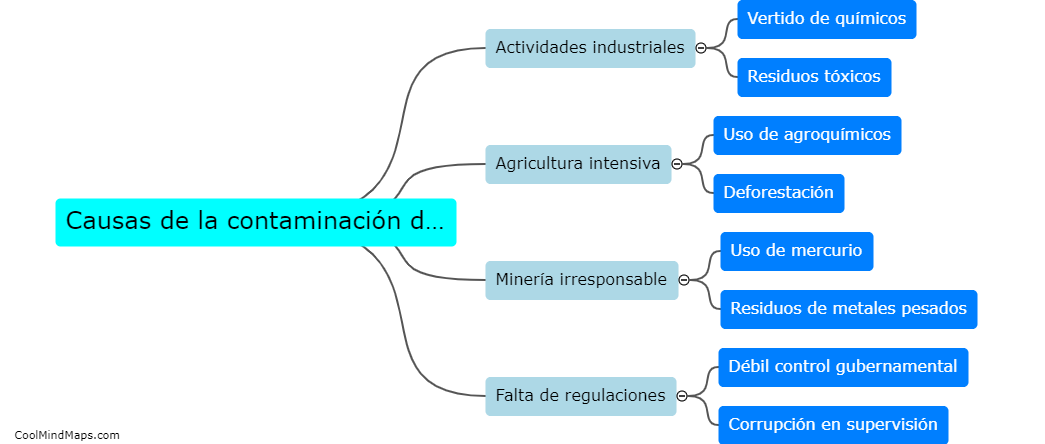
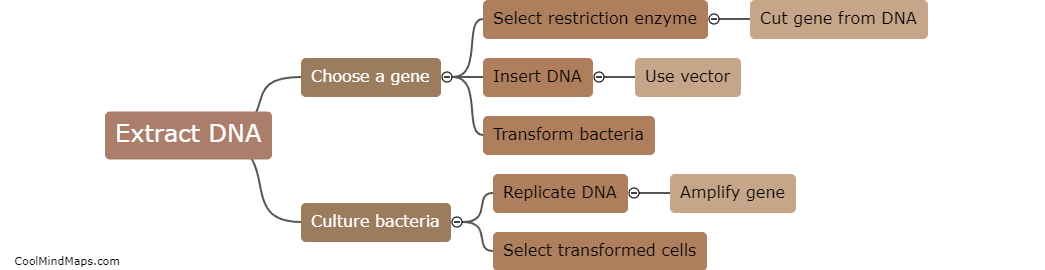
How is DNA cloning performed?
DNA cloning is performed by isolating a DNA sequence of interest, such as a gene, and inserting it into a vector, typically a plasmid, using restriction enzymes to cut the DNA at specific sites and DNA ligase to attach the gene to the vector. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into a host organism, such as bacteria, which will replicate the DNA along with its own genome. This process allows for the production of multiple copies of the gene of interest, which can be studied or used for various applications in research and biotechnology.
This mind map was published on 18 March 2024 and has been viewed 76 times.