What are antimicrobial peptides?
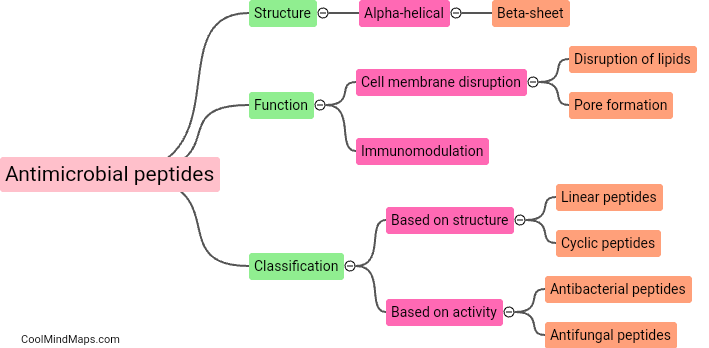
Antimicrobial peptides are small proteins that are part of the innate immune system and play a crucial role in defending the body against pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. They work by disrupting the cell membranes of these pathogens, leading to their destruction. Antimicrobial peptides are produced by various cells in the body, including immune cells and skin cells, and are considered a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and lower likelihood of developing resistance.
This mind map was published on 22 October 2024 and has been viewed 23 times.