What is excitation-contraction coupling?
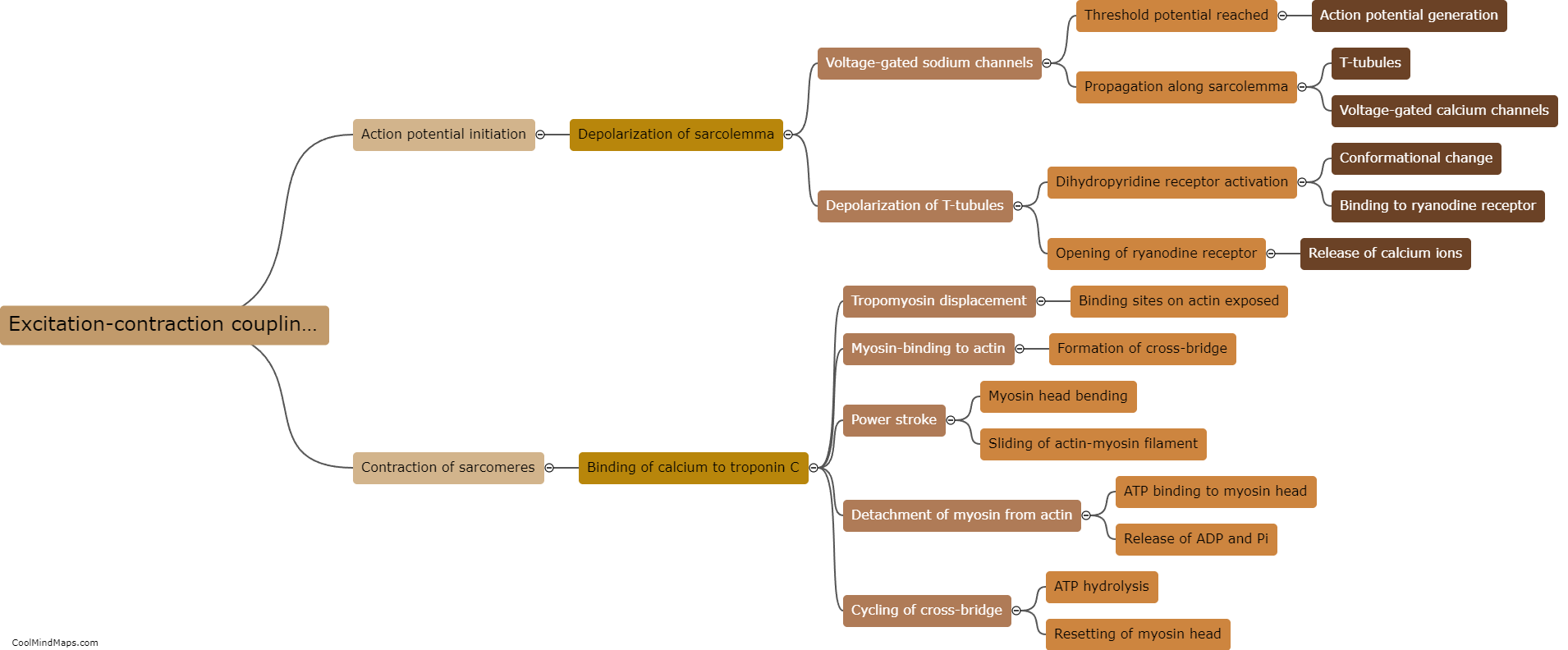
Excitation-contraction coupling is a fundamental process that occurs in muscle cells, particularly skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, to initiate muscle contraction. It involves the sequential events of electrical excitation and mechanical contraction. When an action potential, an electrical signal, is triggered in a muscle cell, it travels along the cell membrane, or sarcolemma, and reaches the specialized intracellular membrane system called the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The action potential causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions into the cytoplasm of the muscle cell. These calcium ions then bind to a protein called troponin, which results in a conformational change of tropomyosin. This conformational change exposes the binding sites on the actin filaments of the muscle cell. Subsequently, myosin heads, which are part of the thick myosin filaments, can bind to these exposed sites on actin, leading to the sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other, ultimately resulting in muscle contraction. Thus, excitation-contraction coupling is a tightly regulated process that allows electrical signals to be translated into mechanical force generation in muscle cells.

This mind map was published on 12 July 2023 and has been viewed 101 times.