How is BPH diagnosed?
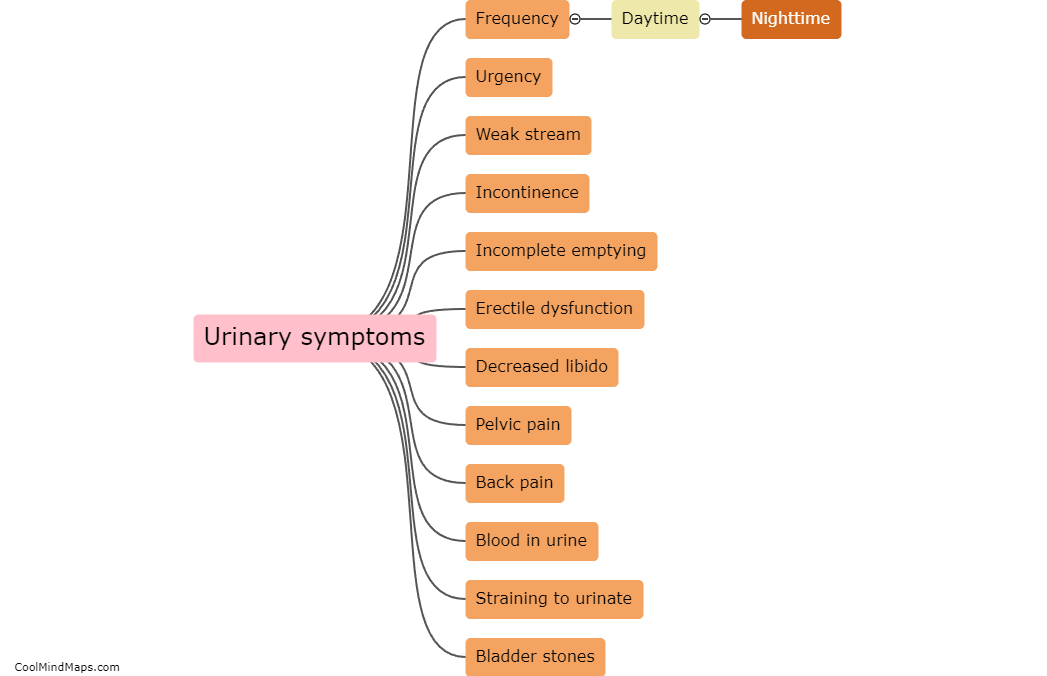
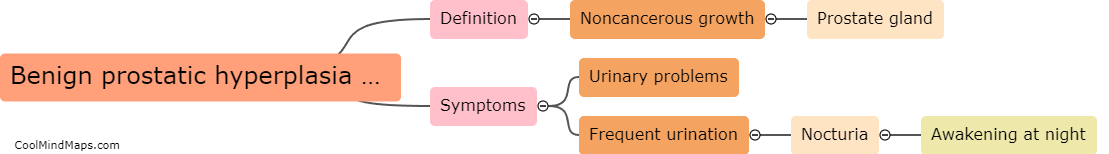
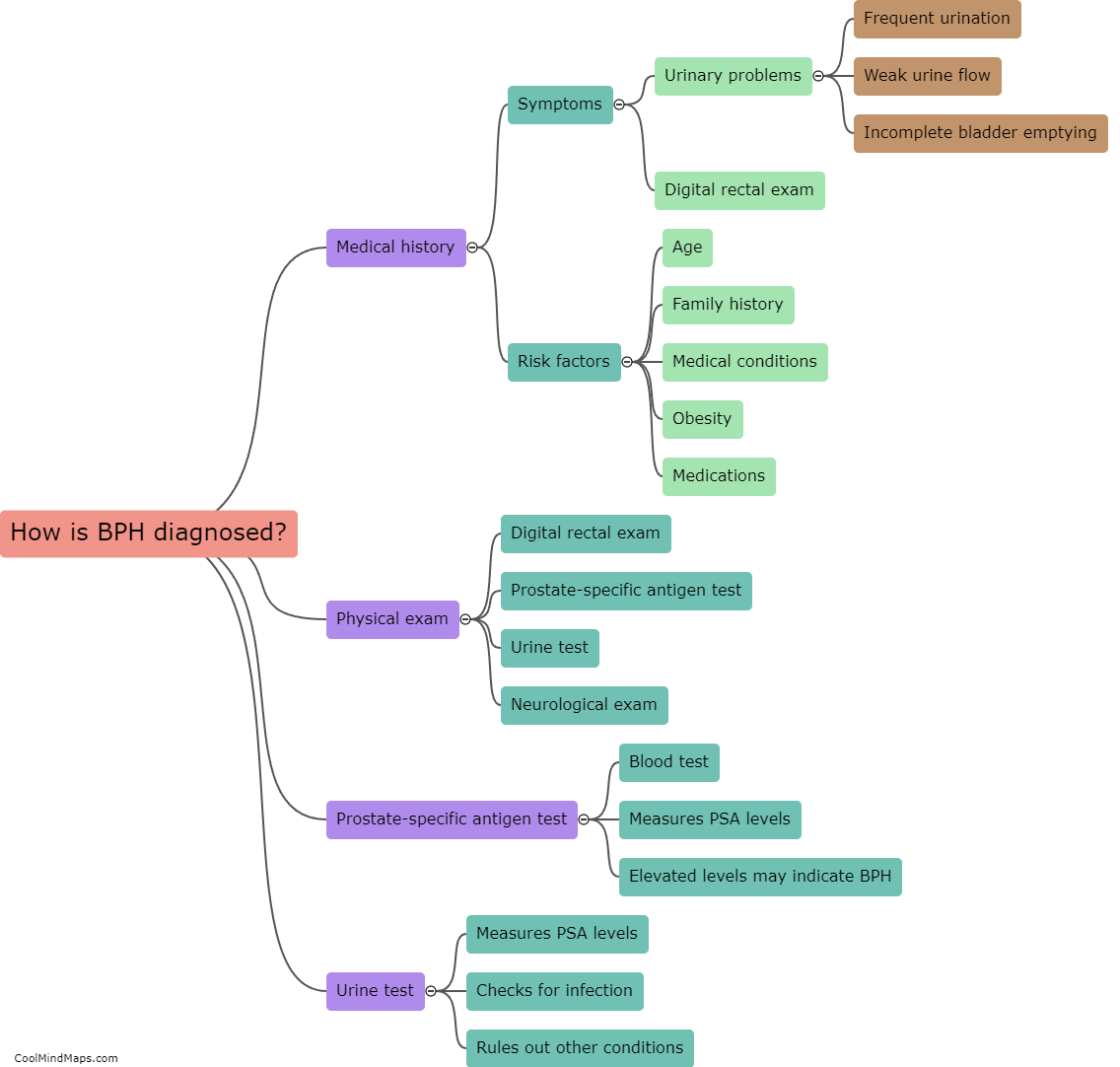
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The healthcare provider may ask about symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, and whether there is a history of prostate problems in the family. A digital rectal exam may be performed to assess the size and condition of the prostate gland. Additional tests, such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test or imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI, may also be ordered to confirm a diagnosis of BPH and rule out other potential causes of symptoms.
This mind map was published on 23 June 2024 and has been viewed 70 times.