How does computer vision work?
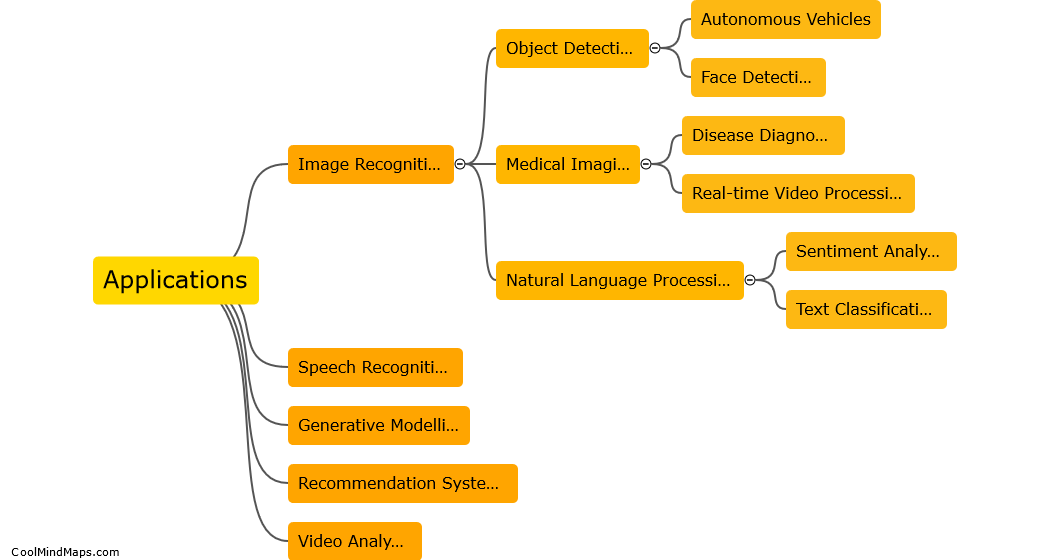
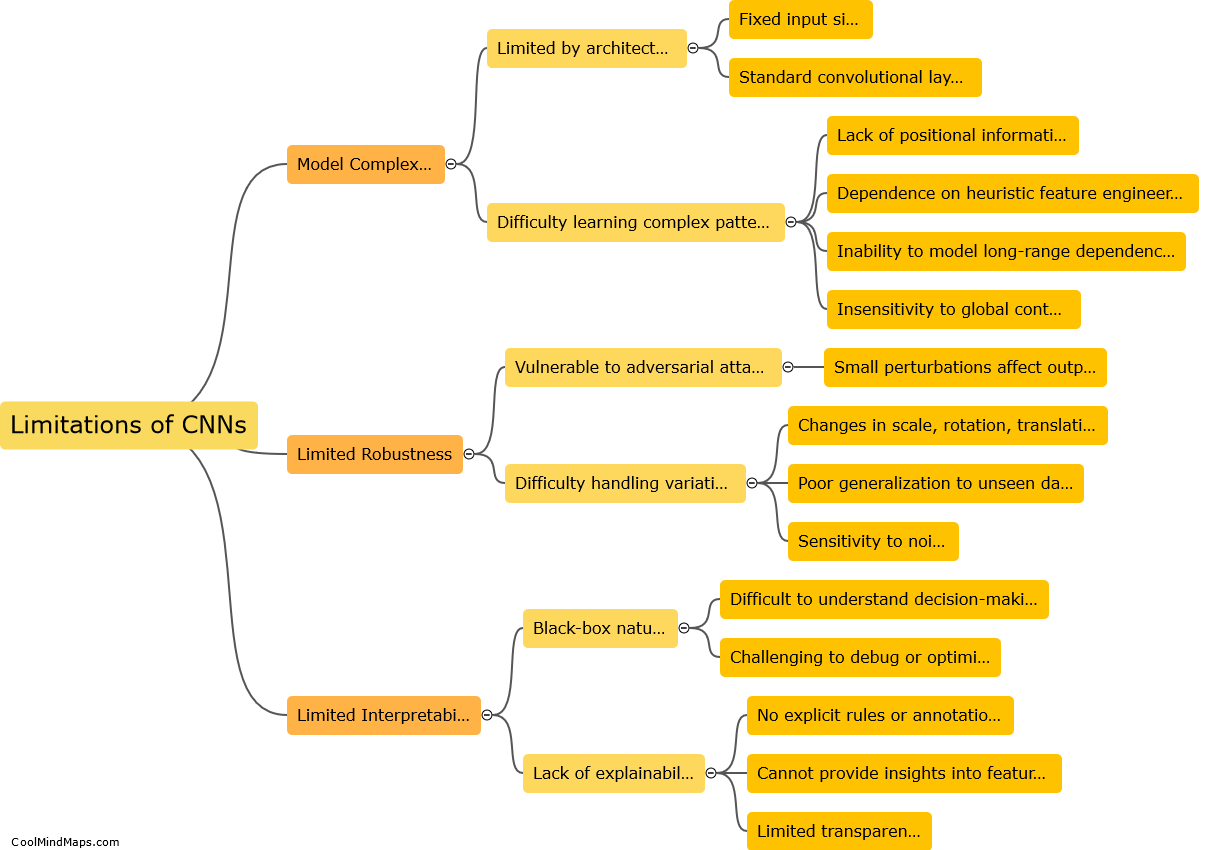
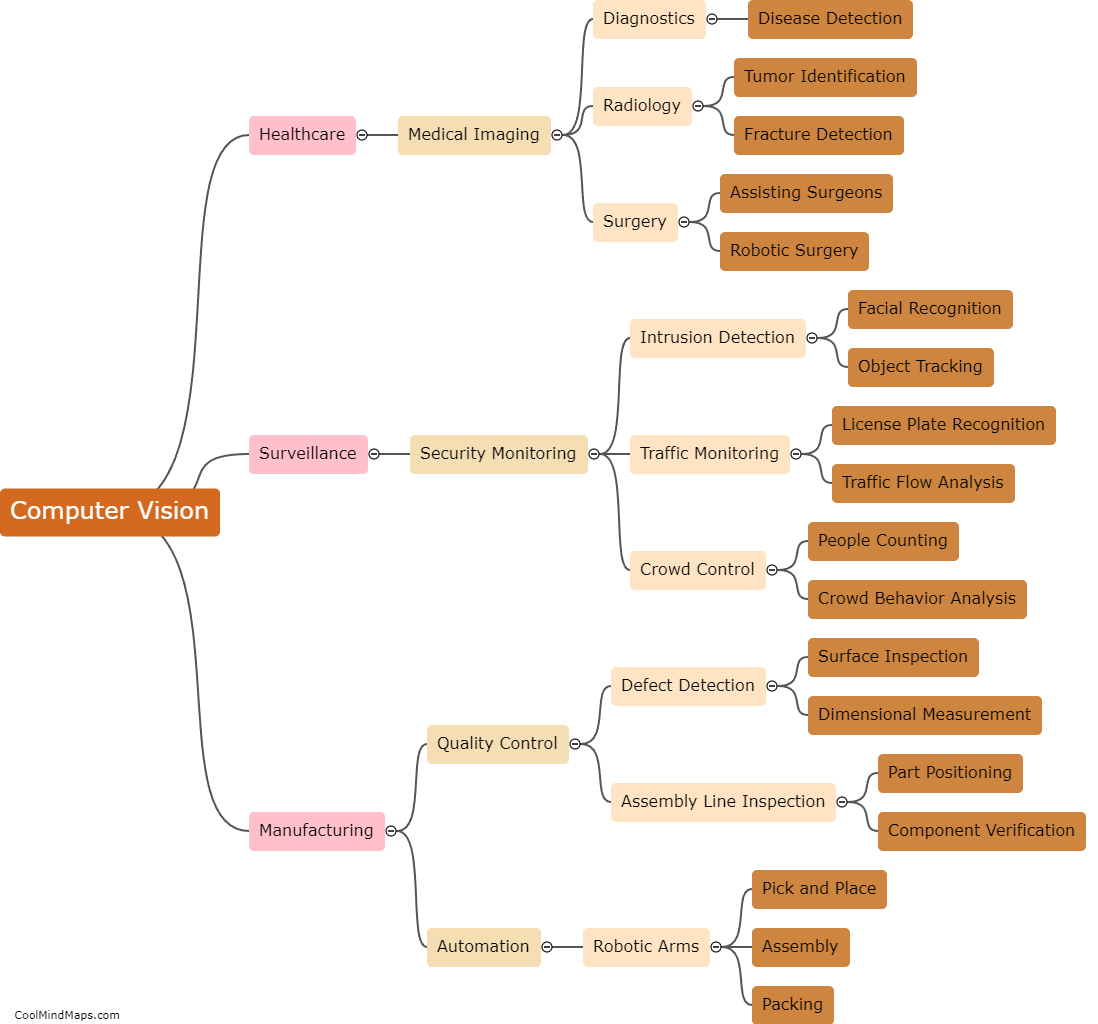
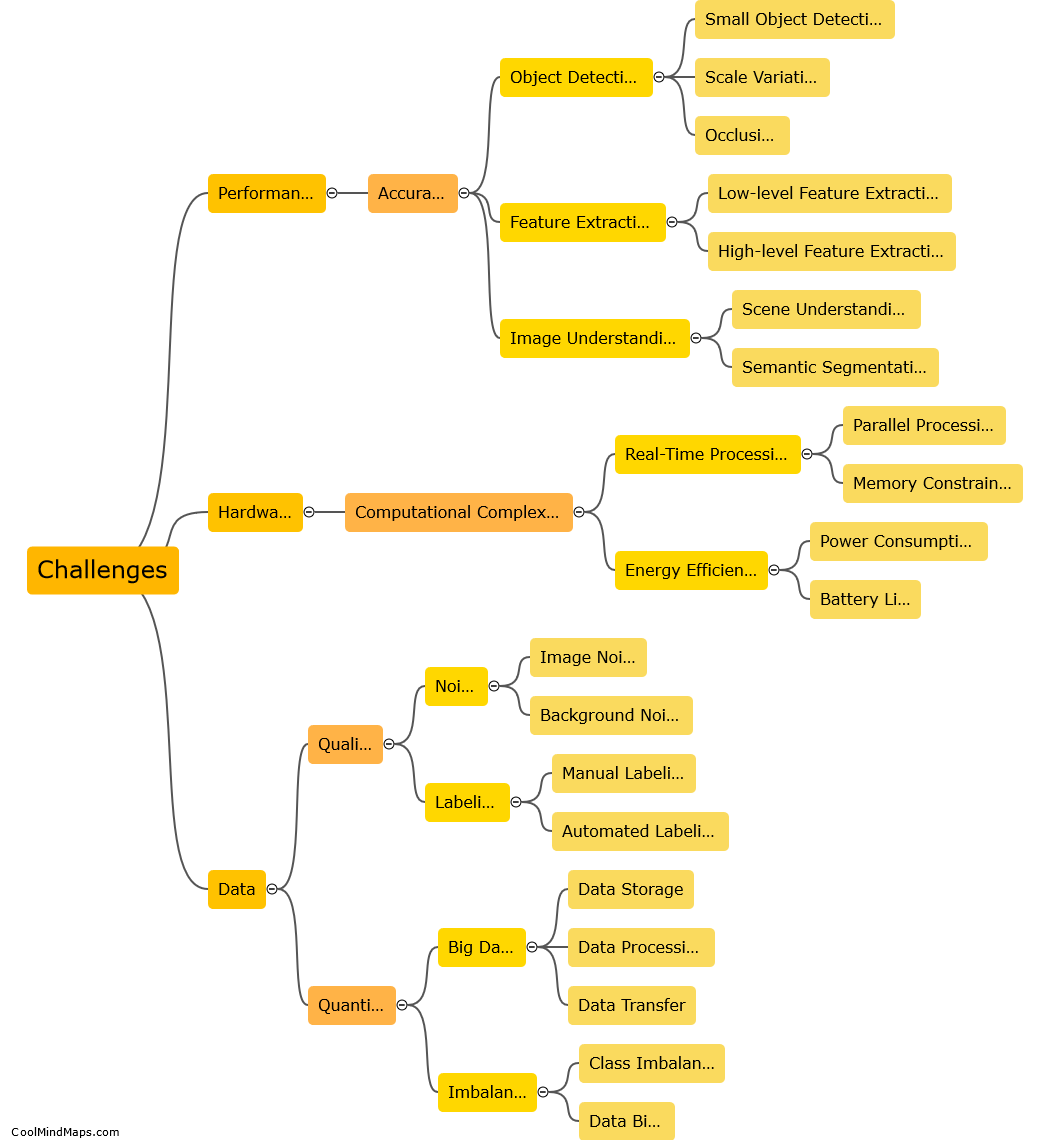
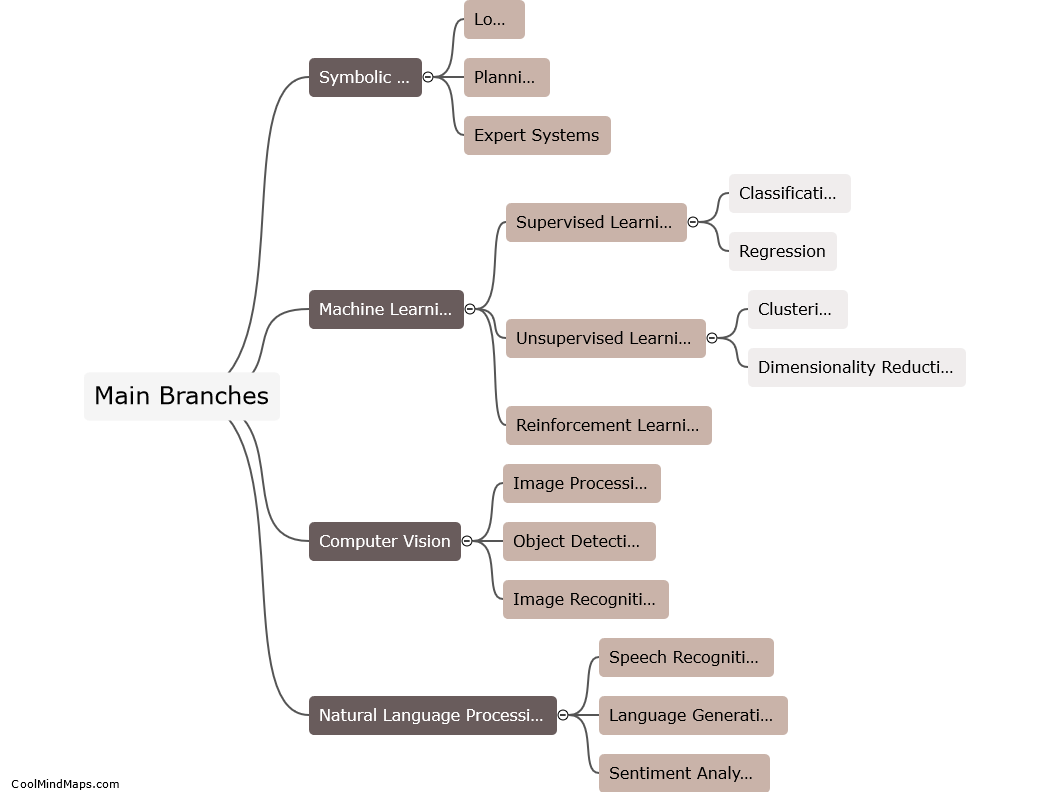
