What are the mechanisms underlying the development of hyperalgesia?
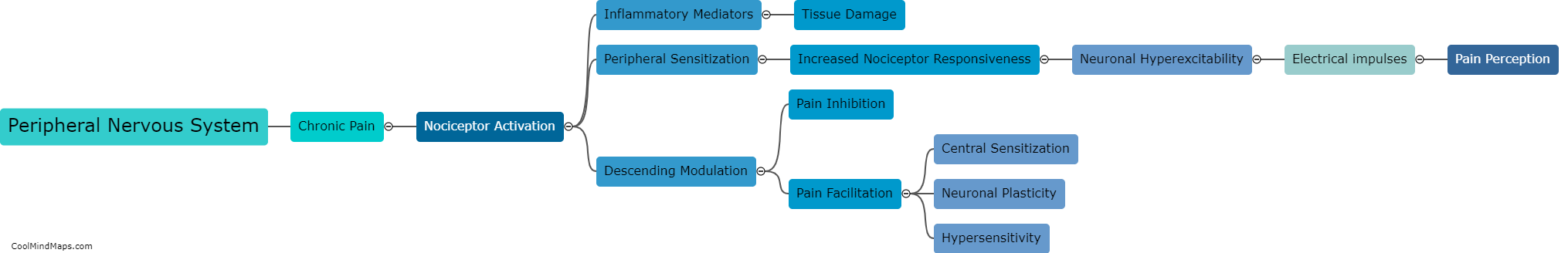
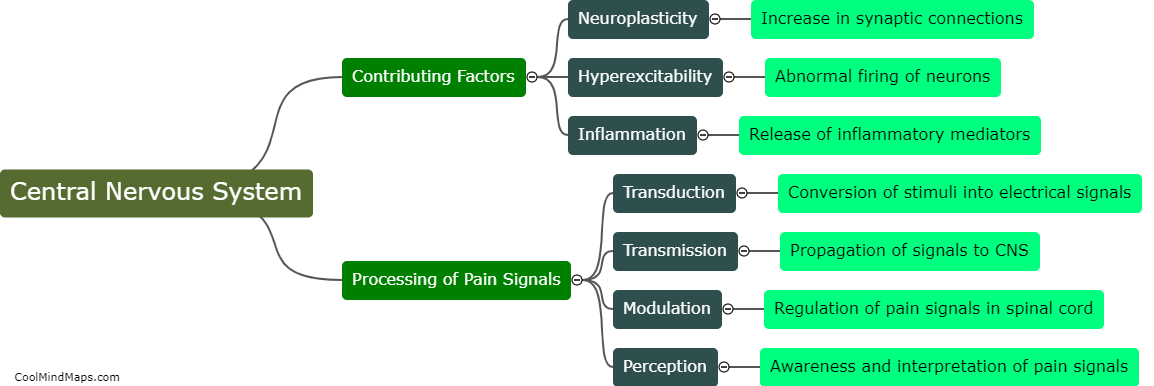
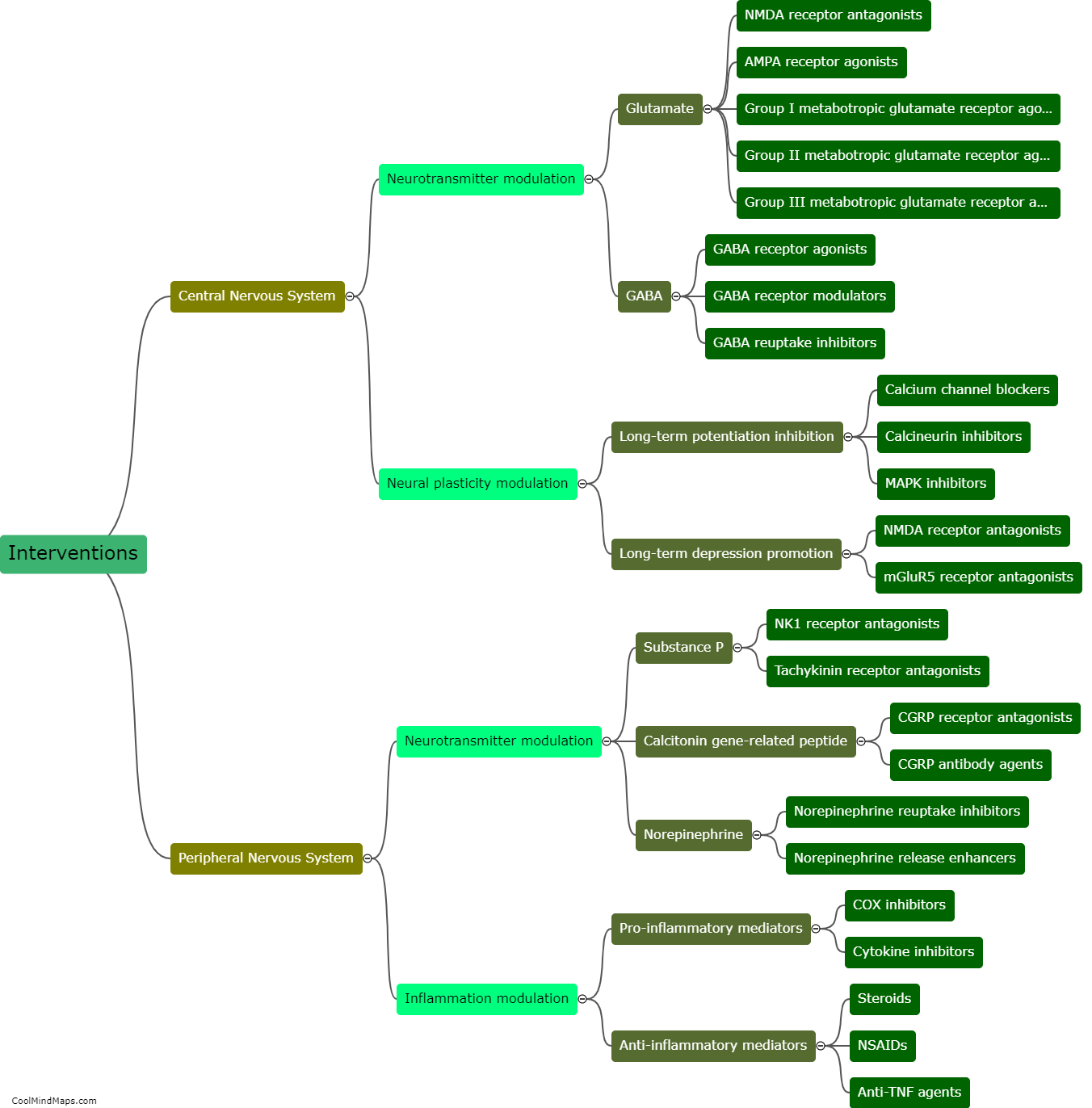
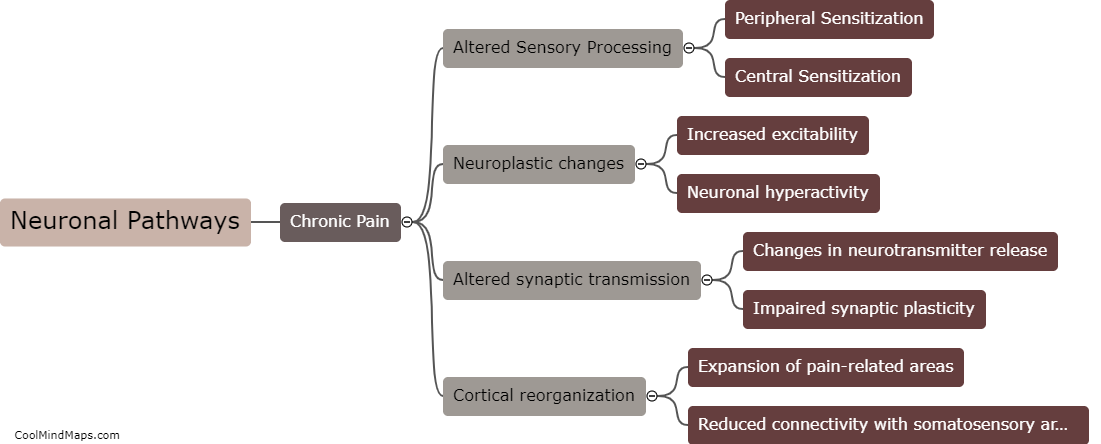
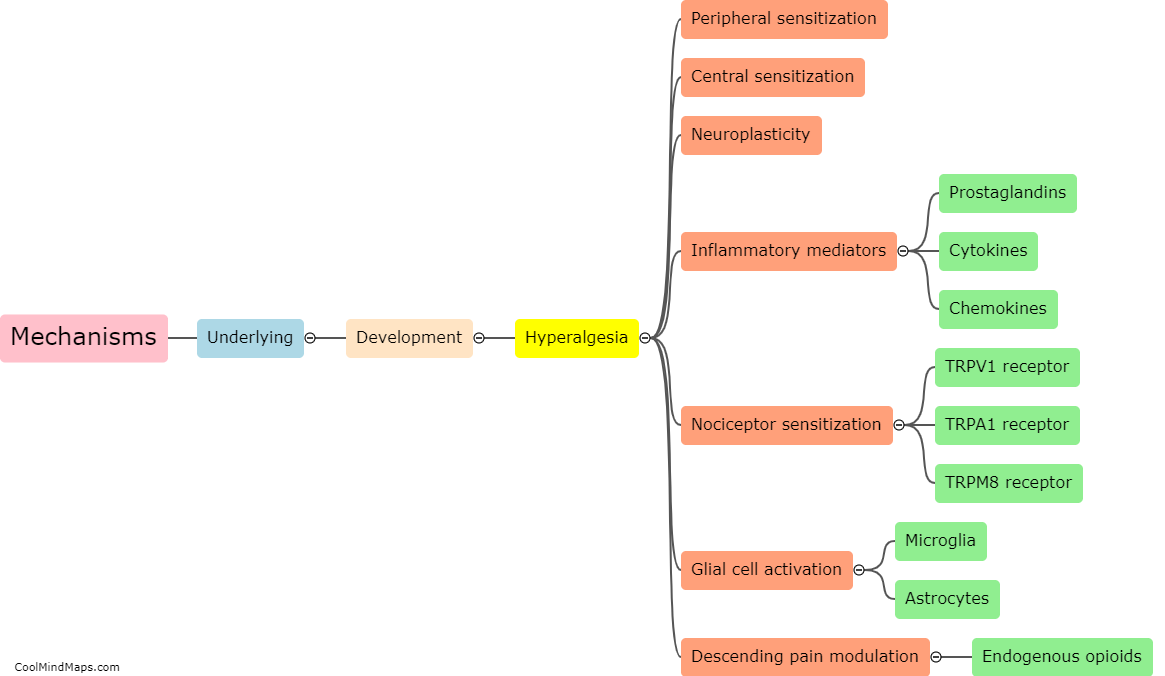
Hyperalgesia refers to an increased sensitivity to pain, where even mild stimuli are perceived as highly painful. The development of hyperalgesia involves complex mechanisms that can be broadly categorized into peripheral and central sensitization. Peripheral sensitization occurs at the site of tissue damage or inflammation. It involves the release of inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins and bradykinin, which activate nociceptors, the pain-sensing nerve fibers. This activation leads to an increased responsiveness of the nociceptors, lowering their threshold for pain. Central sensitization, on the other hand, occurs in the spinal cord and brain. It is characterized by enhanced excitability of neurons involved in pain processing. This heightened excitability is influenced by various factors, including the release of neurotransmitters like glutamate and the activation of NMDA receptors. Moreover, changes in gene expression and protein synthesis contribute to the long-lasting nature of hyperalgesia. Understanding these underlying mechanisms is crucial for the development of effective treatments for hyperalgesia.
This mind map was published on 2 December 2023 and has been viewed 88 times.