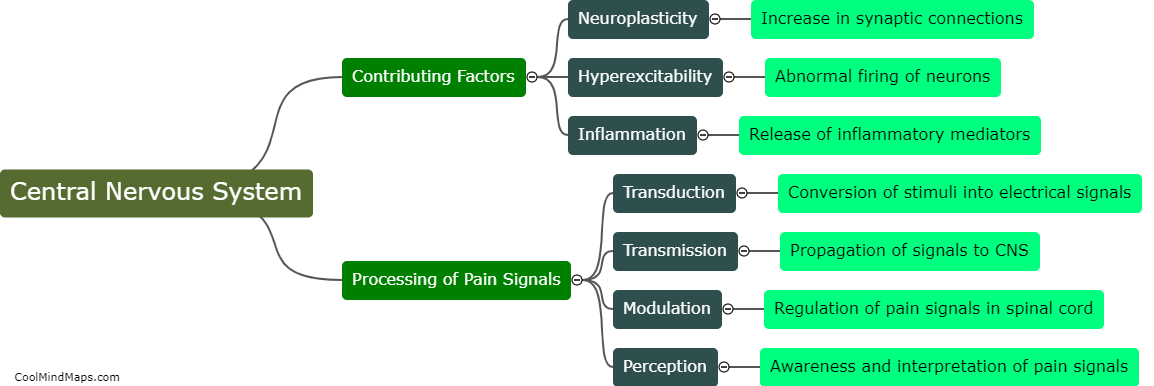
How does the central nervous system contribute to chronic pain?
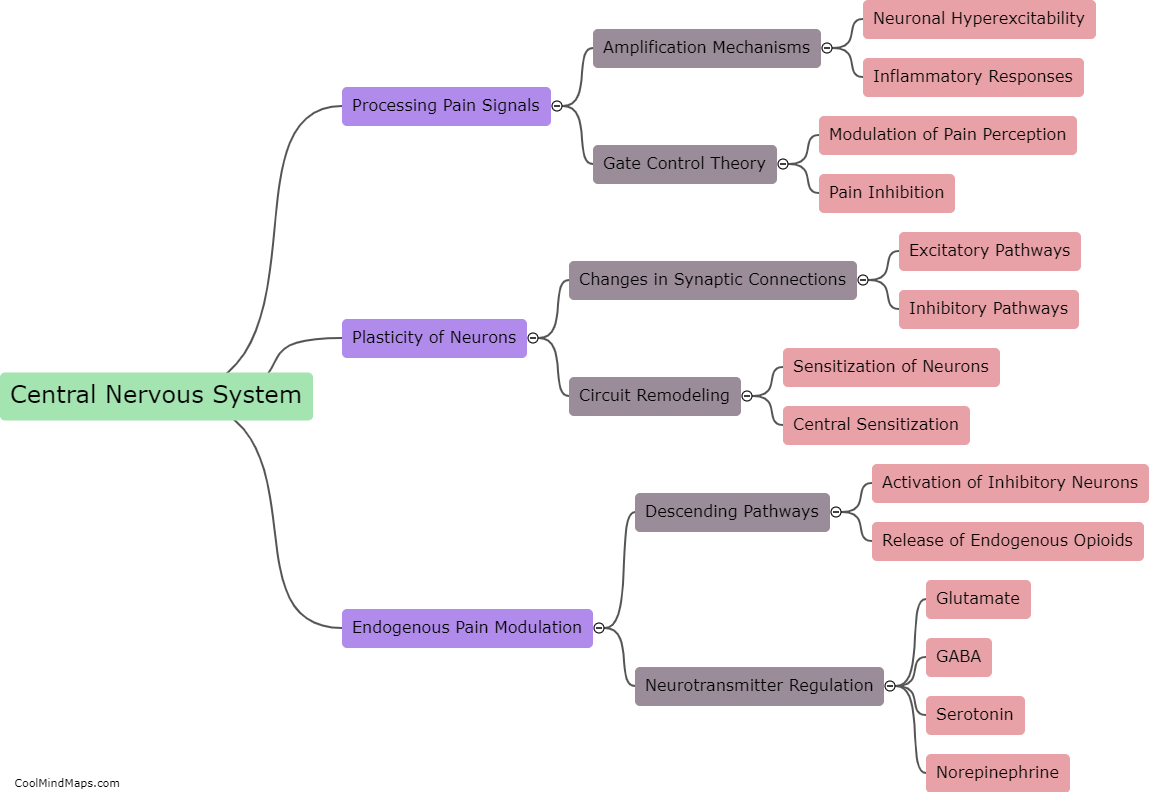
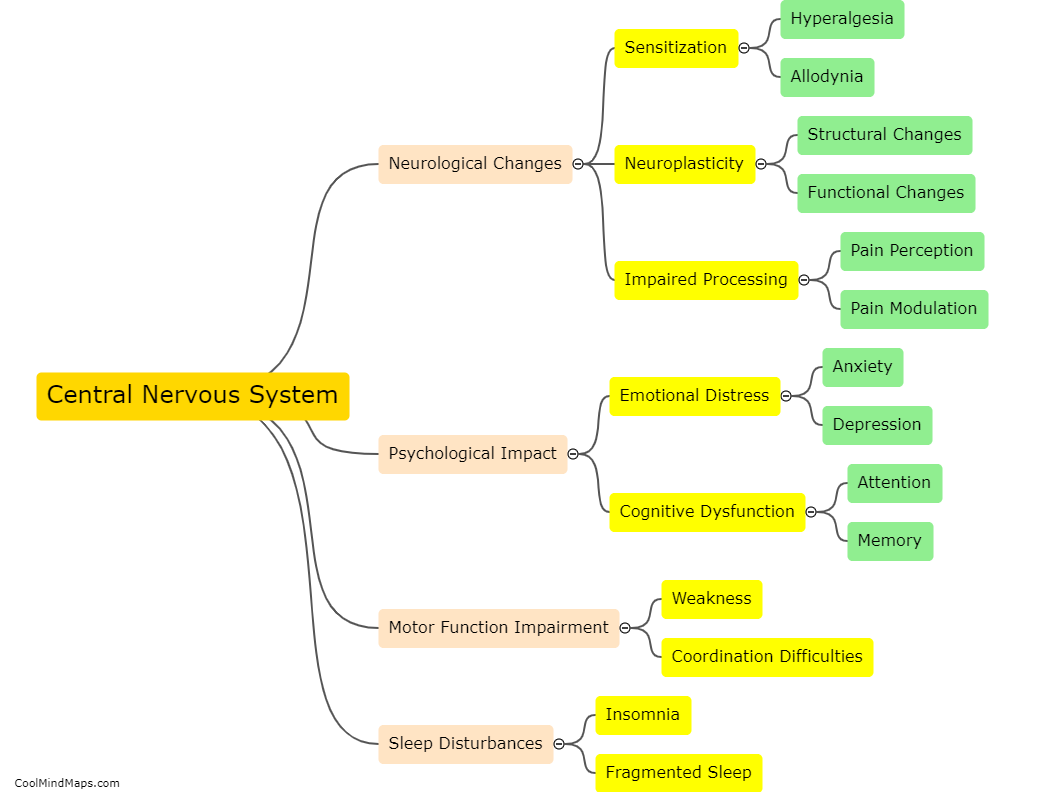
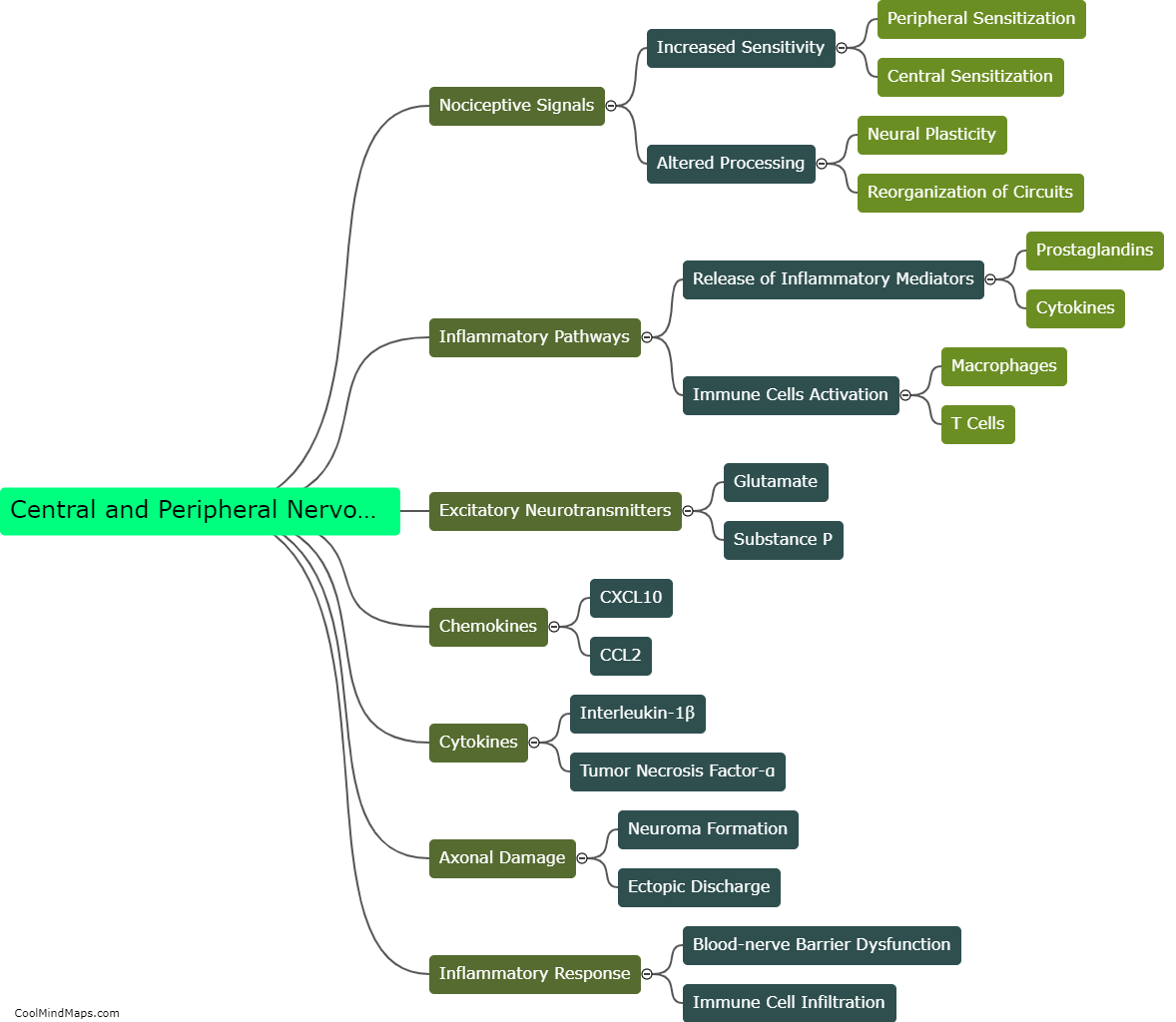
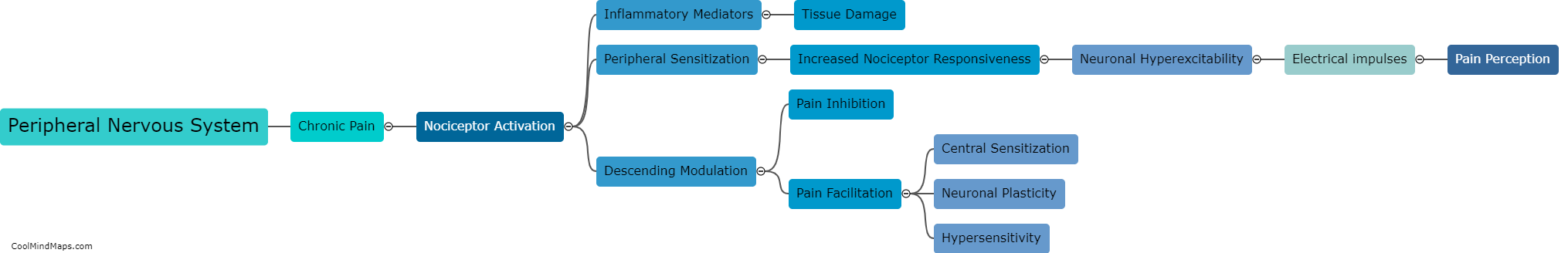
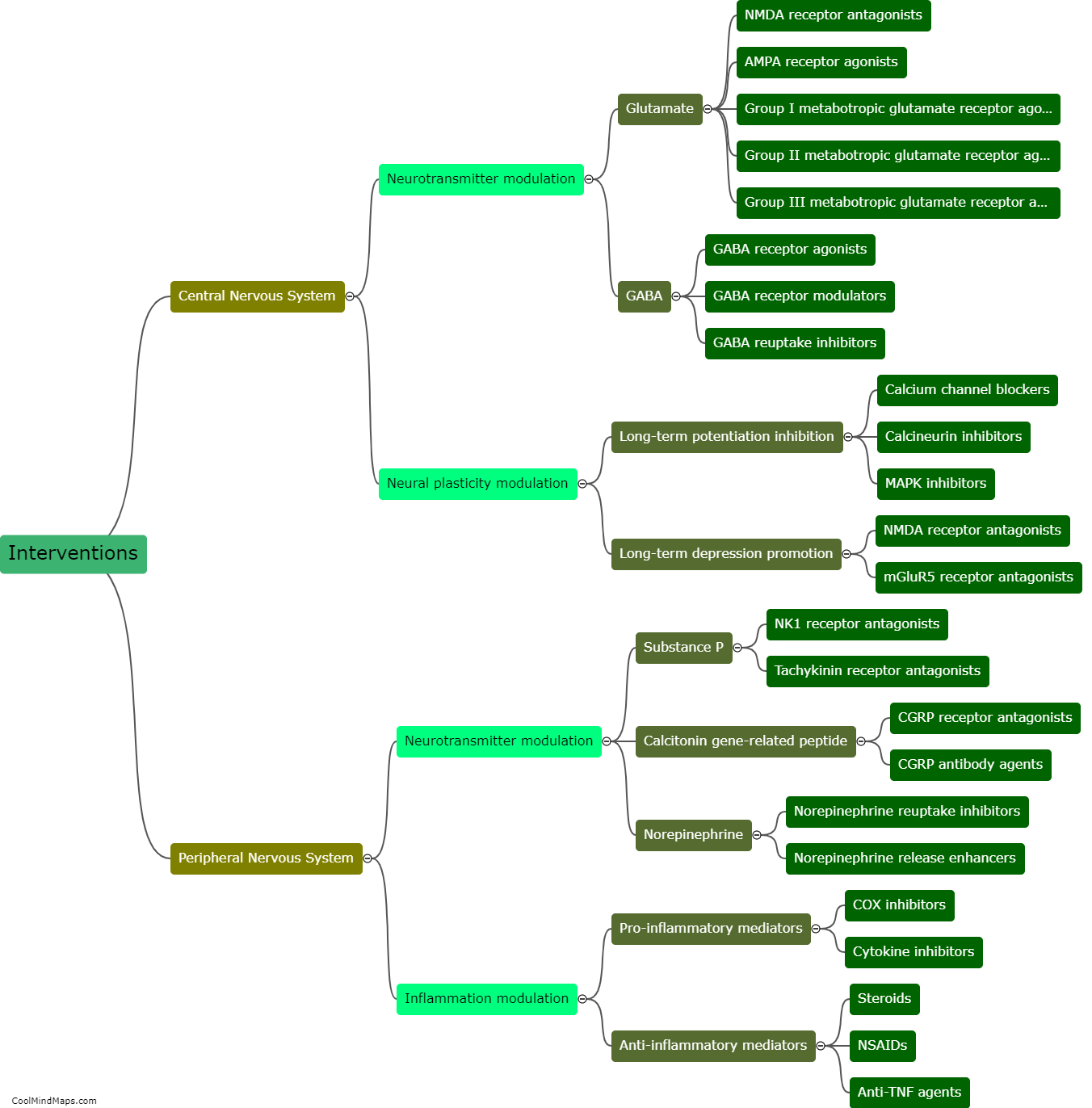
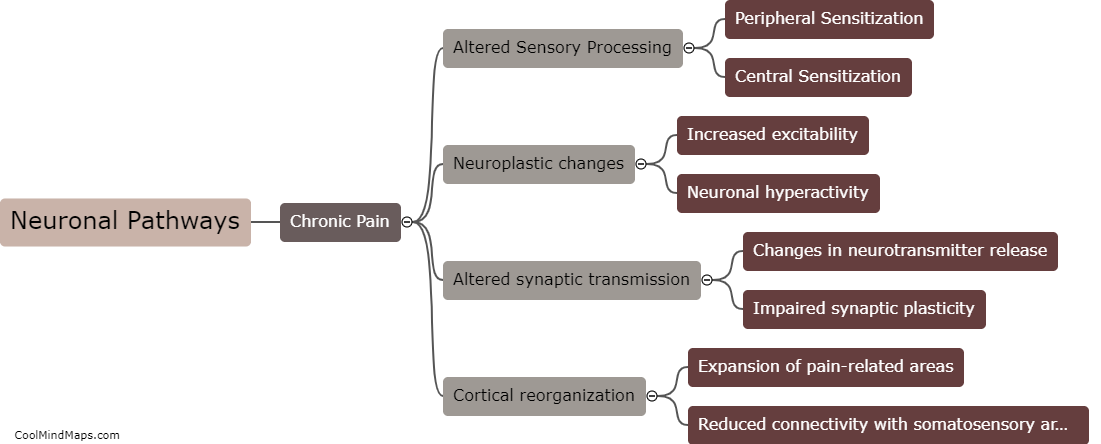
The central nervous system (CNS) plays a key role in chronic pain by amplifying and perpetuating pain signals. Chronic pain is typically characterized by persistent pain lasting for more than three months, often without an apparent cause or after the initial injury or illness has healed. In this regard, the CNS becomes sensitized and undergoes changes in the way it processes pain signals. This phenomenon, known as central sensitization, involves an increased responsiveness of neurons in the spinal cord and brain to pain stimuli. It leads to hypersensitivity to pain and can result in the establishment of chronic pain pathways. Various factors can contribute to central sensitization, including ongoing inflammation, nerve damage, and psychological factors, creating a self-sustaining cycle of pain. Strategies to manage chronic pain often involve targeting the central nervous system to modulate pain signals and reduce the amplification of pain sensations.
This mind map was published on 2 December 2023 and has been viewed 124 times.