How does the immune system work?
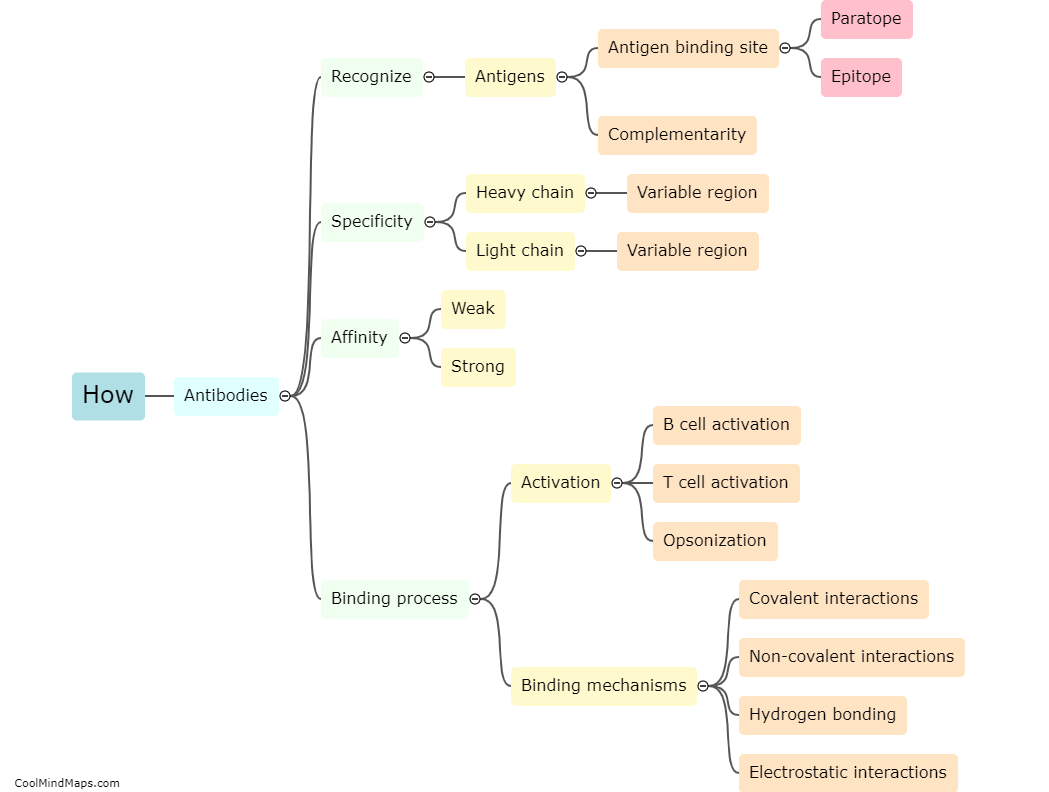
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens. It comprises various components, such as white blood cells, antibodies, and lymphoid organs. When a pathogen enters the body, specific immune cells, such as macrophages, recognize and engulf it. These cells then present pieces of the pathogen, called antigens, to helper T-cells. Helper T-cells activate other immune cells, such as B-cells, to produce antibodies that bind to the antigens and mark them for destruction. Additionally, killer T-cells directly attack infected cells. The immune system also has a memory function, which allows it to recognize specific pathogens it has encountered before, leading to a quicker and more effective response in future encounters. Overall, the immune system works diligently to protect the body from harmful invaders and maintain its overall health.

This mind map was published on 2 January 2024 and has been viewed 94 times.