How do TRP channels contribute to inflammatory pain?
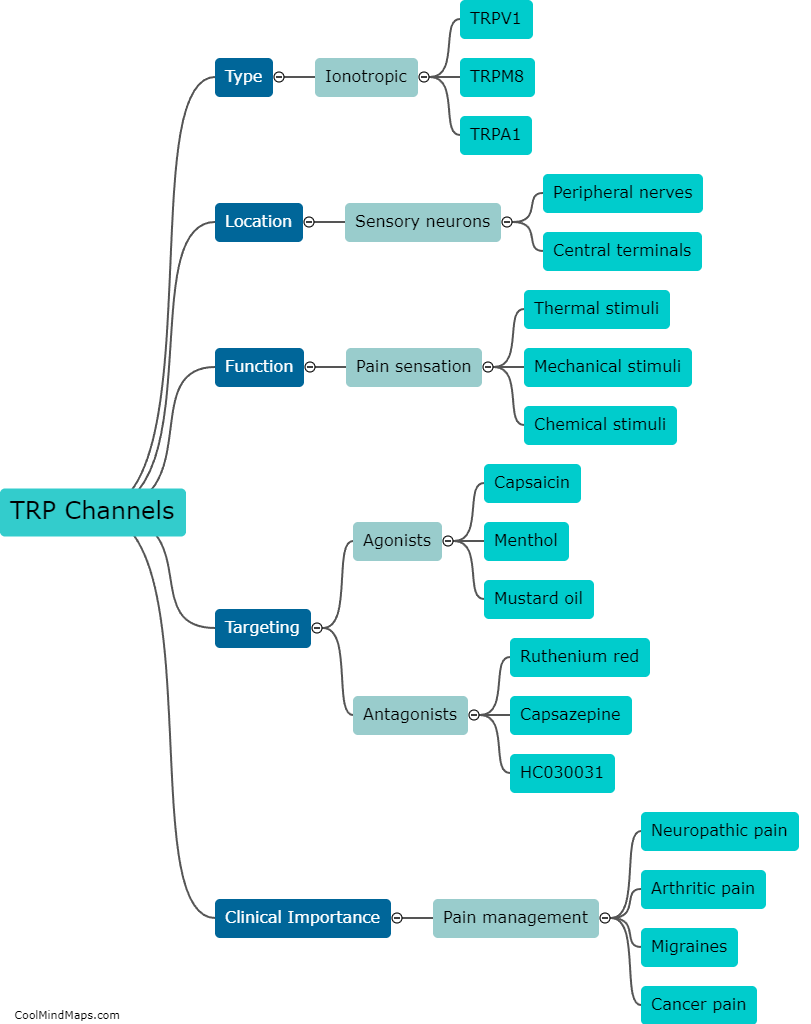
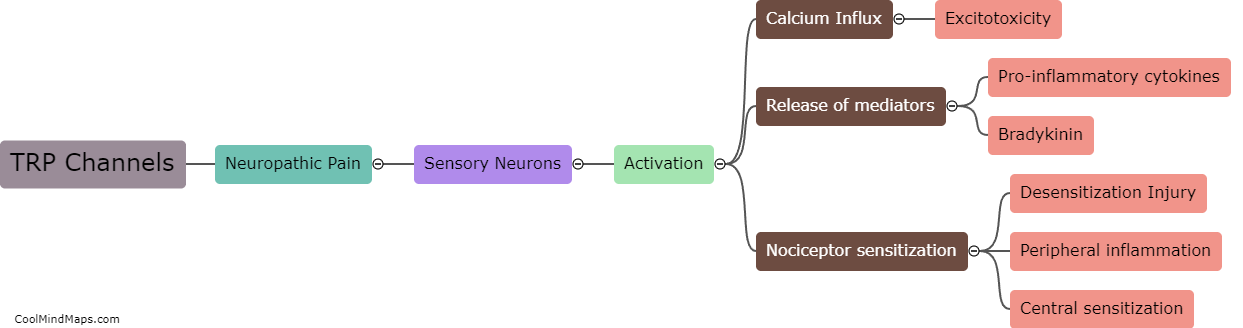
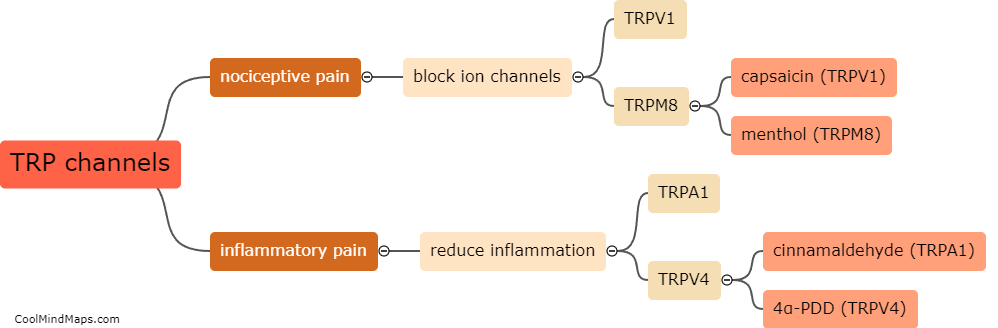
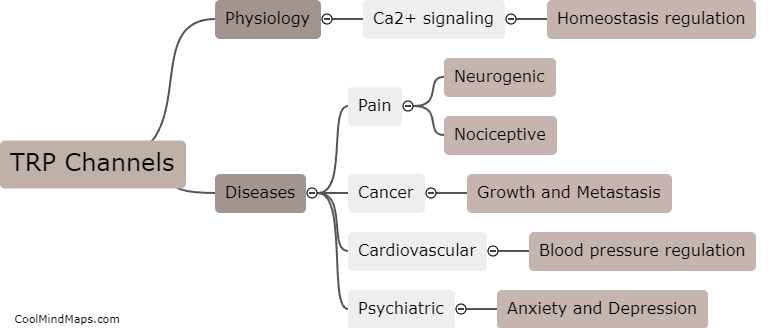
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are known to play a crucial role in the transmission and regulation of nociceptive signals, including inflammatory pain. These channels are expressed in different cell types, including sensory neurons, immune cells, and non-neuronal cells, where they can be activated by various stimuli, such as heat, cold, mechanical pressure, and chemical irritants. In the context of inflammatory pain, TRP channels are activated by pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and other molecules released by damaged tissues or immune cells. This activation leads to the influx of calcium ions into the cells, causing depolarization and the release of neurotransmitters and pro-inflammatory mediators. These, in turn, sensitize sensory neurons and recruit immune cells, amplifying the signals of inflammation and pain. Therefore, TRP channels are considered promising targets for the development of novel analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.

This mind map was published on 22 June 2023 and has been viewed 112 times.