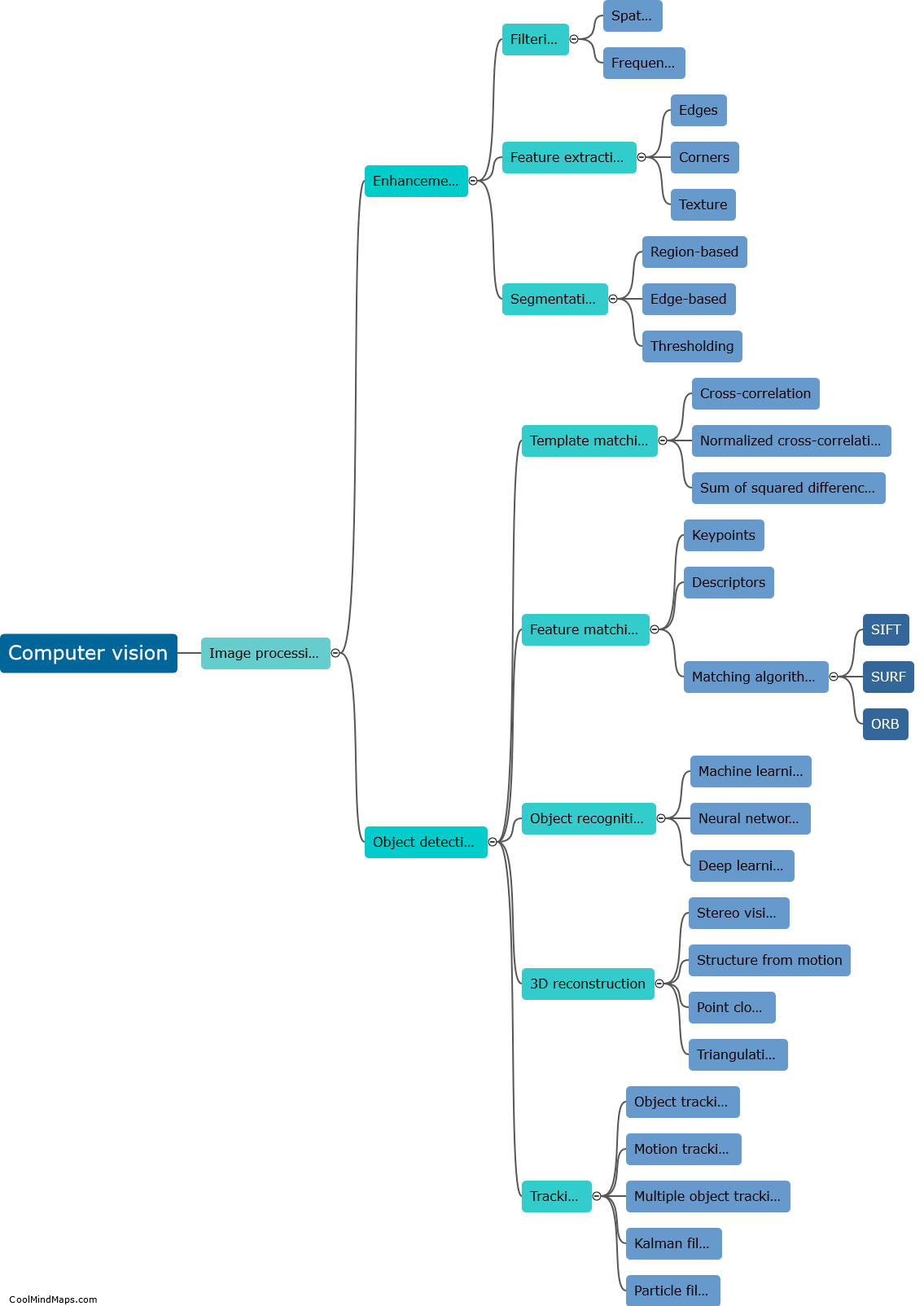
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that enables computers to understand and interpret visual data, simulating human vision. It involves processing and analyzing digital images or videos to extract meaningful information. Computer vision algorithms employ various techniques such as image recognition, object detection, semantic segmentation, and tracking to interpret visual data. These algorithms utilize machine learning models, specifically deep neural networks, which are trained on massive labeled datasets. By learning patterns, textures, shapes, and colors from the data, these models can classify and recognize objects, detect and localize them in an image or video, and even understand their context. Computer vision finds applications in diverse areas, including autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, medical imaging, facial recognition, and augmented reality.
This mind map was published on 20 August 2023 and has been viewed 97 times.