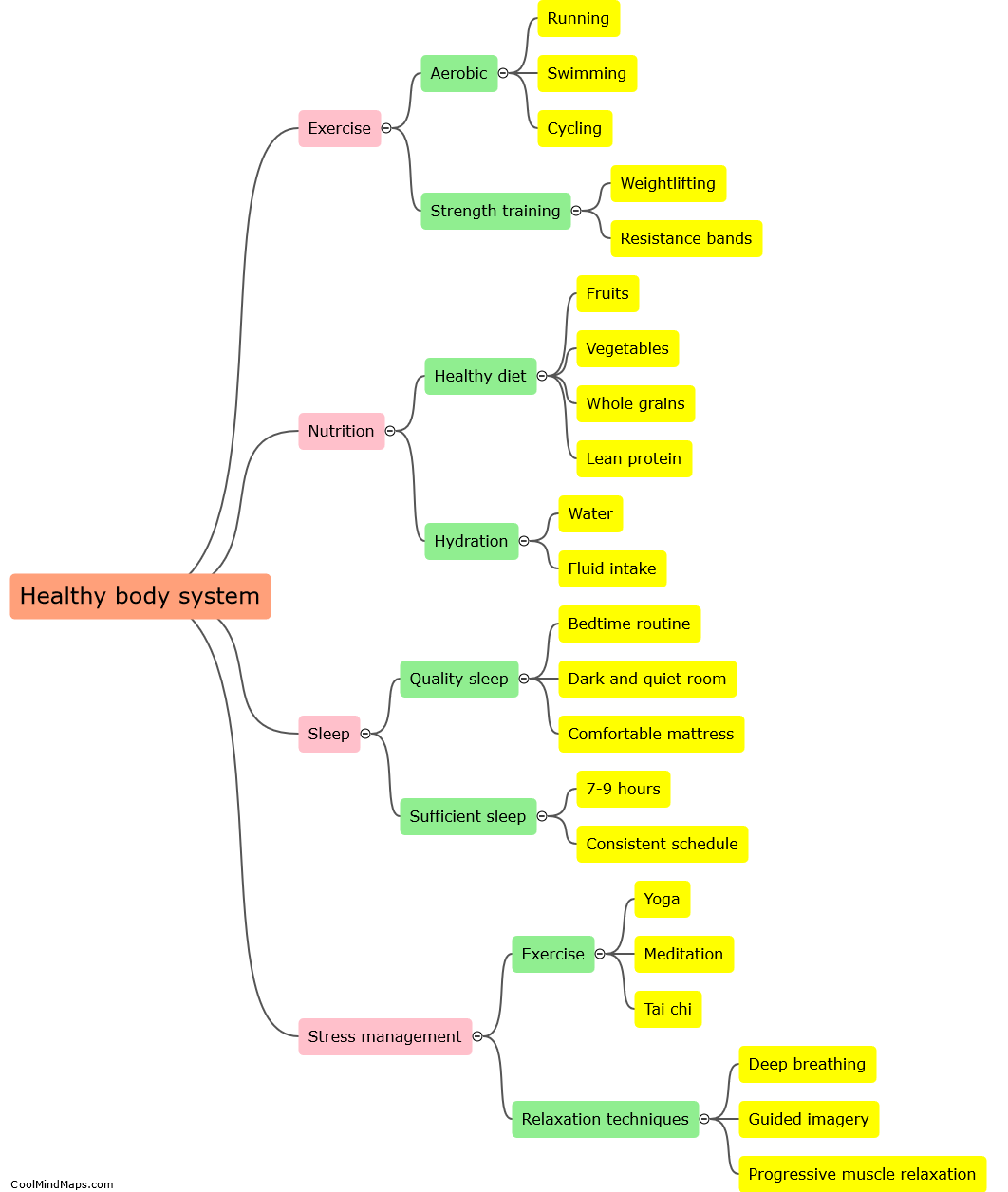
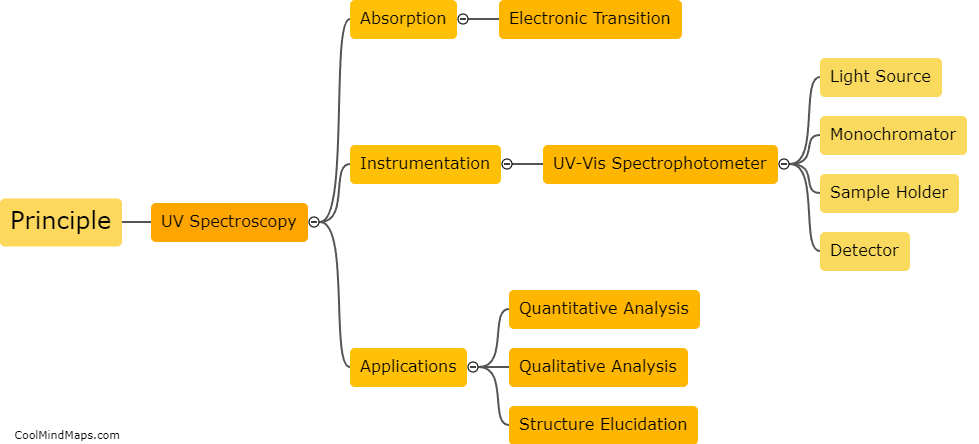
What is the principle behind UV spectroscopy?
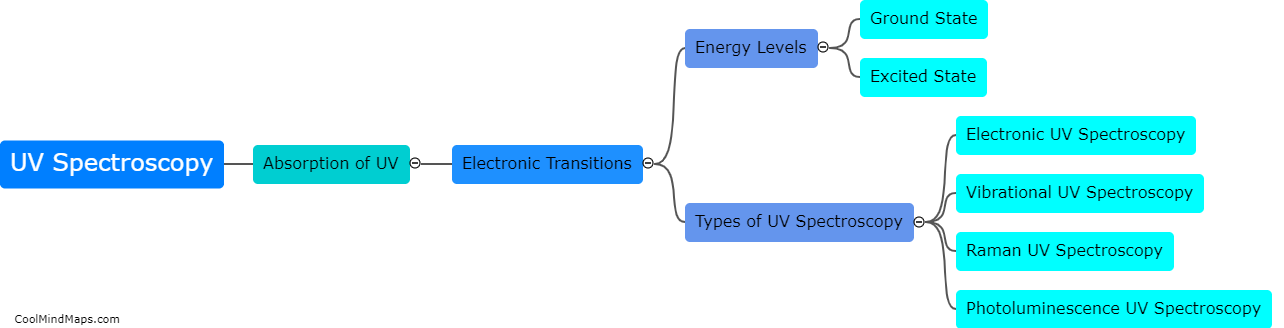
UV spectroscopy is based on the principle that molecules absorb ultraviolet (UV) light at specific wavelengths due to electronic transitions. Molecules contain electrons in different energy levels, and as UV light is absorbed, these electrons move from their ground state to higher energy levels. The transitions result in the absorption of specific wavelengths of UV light, which can be measured using a UV spectrophotometer. By analyzing the absorption spectrum of a sample, scientists can identify the presence of certain molecules and determine their concentration. UV spectroscopy is widely used in various fields such as pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, and biochemistry for its ability to provide qualitative and quantitative analysis of substances.
This mind map was published on 8 October 2023 and has been viewed 85 times.