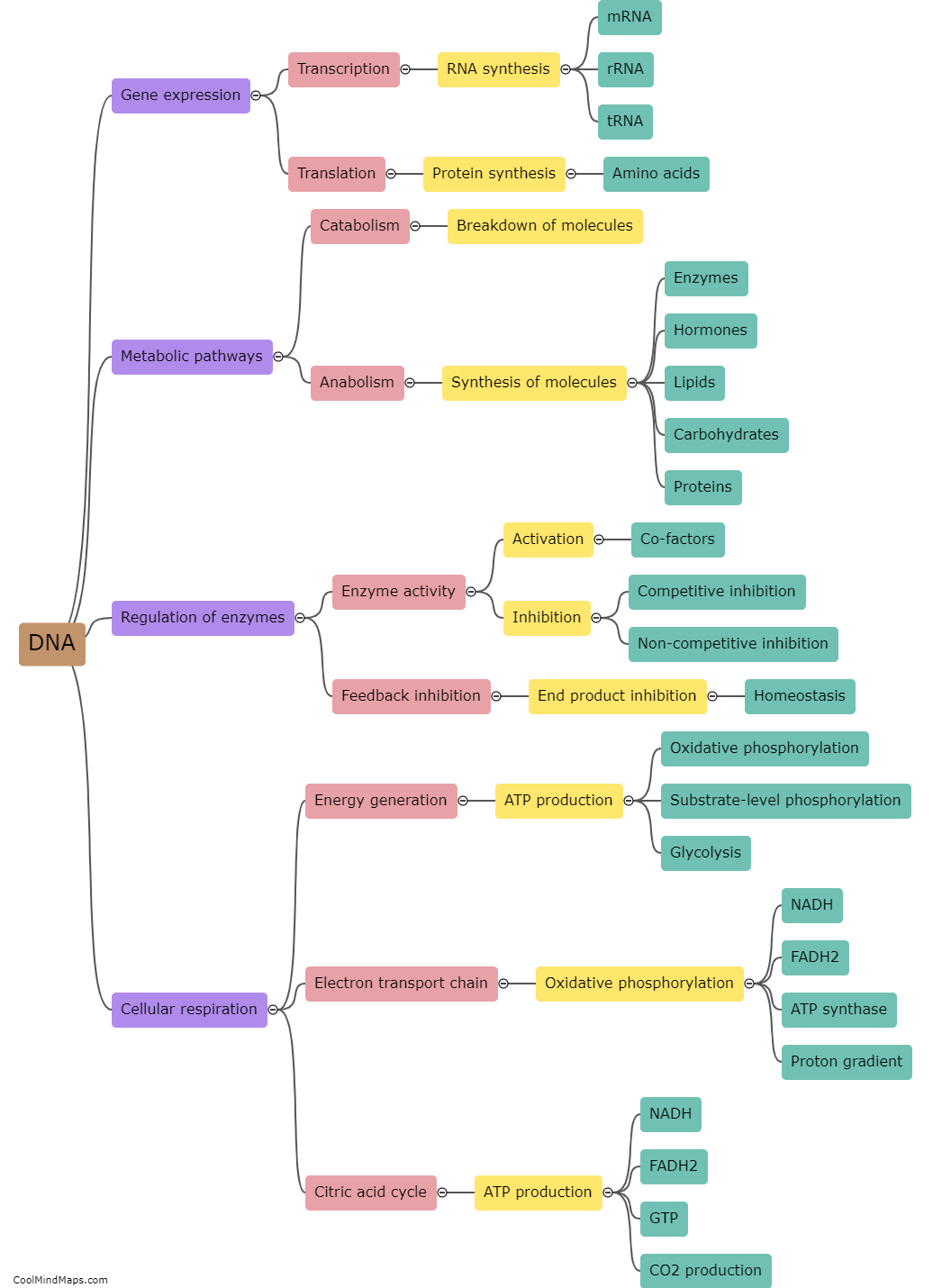
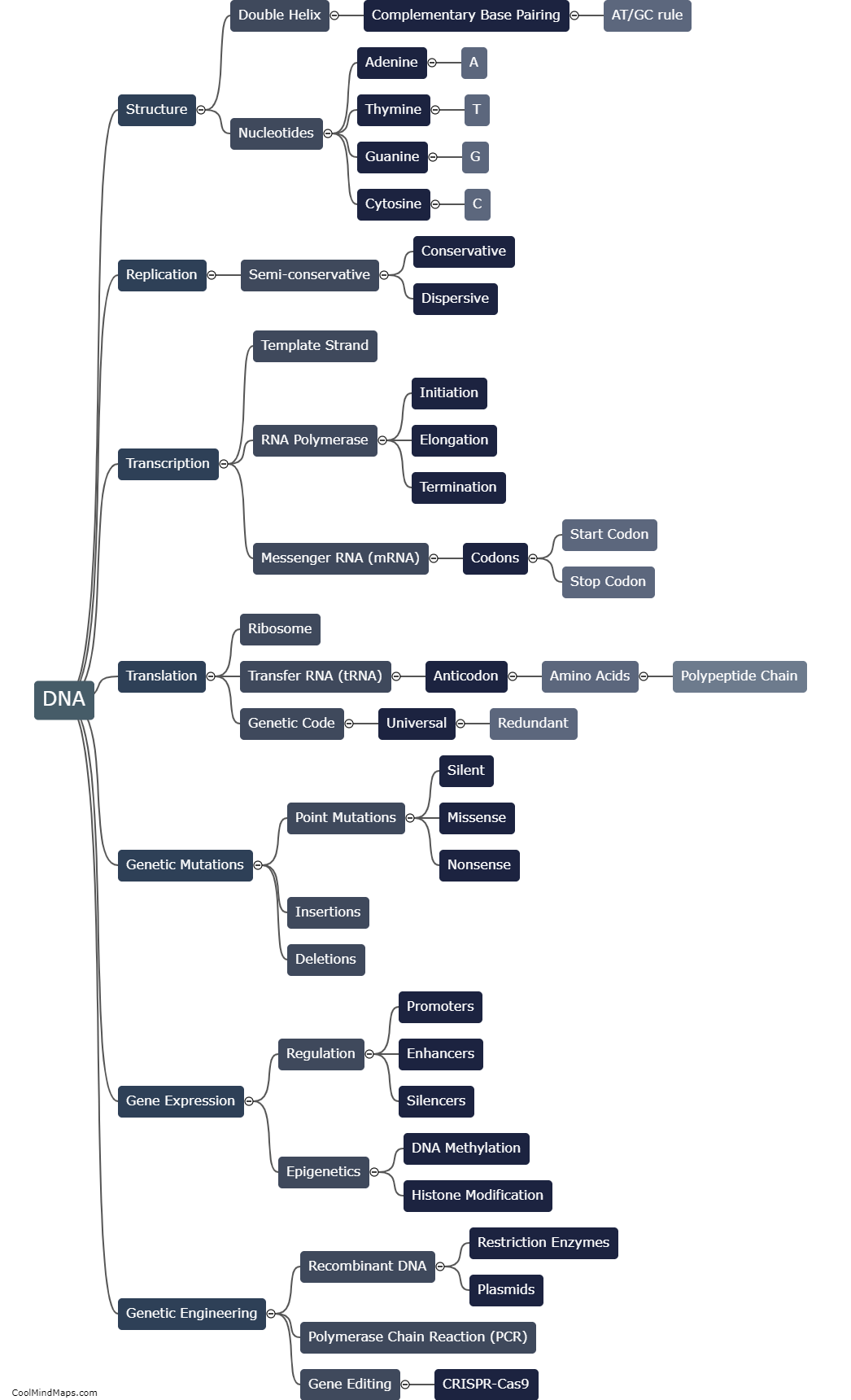
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, plays a pivotal role in molecular biology by providing the blueprint for the synthesis of proteins, the building blocks of life. DNA consists of sequences of nucleotides, each containing a specific arrangement of the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These sequences are transcribed into RNA and subsequently translated to produce proteins. The information encoded in DNA is responsible for determining an organism's genetic traits, including its physical characteristics, susceptibility to diseases, and even behavior. By understanding and manipulating DNA, scientists can unravel the mysteries of life, study genetic disorders, develop new drugs, and engineer novel organisms. Thus, DNA is at the core of molecular biology and its understanding has revolutionized this field of science.
This mind map was published on 22 November 2023 and has been viewed 96 times.