What are the main characteristics of eukaryotic cells?
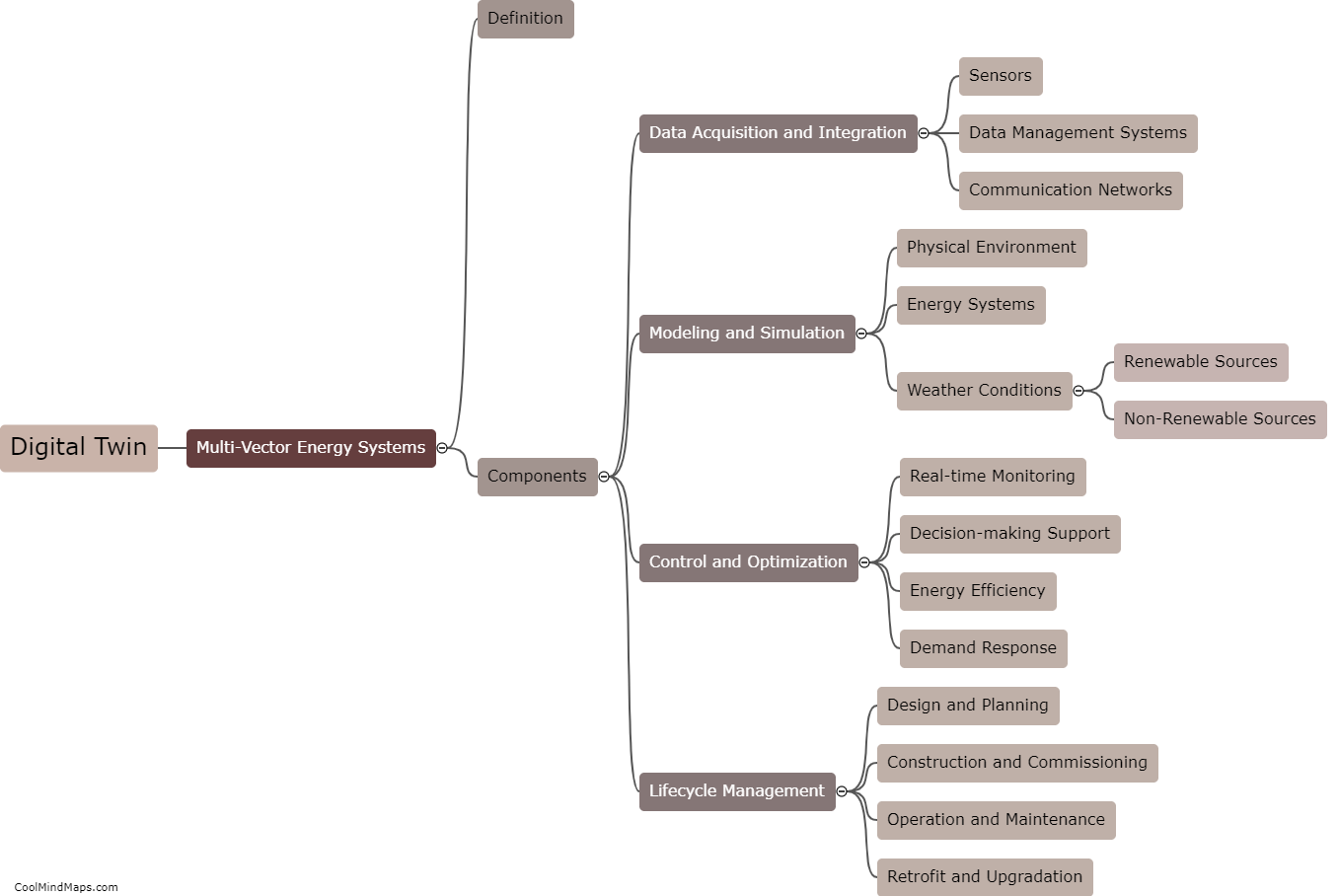
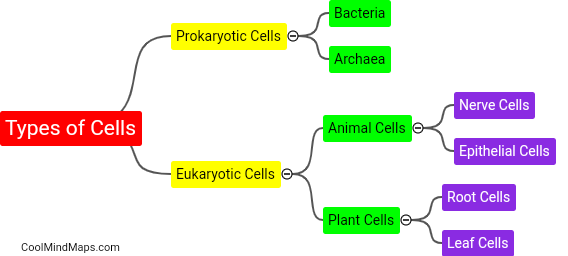
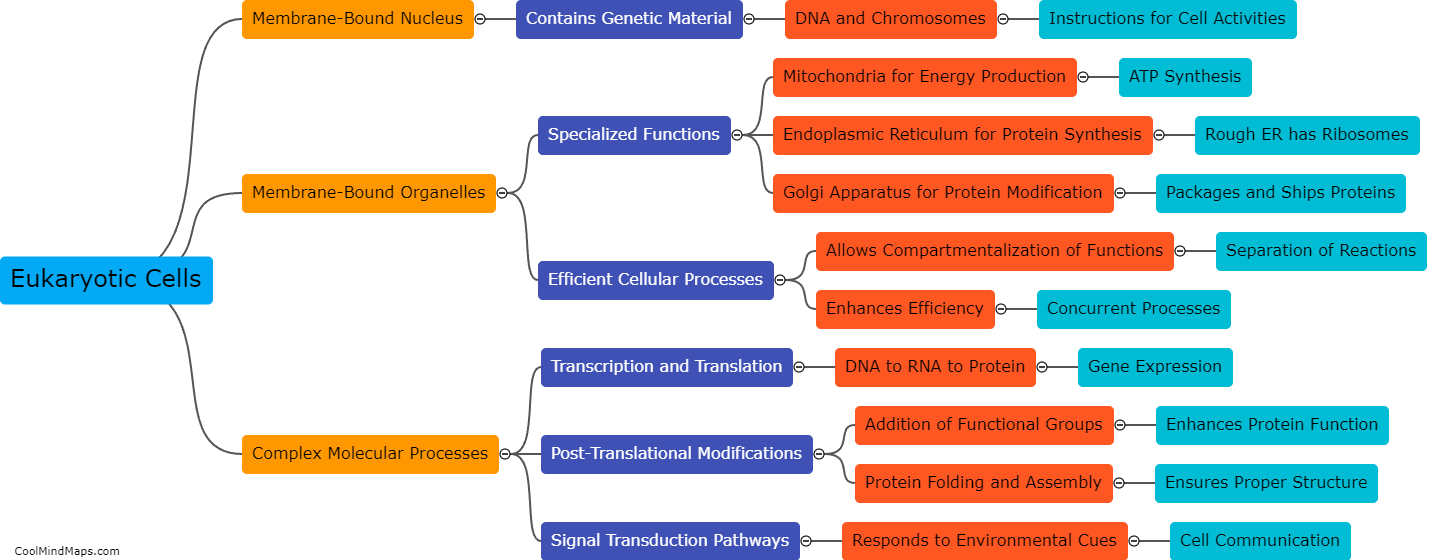
Eukaryotic cells are characterized by several key features that set them apart from their prokaryotic counterparts. Firstly, eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus enclosed by a double membrane, which houses the cell's genetic material, DNA. This nucleus allows for more complex functions and regulation of gene expression. Moreover, eukaryotic cells contain a variety of membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, each playing specific roles in cellular processes. These organelles compartmentalize the activities within the cell, enhancing efficiency and specialized functions. Additionally, eukaryotic cells are typically larger and more structurally complex compared to prokaryotes and possess a cytoskeleton composed of microtubules and microfilaments, enabling cell shape, motility, and intracellular transport. Lastly, eukaryotic cells can be found in both single-celled organisms (e.g., protists) and multicellular organisms (e.g., plants, animals, fungi), contributing to organismal complexity and specialization.
This mind map was published on 26 October 2023 and has been viewed 99 times.