What is the mechanism of action of azithromycin?
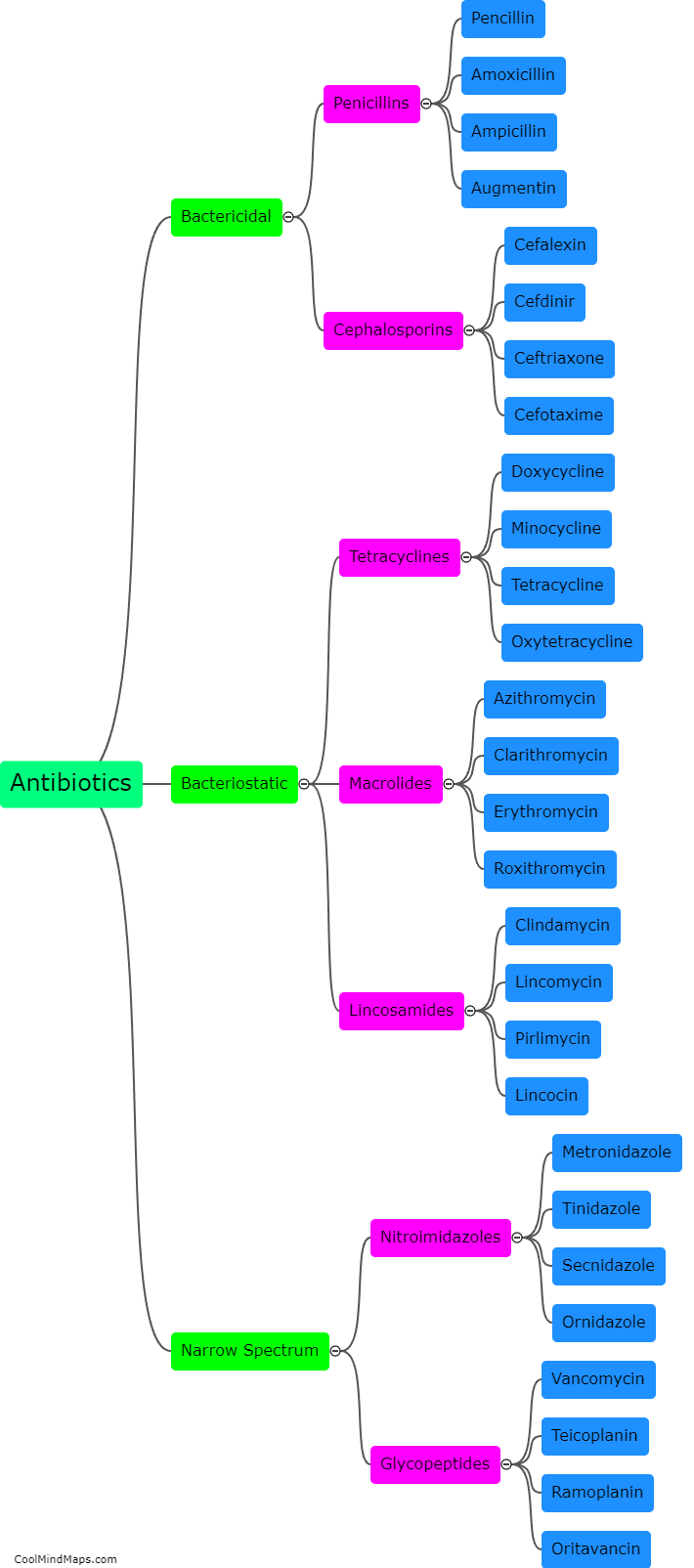
Azithromycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic commonly used to treat various bacterial infections. The mechanism of action of this medication involves inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Specifically, azithromycin binds to the 50S subunit of the ribosome, a vital component in the process of protein synthesis within bacteria. This binding prevents the transfer of peptide chains from one site to another, disrupting the synthesis of essential proteins needed for bacterial growth and replication. As a result, the bacteria are unable to proliferate and are ultimately eradicated by the body's immune system. The unique characteristics of azithromycin, such as its long half-life and ability to concentrate in infected tissues, allow for once-daily dosing and make it particularly effective against respiratory, skin, and genitourinary infections.

This mind map was published on 25 December 2023 and has been viewed 90 times.