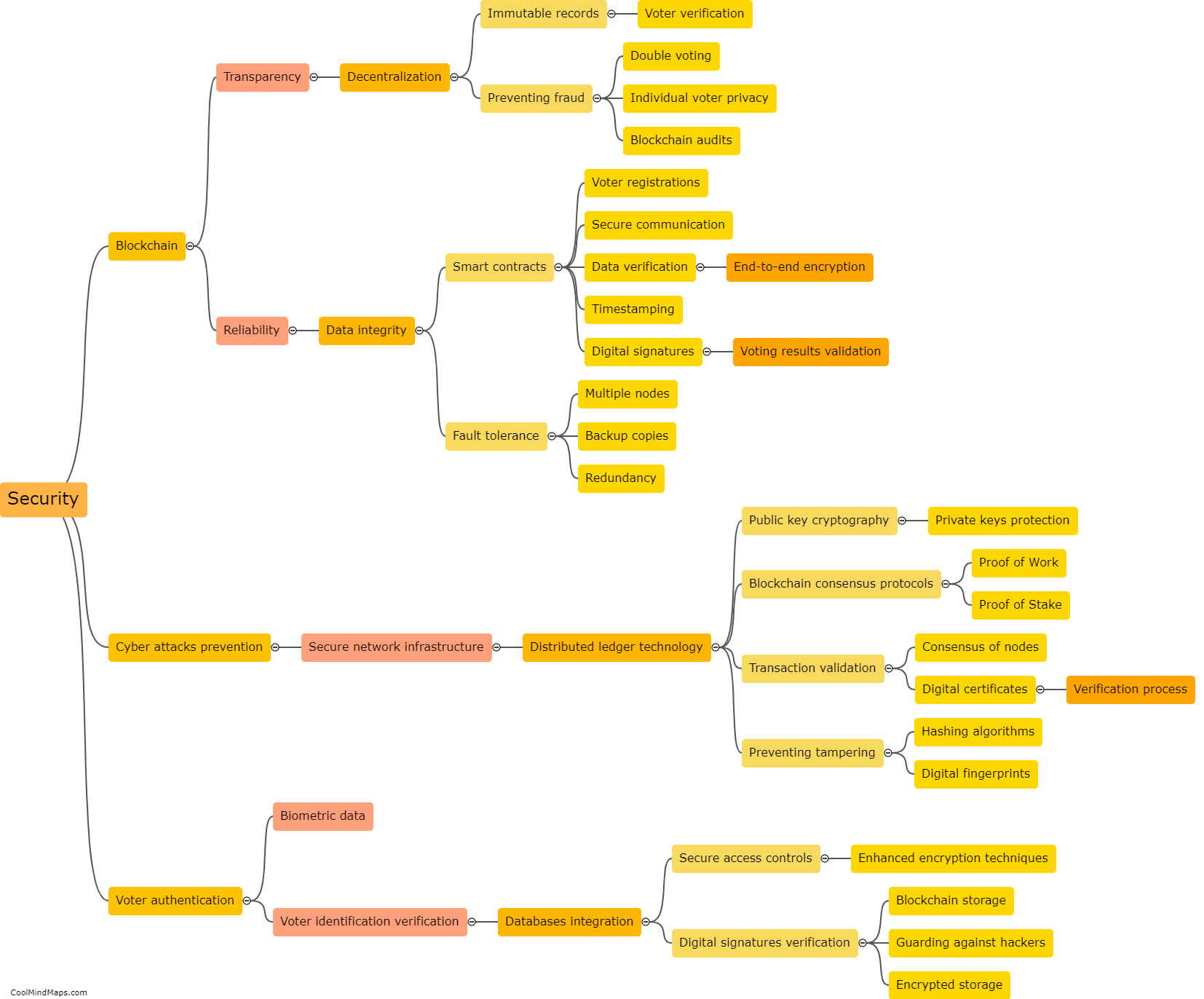
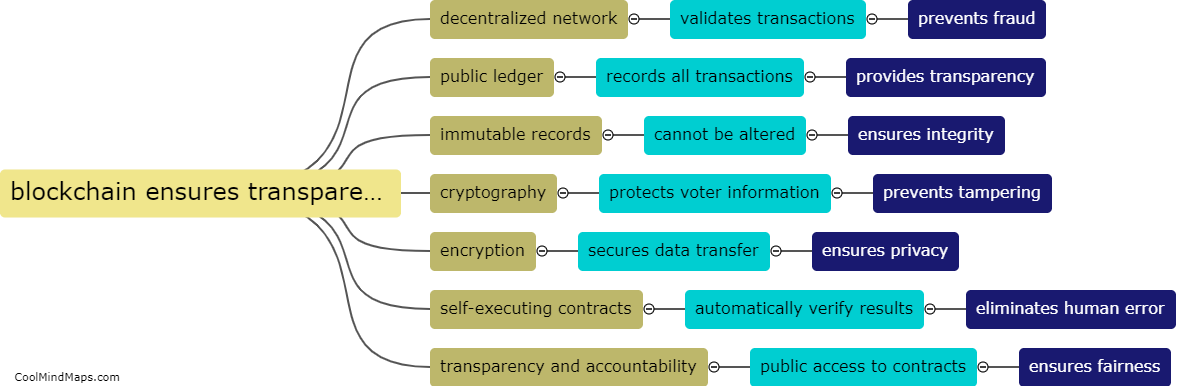
