How do Newton's laws explain motion?
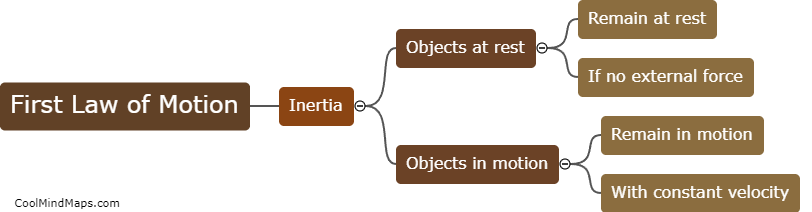
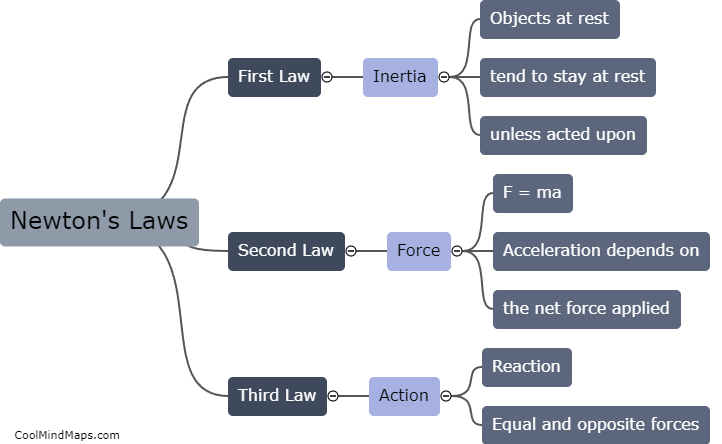
Newton's laws of motion provide a comprehensive explanation of how motion occurs in the physical world. These laws, formulated by Sir Isaac Newton, lay the foundation for classical mechanics. The first law, often referred to as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an external force. The second law introduces the concept of force and its relationship with acceleration, stating that the force acting on an object is directly proportional to its mass and the acceleration it experiences. Lastly, the third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. These laws collectively explain the cause and effect relationship between forces, motion, and acceleration in various scenarios, forming the basis for understanding the mechanics of objects in motion.

This mind map was published on 10 November 2023 and has been viewed 83 times.