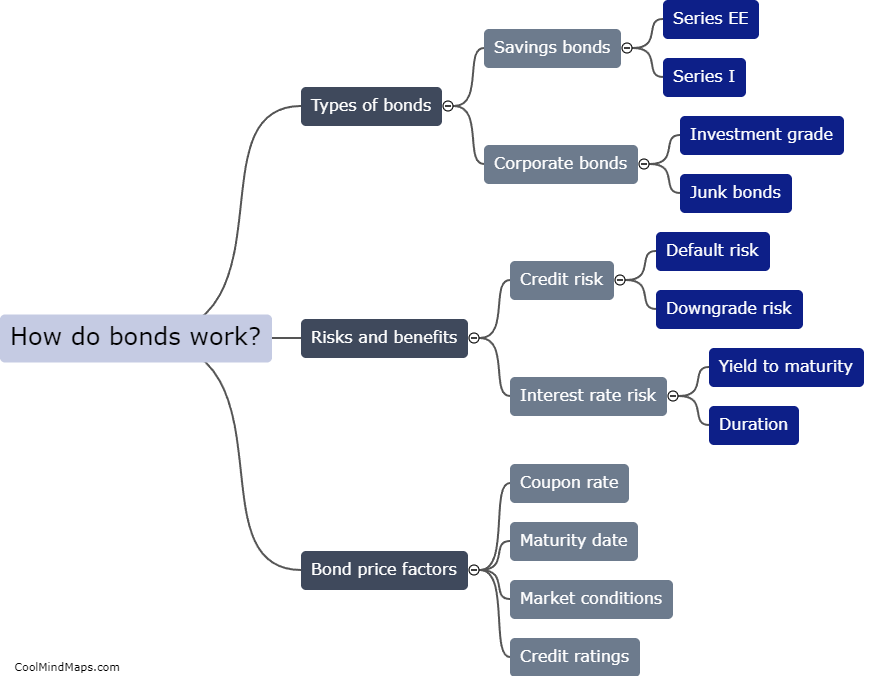
How do bonds work?
Bonds are a form of debt instrument issued by companies, organizations or governments to fund their operations. When an investor buys a bond, they are essentially lending money to the bond issuer for a set period of time. In return, the investor receives regular interest payments called coupon payments until the maturity date of the bond when the principal amount is returned. The interest rate on a bond is determined by a range of factors, such as the creditworthiness of the issuer, prevailing interest rates, and market supply and demand. Bonds are traded on financial markets, and their prices can fluctuate based on changes in market conditions and investor sentiment.
This mind map was published on 19 April 2023 and has been viewed 152 times.