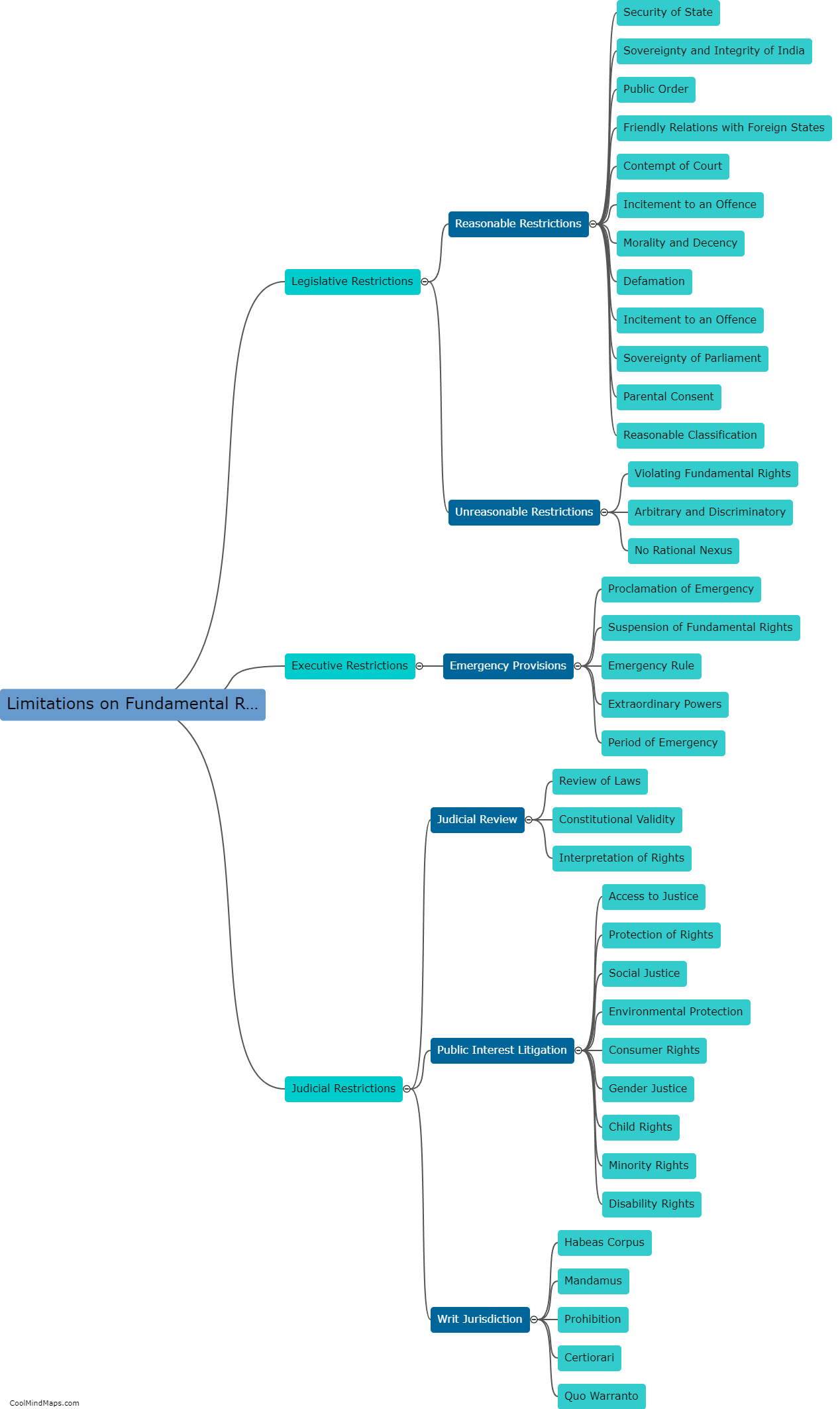
How are fundamental rights limited in India?
