What are the key concepts of Piaget's theory?
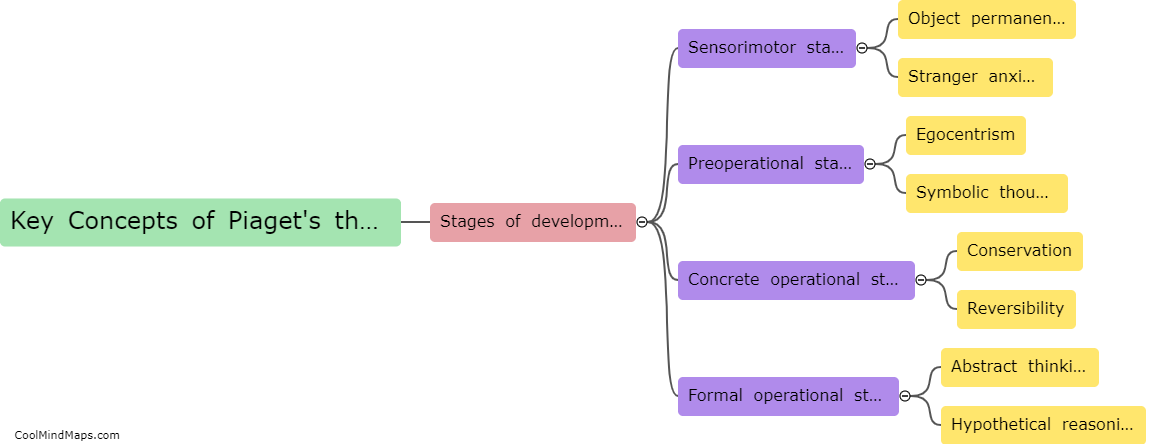
Piaget's theory of cognitive development is based on the key concepts of assimilation, accommodation, and stages of development. According to Piaget, children are active learners who construct their understanding of the world through their interactions with the environment. Assimilation is the process where individuals incorporate new information into their existing cognitive schemas, while accommodation involves modifying existing schemas to accommodate new information. Piaget proposed four stages of cognitive development: the sensorimotor stage (0-2 years), the preoperational stage (2-7 years), the concrete operational stage (7-11 years), and the formal operational stage (11 years and older). These stages represent distinctive cognitive structures and abilities that individuals progress through as they develop. Overall, Piaget's theory emphasizes the importance of both individual exploration and social interaction in the cognitive development of children.
This mind map was published on 6 July 2023 and has been viewed 205 times.