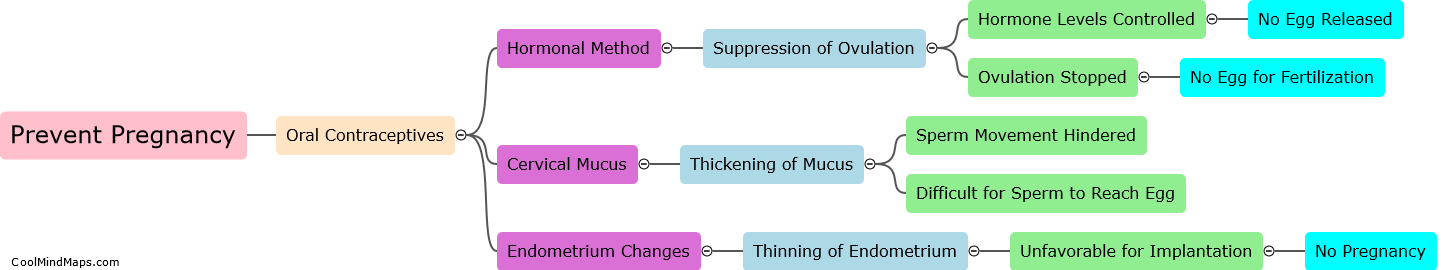
How do oral contraceptives prevent pregnancy?
Oral contraceptives, commonly known as birth control pills, are hormonal medications taken to prevent pregnancy in women. These pills contain synthetic versions of the hormones estrogen and progestin, which are naturally produced by the ovaries. The primary mechanism by which oral contraceptives prevent pregnancy is by suppressing the release of eggs from the ovaries, a process called ovulation. By inhibiting ovulation, there are no eggs available for fertilization, effectively preventing pregnancy. Additionally, these medications also thicken the cervical mucus, making it more difficult for sperm to reach the uterus and fertilize an egg. Furthermore, oral contraceptives alter the lining of the uterus, making it less receptive to the implantation of a fertilized egg. Collectively, these actions increase the effectiveness of oral contraceptives in preventing pregnancy, providing women with a reliable method of birth control.
This mind map was published on 29 November 2023 and has been viewed 91 times.