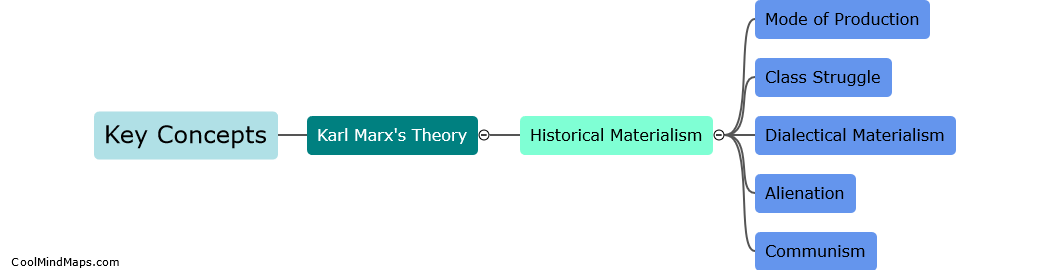
What are the key concepts in Karl Marx's theory?
Karl Marx's theory is built upon several key concepts that form the foundation of his critique of capitalism and his vision for a socialist society. One of the central ideas in Marx's theory is historical materialism, which argues that the organization of society is determined by the material conditions of production. He believed that economic forces have shaped human history and that class struggle is the driving force behind societal change. Another key concept is the labor theory of value, which asserts that the value of commodities is derived from the amount of labor power required to produce them. Marx also introduced the concept of alienation, wherein he argued that under capitalism, workers are disconnected from the products of their own labor and are exploited by the capitalist class. Additionally, Marx highlighted the role of capitalism in perpetuating inequality and exploitation, with the bourgeoisie and proletariat being the opposing classes in this system. These key concepts form the basis of Marx's theory and serve to analyze and critique the inequalities and contradictions inherent in capitalist societies.
This mind map was published on 2 July 2023 and has been viewed 123 times.