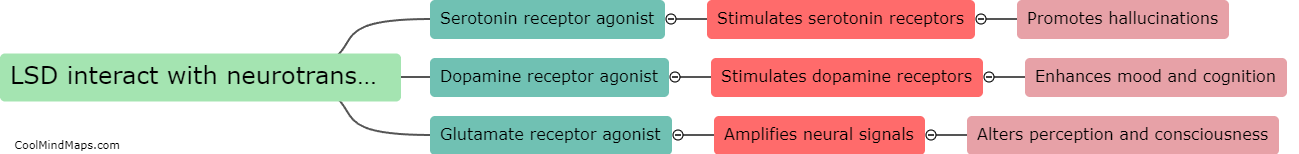
How does LSD interact with neurotransmitters?
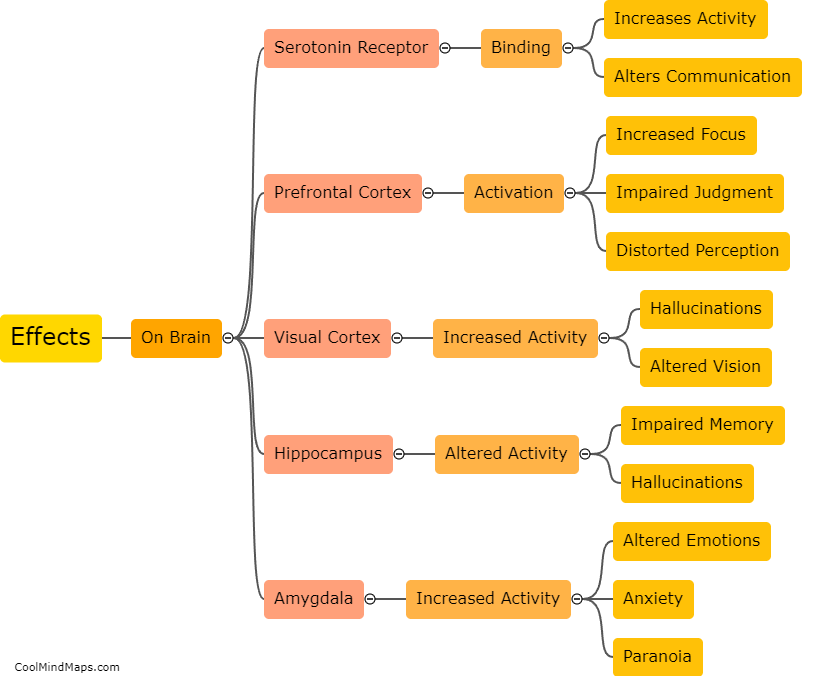
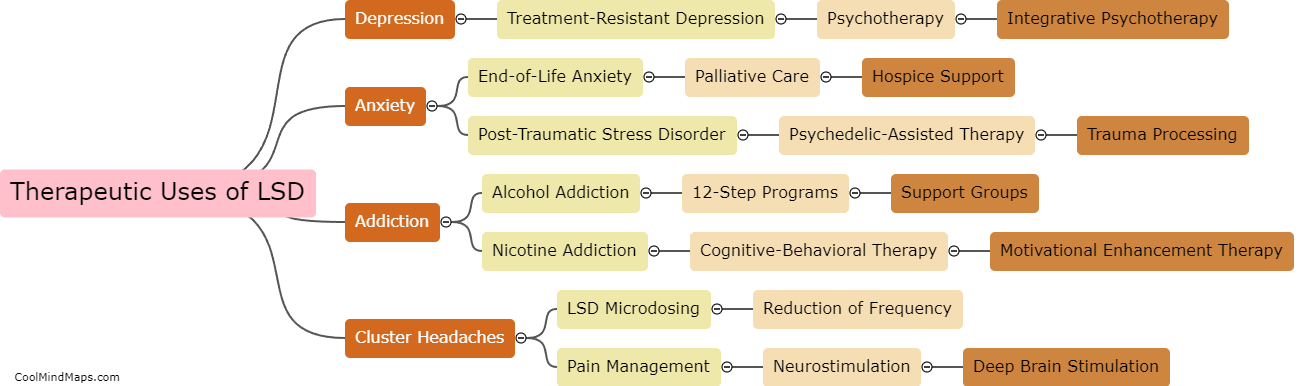
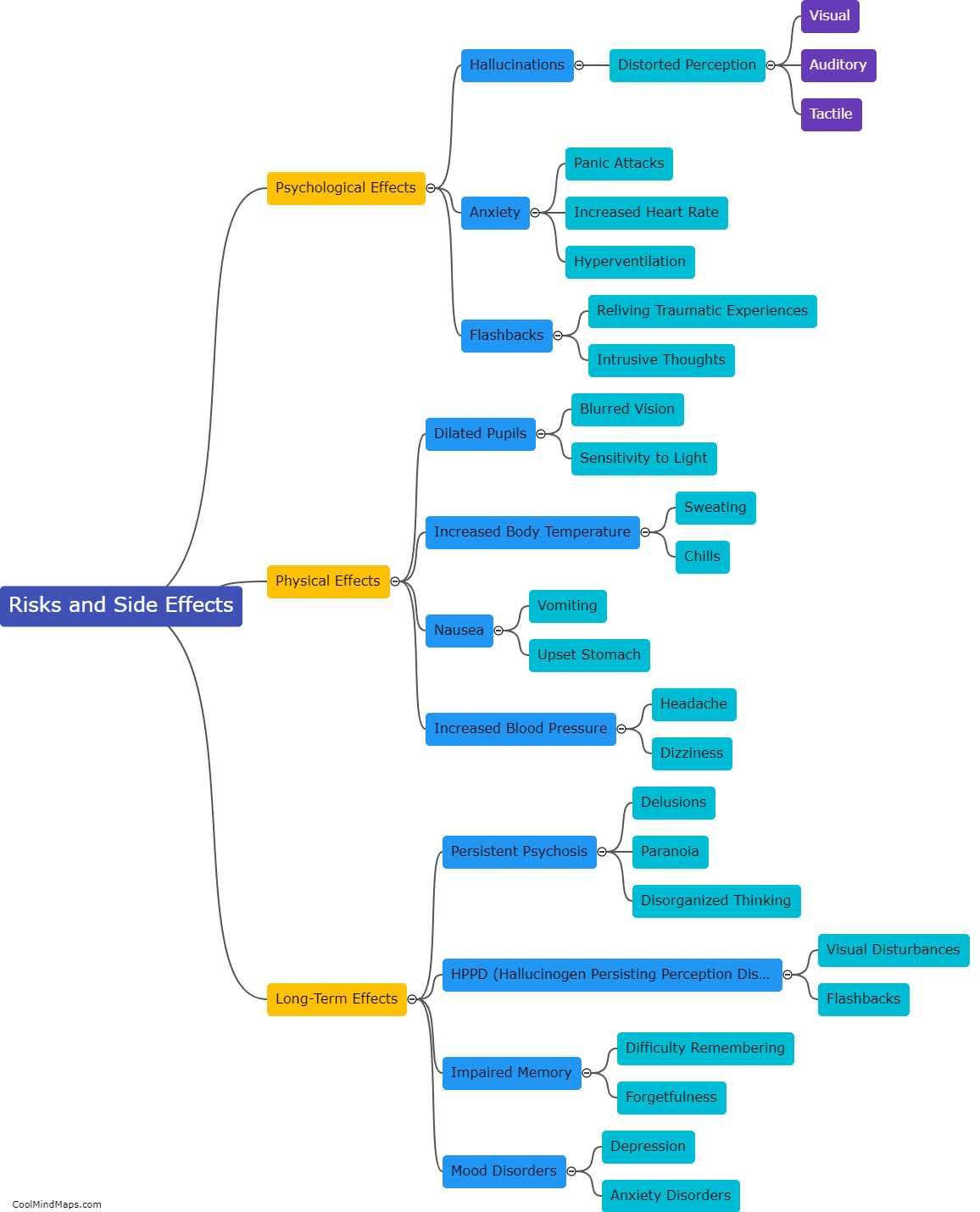
LSD, also known as lysergic acid diethylamide, interacts mainly with the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain. It binds to serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, leading to a cascade of effects. LSD's interaction with these receptors alters the release, uptake, and availability of serotonin, which is key in regulating mood, perception, and cognition. Additionally, LSD has been shown to indirectly affect other neurotransmitters by influencing the release and activity of dopamine and norepinephrine. These interactions explain how LSD produces its characteristic hallucinogenic effects and may contribute to its potential therapeutic applications in certain disorders like depression and addiction. However, further research is still needed to fully understand the complex interactions between LSD and neurotransmitters.
This mind map was published on 20 December 2023 and has been viewed 82 times.