What is glutamate?
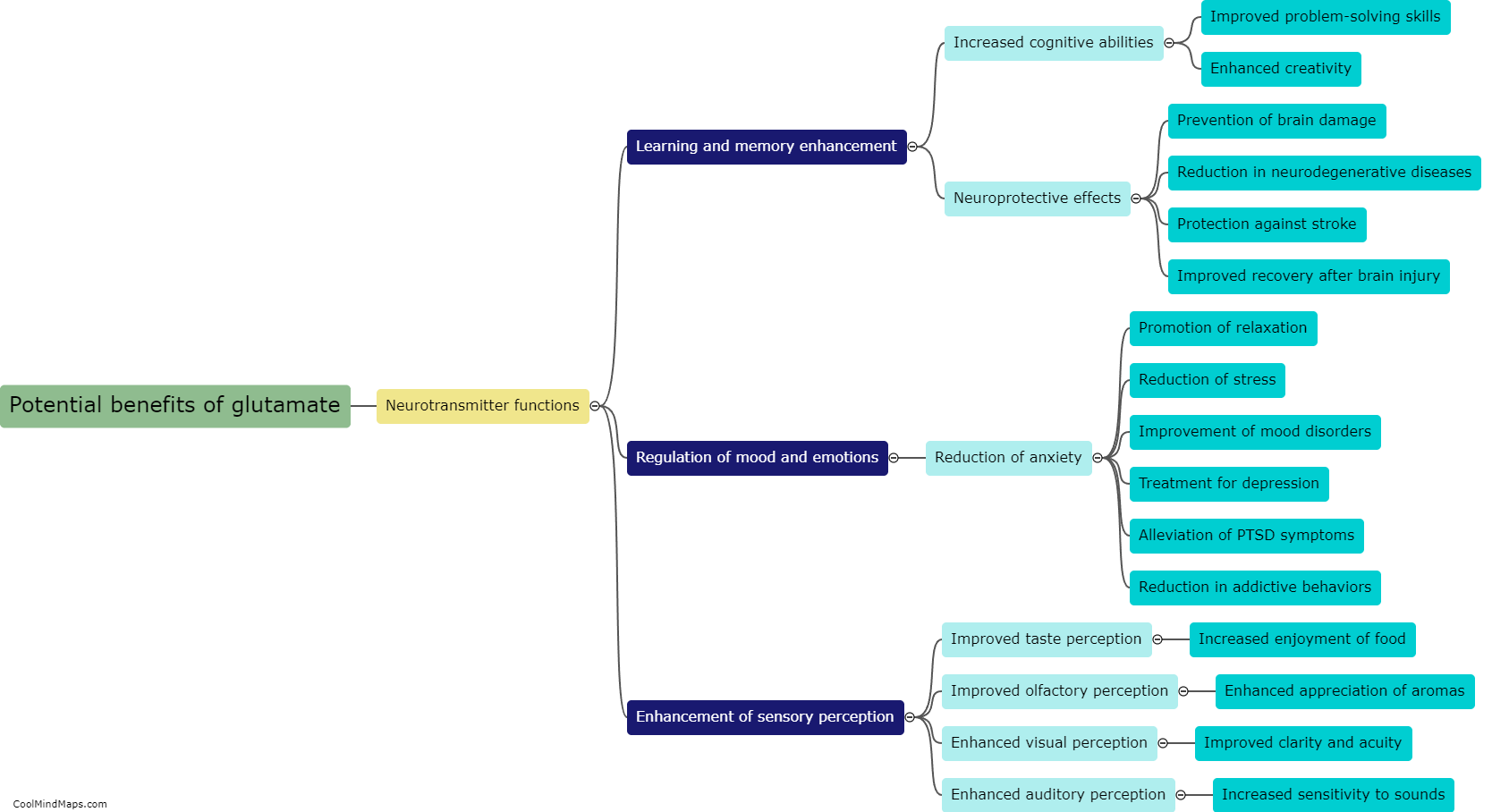
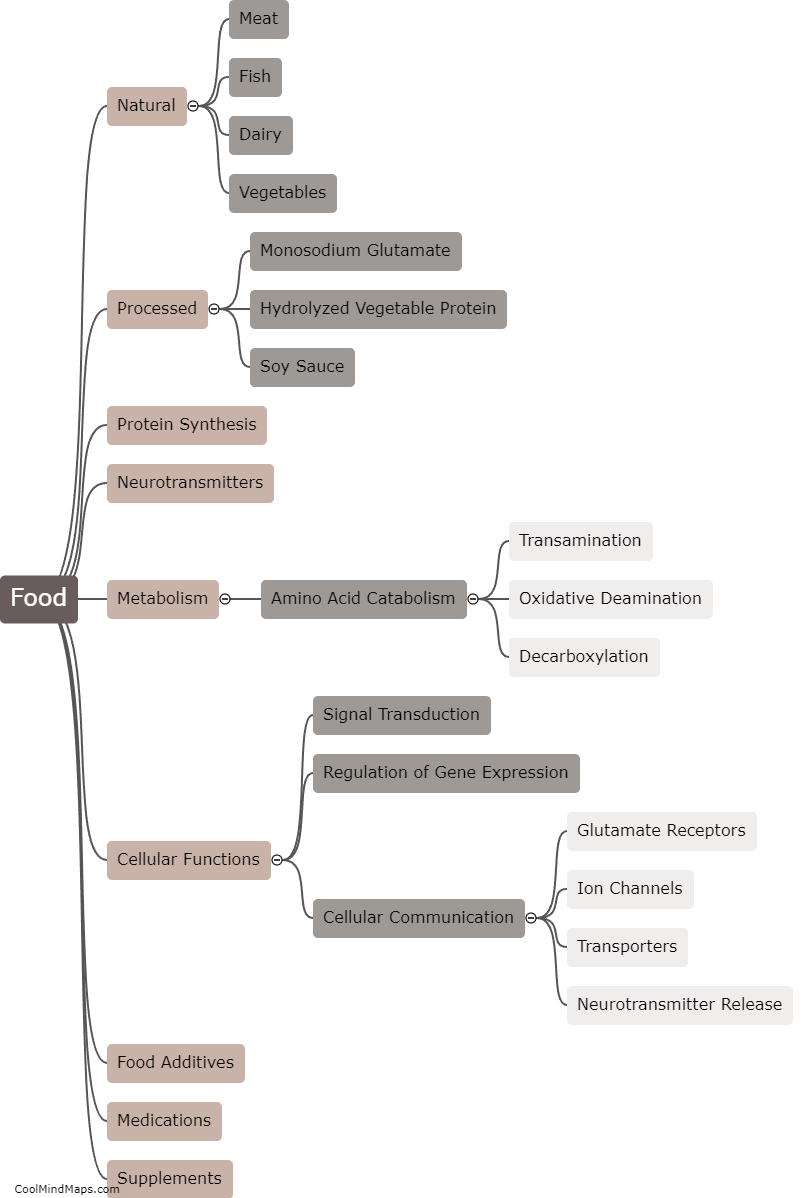
Glutamate is an essential amino acid that serves as a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. It is involved in various physiological functions, including cognitive processes, memory formation, and learning. Glutamate is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, responsible for stimulating neurons and facilitating communication between them. It plays a crucial role in maintaining brain health and promoting synaptic plasticity—the ability of the brain to adapt and form new connections. However, excessive glutamate levels can be harmful and lead to excitotoxicity, contributing to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.

This mind map was published on 17 October 2023 and has been viewed 170 times.