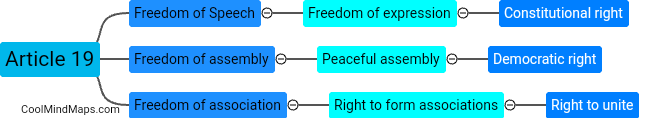
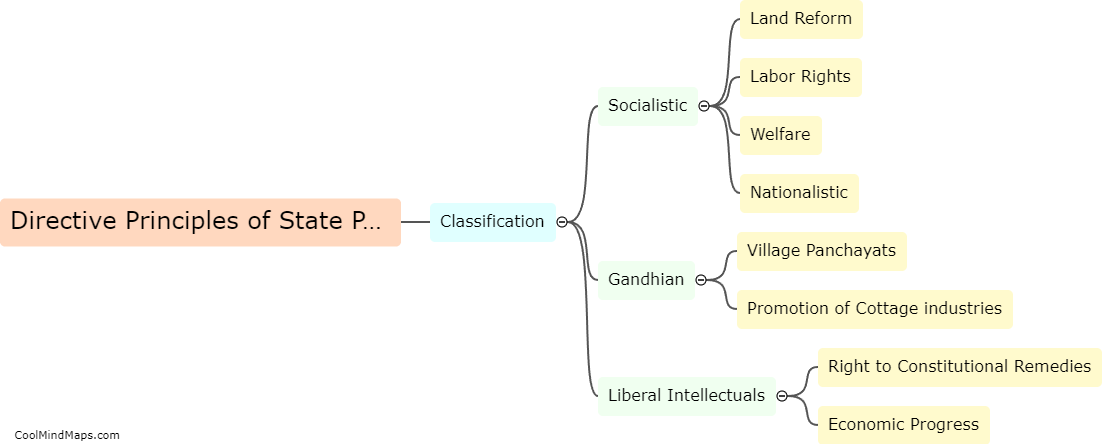
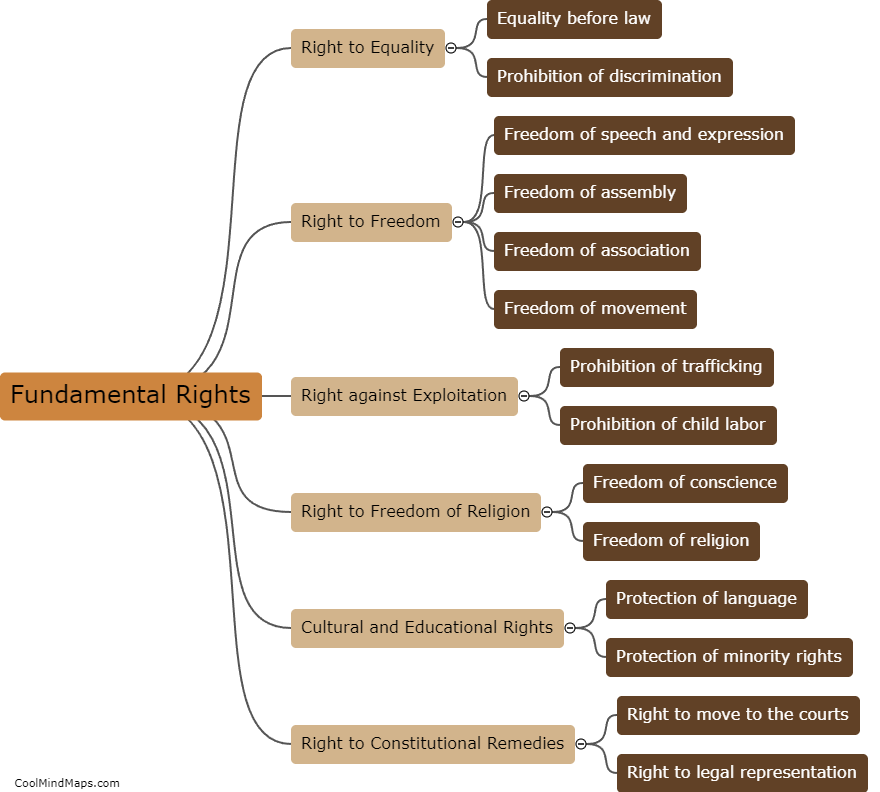
In India, while fundamental rights are considered crucial and are protected by the Constitution, they are not absolute and can be limited under certain circumstances. The Indian Constitution provides for reasonable restrictions on the exercise of fundamental rights in the interest of various compelling factors such as public order, morality, security, and the sovereignty and integrity of the nation. These limitations aim to strike a balance between protecting the rights of individuals and ensuring the welfare and stability of society as a whole. The Supreme Court of India acts as a safeguard to prevent excessive or arbitrary limitations on fundamental rights, and it regularly reviews and interprets these limitations to ensure they align with the principles of justice, equality, and democracy.
This mind map was published on 7 September 2023 and has been viewed 107 times.