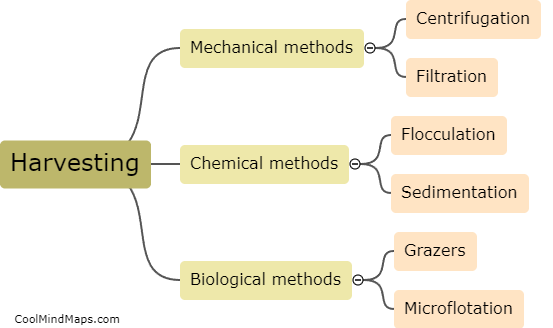
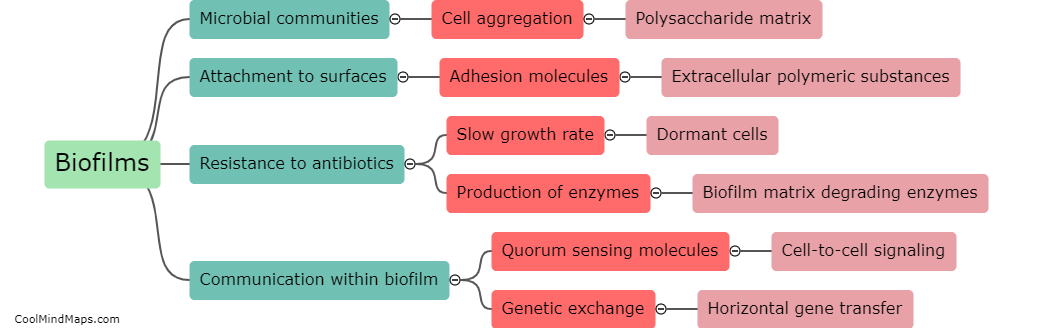
What are biofilms and their characteristics?
Biofilms are complex communities of microorganisms that adhere to various surfaces, such as teeth, medical implants, and pipes. They are composed of a mixture of different microbial species, including bacteria, fungi, and algae, encapsulated within a self-produced protective matrix of extracellular polymeric substances. This matrix not only anchors the biofilm to the surface but also provides protection to the microorganisms from environmental threats, including antibiotics and the host's immune system. The characteristics of biofilms include their ability to rapidly grow and colonize surfaces, their resistance to antimicrobial agents, their enhanced genetic exchange between different species, and their ability to cause chronic infections and complications in various environments. Understanding the characteristics of biofilms is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent and control biofilm-associated infections.
This mind map was published on 4 October 2023 and has been viewed 125 times.