How is nitrogen cycled in ecosystems?
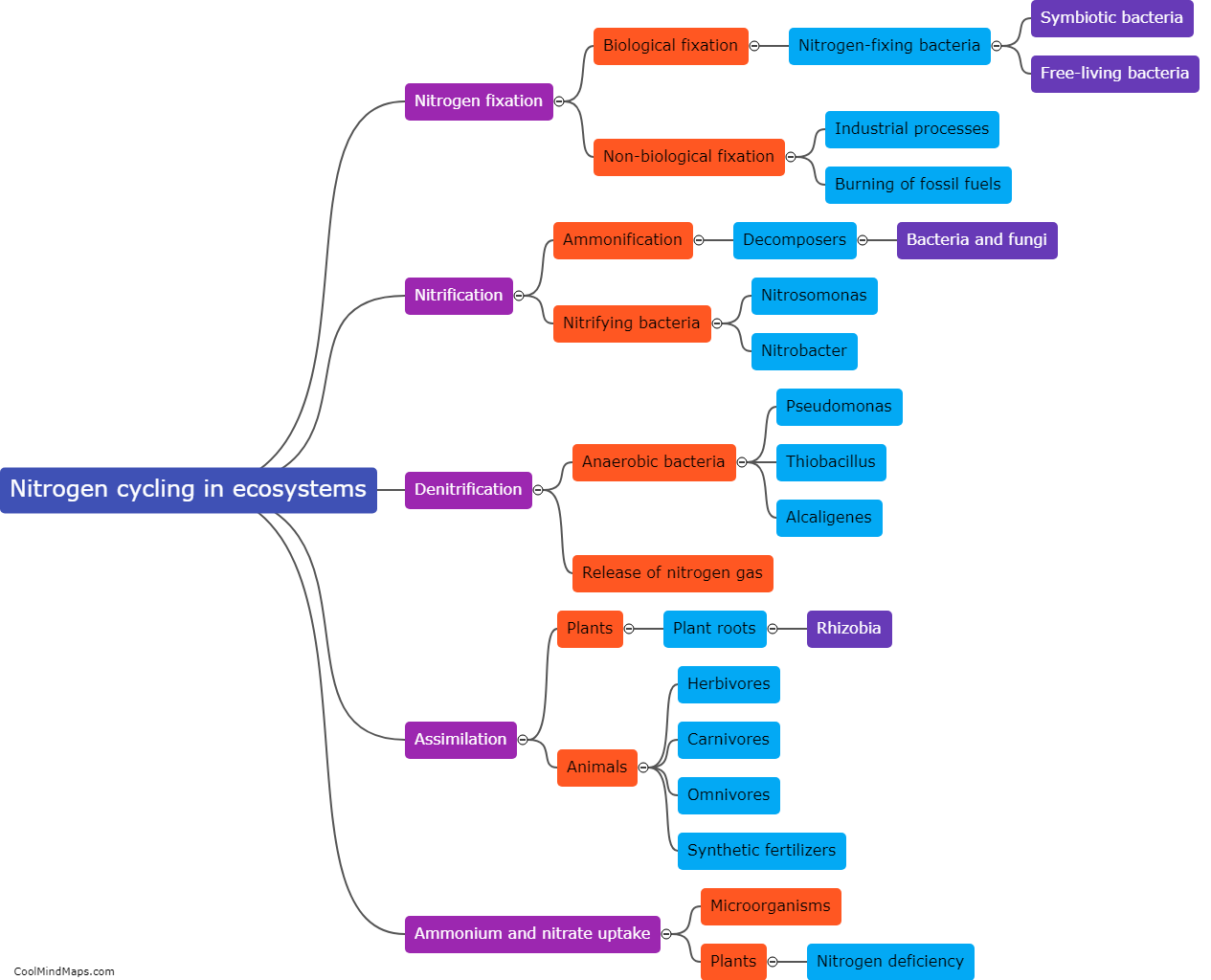
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for all living organisms, and its cycling in ecosystems is crucial for maintaining the balance of nutrients. The nitrogen cycle begins with nitrogen fixation, where certain bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen gas into a usable form such as ammonia or nitrate. These forms are then taken up by plants through their roots and used to build proteins and other nitrogen-containing compounds. Animals obtain nitrogen by consuming plants or other animals. Decomposers break down dead organisms and waste materials, releasing nitrogen back into the soil as ammonia. This ammonia can then be converted by nitrifying bacteria into nitrite and nitrate forms, which can be taken up by plants again, completing the cycle. Additionally, denitrifying bacteria convert nitrates back into atmospheric nitrogen, thus closing the loop of the nitrogen cycle. Overall, the nitrogen cycle plays a critical role in maintaining the availability of nitrogen in ecosystems, enabling the growth and survival of all organisms.
This mind map was published on 3 October 2023 and has been viewed 113 times.